Author Affiliations
11. National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Advanced Composites in Special Environments/Center for Composite Materials and Structures, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China22. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Normal University, Harbin 150025, Chinashow less
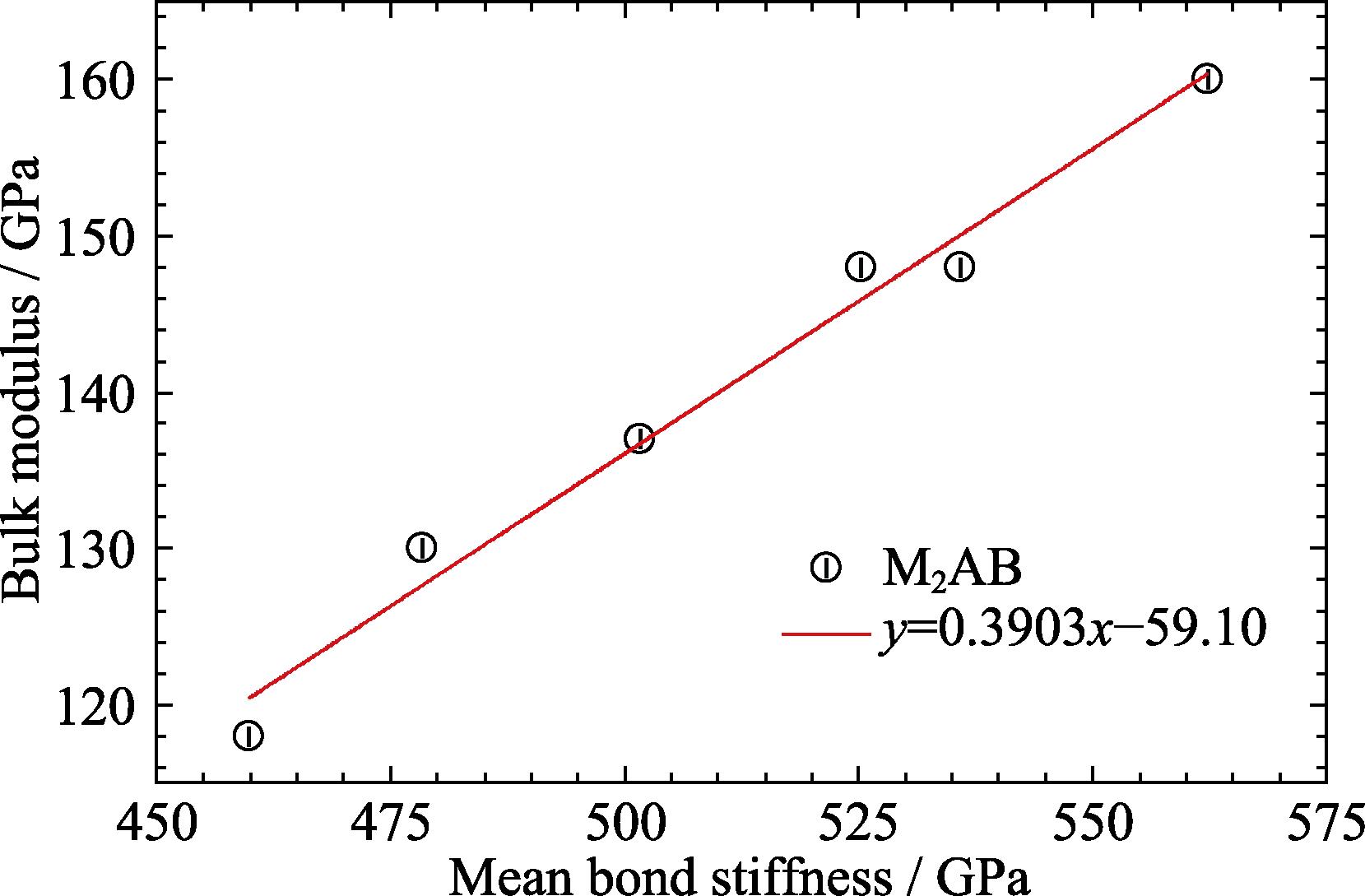
1. Bulk moduli against mean bond stiffness for M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
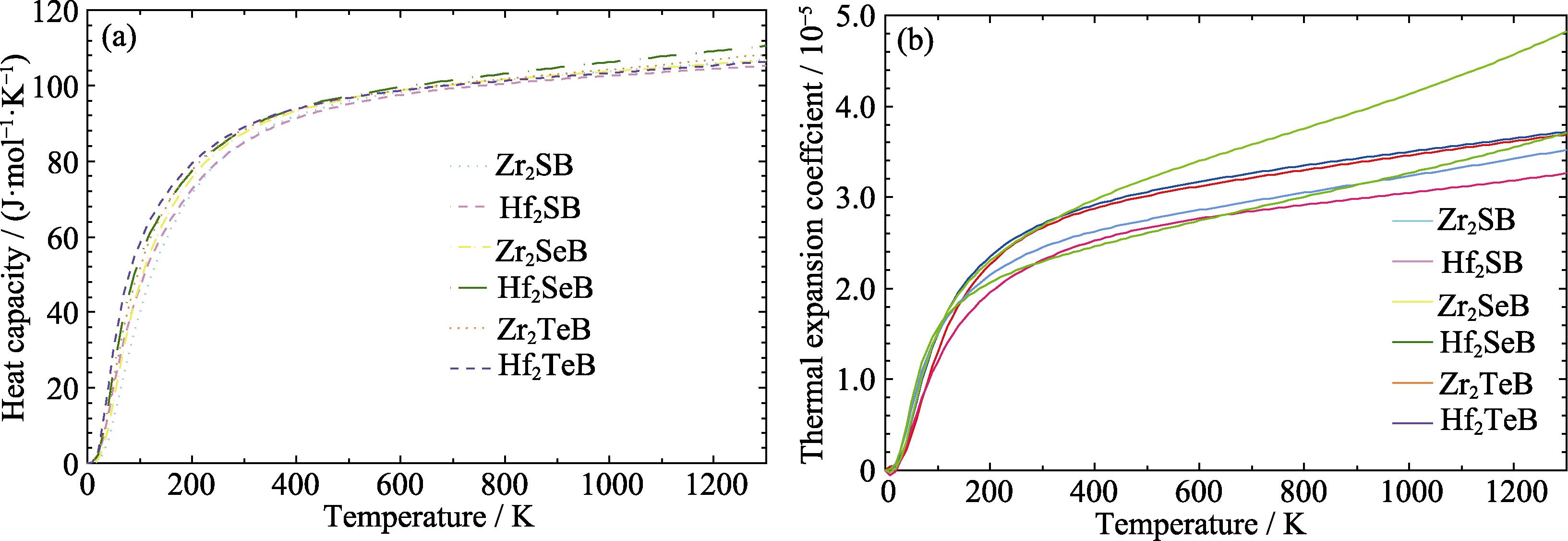
2. Temperature dependence of (a) CP and (b) αl of M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
S1. (a) Side and (b) top views of 211 type MAX phase
S2. Phonon dispersions (left) and density of states (right) of (a) Zr2SB, (b) Hf2SB, (c) Zr2SeB, (d) Hf2SeB, (e) Zr2TeB, and (f) Hf2TeB along the high symmetry directions
S3. Pressure dependence of normalized bond length d/d0 of (a) M-A and (b) M-B bonds in M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
| Compound | a/Å
| c/Å
| V/Å3 | Most competing phases | ΔHcomp/(eV·atom-1)
|
|---|
| Zr2SB | 3.521 | 12.302 | 132.12 | 0.6Zr2S + 0.1Zr3S4 + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0749 | | Exp.[8] | 3.500 | 12.271 | 130.19 | | Hf2SB | 3.484 | 12.122 | 127.40 | 0.5Hf2S + 0.5HfS + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0512 | | Exp.[8] | 3.467 | 12.105 | 126.01 | | Zr2SeB | 3.573 | 12.733 | 140.78 | 0.5Zr2Se + 0.5ZrSe + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0259 | | Exp.[9] | 3.644 | 12.632 | 145.27 | | Hf2SeB | 3.538 | 12.544 | 136.01 | 0.0185Hf23Se25 + 0.5370Hf2Se + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0838 | | Exp.[9] | 3.523 | 12.478 | 134.11 | | Hf2TeB | 3.619 | 13.239 | 150.14 | 0.5Hf3Te2 + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0100 | | Exp.[10] | 3.605 | 13.127 | 147.72 |
|
Table 1. M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) of which formation enthalpy ΔHcomp<0
| Compound | Included phase | a/Å
| c/Å
| V/Å3 | Most competing phases | ΔHcomp/(eV·atom-1)
|
|---|
| Zr2SB | Zr, S, B, Zr2S, Zr3S4, Zr9S2, ZrS, ZrS2, ZrS3, ZrB2, B2S3, BS2 | 3.521 | 12.302 | 132.12 | 0.6Zr2S + 0.1Zr3S4 + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0749 | | Exp.[8] | 3.500 | 12.271 | 130.19 | | Zr3SB2 | | | | 0.0833Zr9S2 + 0.5833ZrB2 + 0.8333Zr2SB | 0.0919 | | Zr4SB3 | | | | 0.1667Zr9S2 + 1.1667ZrB2 + 0.6667Zr2SB | 0.1588 | | Hf2SB | Hf, S, B, Hf2S, HfS, HfS2, HfS3, HfB2, B2S3, BS2 | 3.484 | 12.122 | 127.40 | 0.5Hf2S + 0.5HfS + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0512 | | Exp.[8] | 3.467 | 12.105 | 126.01 | | Hf3SB2 | | | | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2SB | 0.0807 | | Hf4SB3 | | | | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2SB | 0.1422 | | Zr2SeB | Zr, Se, B, Zr2Se, Zr2Se3, ZrSe, ZrSe2, ZrSe3, ZrB2, BSe2 | 3.573 | 12.733 | 140.78 | 0.5Zr2Se + 0.5ZrSe + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0259 | | Exp.[9] | 3.644 | 12.632 | 145.27 | | Zr3SeB2 | | | | 0.5Zr + 0.5ZrB2 + Zr2SeB | 0.1649 | | Zr4SeB3 | | | | Zr + ZrB2 + Zr2SeB | 0.1559 | | Hf2SeB | Hf, Se, B, Hf2Se, Hf2Se3, HfSe2, HfSe3, Hf23Se25, HfB2, BSe2 | 3.538 | 12.544 | 136.01 | 0.0185Hf23Se25 +0.5370Hf2Se + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0838 | | Exp.[9] | 3.523 | 12.478 | 134.11 | | Hf3SeB2 | | | | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2SeB | 0.0836 | | Hf4SeB3 | | | | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2SeB | 0.1457 | | Zr2TeB | Zr, Te, B, Zr2Te3, Zr3Te, Zr5Te4, ZrTe, ZrTe2, ZrTe3, ZrTe5, ZrB2 | 3.650 | 13.415 | 154.77 | 0.2143Zr5Te4 + 0.1429Zr3Te + 0.5ZrB2 | 0.0305 | | Zr3TeB2 | | | | 0.1429Zr5Te4 + 0.4286Zr3Te + ZrB2 | 0.1321 | | Zr4TeB3 | | | | 0.0174Zr5Te4 + 0.7143Zr3Te + 1.5ZrB2 | 0.1960 | | Hf2TeB | Hf, Te, B, Hf3Te2,Hf5Te4, HfTe2, HfTe5, HfB2 | 3.619 | 13.239 | 150.14 | 0.5Hf3Te2 + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0100 | | Exp.[10] | 3.605 | 13.127 | 147.72 | | Hf3TeB2 | | | | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2TeB | 0.0994 | | Hf4TeB3 | | | | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2TeB | 0.1613 |
|
Table 1. Formation enthalpy ΔHcomp of M2AB, M3AB2 and M4AB3 (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
| Compound | Curve fitting equation (300-1300 K) | TEC (300-1300 K)/ K-1 |
|---|
| Zr2SB | CP = 0.83×10-2T + 96.9 - 1.28×106T-2 | 10.97×10-6 K-1 | | Hf2SB | CP = 0.74×10-2T + 96.6 - 1.25×106T-2 | 9.66×10-6 K-1 | | Zr2SeB | CP = 0.82×10-2T + 96.7 - 1.06×106T-2 | 11.11×10-6 K-1 | | Hf2SeB | CP = 1.28×10-2T + 94.4 - 0.89×106T-2 | 10.17×10-6 K-1 | | Zr2TeB | CP = 1.07×10-2T + 94.7 - 0.84×106T-2 | 12.63×10-6 K-1 | | Hf2TeB | CP = 0.83×10-2T + 96.1 - 0.87×106T-2 | 10.07×10-6 K-1 |
|
Table 2. Heat capacity at constant pressure and the average linear thermal expansion coefficient of M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) in the temperature range of 300-1300 K
| Compound | c11/GPa
| c12/GPa
| c13/GPa
| c33/GPa
| c44/GPa
| G/GPa
| B/GPa
| E/GPa
| μ | G/B | Ref. |
|---|
| Zr2SB | 264 | 76 | 91 | 298 | 135 | 108 | 148 | 262 | 0.206 | 0.730 | This work | | Hf2SB | 296 | 74 | 97 | 318 | 147 | 122 | 160 | 292 | 0.196 | 0.763 | This work | | Zr2SeB | 252 | 64 | 83 | 277 | 125 | 105 | 137 | 250 | 0.197 | 0.766 | This work | | Hf2SeB | 275 | 66 | 90 | 292 | 134 | 113 | 148 | 270 | 0.195 | 0.764 | This work | | Zr2TeB | 198 | 67 | 78 | 225 | 104 | 79 | 118 | 194 | 0.226 | 0.669 | This work | | Hf2TeB | 225 | 61 | 88 | 257 | 119 | 93 | 130 | 225 | 0.211 | 0.715 | This work | | Ti3SiC2 | 366 | 94 | 100 | 352 | 153 | 142 | 187 | 339 | 0.192 | 0.759 | [16] | | Ti3GeC2 | 357 | 94 | 97 | 333 | 143 | 142 | 182 | 340 | 0.196 | 0.780 | [16] | | Hf2InC | 309 | 81 | 80 | 273 | 98 | 105 | 152 | 256 | 0.21 | 0.691 | [37] | | Hf2SnC | 251 | 71 | 107 | 238 | 101 | 87 | 145 | 218 | 0.25 | 0.600 | [37] |
|
Table 2. Second-order elastic constants and engineering elastic moduli of M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) and several typical MAX phases
| Compound | M−A bond | M−B bond | kmin/kmax | Hmicro/GPa
| Hmacro/GPa
|
|---|
| d/nm
| k/GPa
| d/nm
| k/GPa
|
|---|
| Zr2SB | 0.26997 | 458.93 | 0.24124 | 612.75 | 0.7490 | 21.29 | 18.40 | | Exp.[8] | 0.26844 | | 0.24032 | | | 9-12[12] | | Hf2SB | 0.26800 | 472.37 | 0.23722 | 652.32 | 0.7241 | 24.74 | 21.20 | | Exp.[8] | 0.26643 | | 0.23688 | | | | | Zr2SeB | 0.28062 | 442.87 | 0.24282 | 560.54 | 0.7901 | 21.09 | 19.30 | | Exp.[9] | 0.28071 | | 0.24729 | | | | | Hf2SeB | 0.27869 | 455.17 | 0.23899 | 595.24 | 0.7647 | 22.97 | 20.17 | | Exp.[9] | 0.27735 | | 0.23789 | | | | | Zr2TeB | 0.29743 | 432.53 | 0.24526 | 487.09 | 0.8880 | 14.45 | 13.12 | | Hf2TeB | 0.29604 | 439.17 | 0.24156 | 517.33 | 0.8489 | 17.90 | 16.16 |
|
Table 3. Bond length, bond stiffness and kmin/kmax in M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)