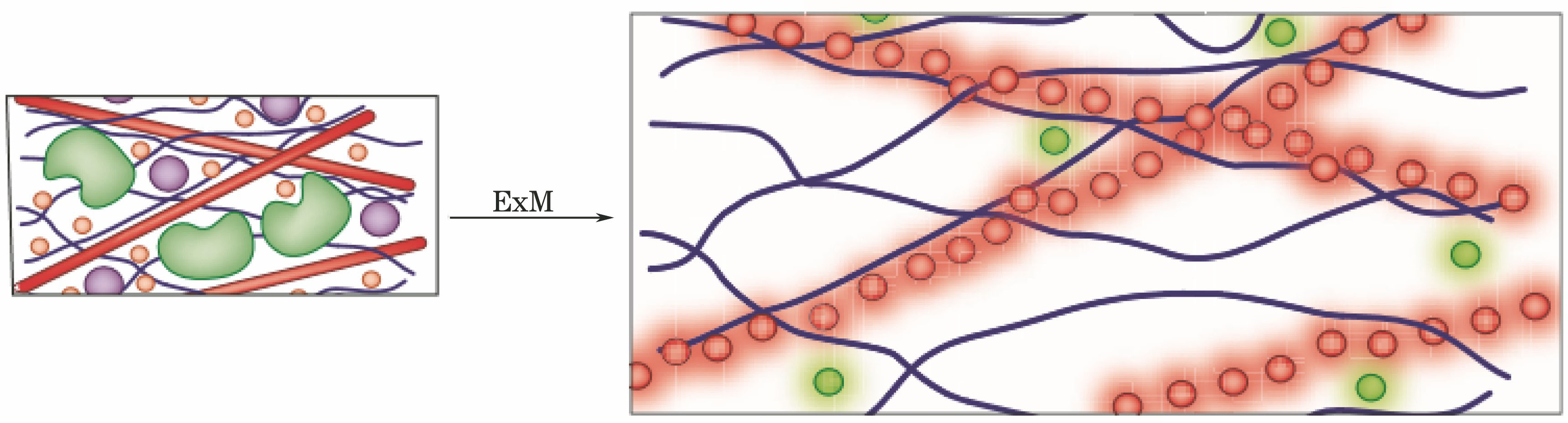
[10] Chen F, Tillberg P W, Boyden E S. Expansion microscopy[J]. Science, 347, 543-548(2015).
[15] Chang J B, Chen F, Yoon Y G et al. Iterative expansion microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 14, 593-599(2017).
[16] Wei F F, Liu Z W. Plasmonic structured illumination microscopy[J]. Nano Letters, 10, 2531-2536(2010).
[24] Hafi N. Grunwald M, van den Heuvel L S, et al. Reply to "Polarization modulation adds little additional information to super-resolution fluorescence microscopy"[J]. Nature Methods, 13, 8-9(2015).