Author Affiliations
1Guangxi Key Laboratory of Intelligent Control and Maintenance of Power Equipment, School of Electrical Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, Guangxi , China2Guangxi Key Laboratory of Manufacturing System & Advanced Manufacturing Technology, School of Electrical Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, Guangxi , Chinashow less
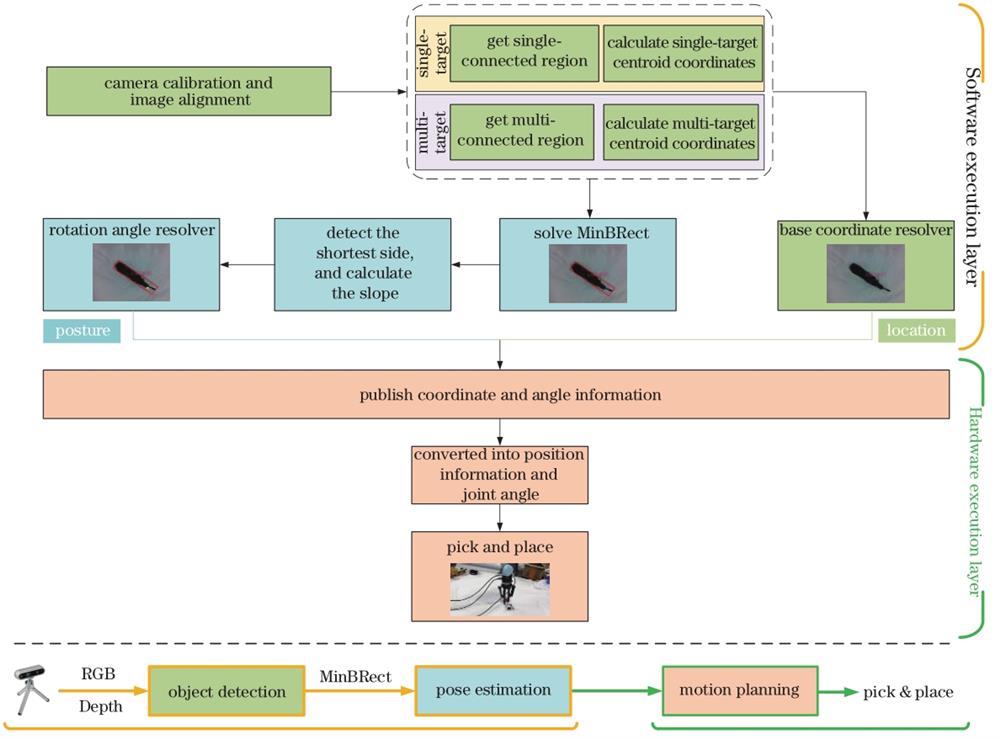
Fig. 1. Structure of visual grasping system
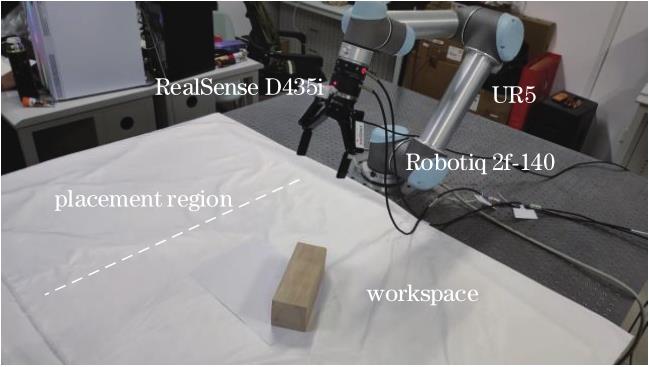
Fig. 2. Hardware platform
Fig. 3. Target detection process
Fig. 4. Marking of centroid points. (a) Original images; (b) marking of the target centroid coordinates
Fig. 5. Flowchart of connected domain marking algorithm
Fig. 6. Extracted minimum bounding rectangle. (a) Images to be detected; (b) minimum bounding rectangle detected by the proposed algorithm for targets
Fig. 7. Schematic of pose angle calculation
Fig. 8. Marking of pose angle
Fig. 9. Schematic of UR5 structure on DH coordinate system
Fig. 10. Grasping process and process perspective. (a)-(d) Robotic arm grasping process; (e)-(h) corresponding perspectives
Fig. 11. Demonstration of single-target grasping experiment. (a) Target detection; (b) moving to target pose; (c) target grasping; (d) target placement
Fig. 12. Position error and angle error
Fig. 13. Demonstration of multi-target grasping experiment. (a) Target detection; (b)-(d) moving to target pose and grasping the targets; (e) target placement
Fig. 14. Comparative experiment display, the red box represents grasping failure, the green box represents grasping success
| Joint number j | Translation along the Z-axis | Translation along the X-axis | Rotation along the X-axis | Rotation along the Z-axis |
|---|
| 1 | = 89.459 | 0 | π/2 | | | 2 | 0 | = -425 | 0 | | | 3 | 0 | = -392.25 | 0 | | | 4 | = 109.15 | 0 | π/2 | | | 5 | = 94.65 | 0 | π/2 | | | 6 | = 82.3 | 0 | 0 | |
|
Table 1. DH parameters of UR5
| Parameter | Wood block | Box | Coke can |
|---|
| Actual pose angle θ /(°) | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | | Measuring pose angle θ' /(°) | 33 | 35 | 53 | 57 | 36 | 38 | 51 | 57 | 29 | 27 | 56 | 57 | | Angle error Δθ /(°) | 3 | 5 | -2 | 2 | 6 | 8 | -4 | 2 | -1 | -3 | 1 | 2 | | Actual distance L/cm | 63 | 59 | 61.8 | 52.8 | 53.1 | 65.2 | 53.8 | 64.9 | 56.1 | 61.2 | 56.3 | 61.8 | | Measured distance L' /cm | 59.5 | 56.6 | 65.1 | 51.7 | 53 | 69.9 | 52.3 | 68.3 | 58.1 | 72.3 | 58.2 | 69.2 | | Distance error ΔL /cm | 3.54 | -2.4 | 3.3 | -1.1 | -0.1 | 4.7 | -1.5 | 3.4 | 2 | 11.1 | 1.9 | 7.4 | | Success rate /% | 100(7/7) | 100(7/7) | 85.7(6/7) | | Algorithm running time /s | 0.8436 | 0.8325 | 0.7344 | 0.8133 | 0.6719 | 0.6903 | 0.9184 | 0.7878 | 0.6777 | 0.7995 | 0.7265 | 0.7939 | | Grasping quality(Excellent is E,Good is G) | E | G | E | E | G | E | E | E | E | - | G | G |
|
Table 2. Grasping results for regular objects
| Parameter | Connector | Stapler | Screwdriver | Umbrella |
|---|
| Actual pose angle θ /(°) | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | | Measuring pose angle θ' /(°) | 27 | 24 | 51 | 60 | 38 | 35 | 56 | 55 | 29 | 33 | 55 | 56 | 35 | 28 | 60 | 51 | | Angle error Δθ /(°) | -3 | -6 | -4 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 5 | -2 | 5 | -4 | | Actual distance L /cm | 56.2 | 62.2 | 56.1 | 65.6 | 54.6 | 62.8 | 55.4 | 63.2 | 61.9 | 55.4 | 61.4 | 55.1 | 65.3 | 58.2 | 64.8 | 57.2 | | Measured distance L' /cm | 57 | 66.4 | 58.4 | 69.9 | 51.7 | 65.2 | 56.7 | 68.1 | 61.1 | 53.7 | 63.6 | 52.3 | 59.4 | 60.3 | 67.7 | 61.1 | | Distance error ΔL /cm | 0.8 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 4.3 | -2.9 | 2.4 | 1.3 | 4.9 | -0.8 | -1.7 | 2.2 | -2.8 | -5.9 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 3.9 | | Success rate /% | 71.4(5/7) | 71.4(5/7) | 57.1(4/7) | 85.7(6/7) | | Algorithm running time /s | 0.7905 | 0.7913 | 0.7907 | 0.7886 | 0.7887 | 0.8318 | 0.7887 | 0.7881 | 0.7879 | 0.7274 | 0.7874 | 0.7881 | 0.7278 | 0.7870 | 0.7883 | 0.7301 | | Grasping quality(Excellent is E,Good is G) | E | ‒ | E | G | G | G | E | ‒ | ‒ | E | ‒ | E | E | E | E | E |
|
Table 3. Grasping results for irregular objects
| Parameter | Equipment-1 | Equipment-2 | Equipment-3 |
|---|
| Actual pose angleθ /(°) | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | 30 | 55 | | Measuring pose angle θ' /(°) | 36 | 34 | 50 | 53 | 30 | 28 | 53 | 54 | 33 | 28 | 58 | 57 | | Angle error Δθ /(°) | 6 | 4 | -5 | -2 | 1 | -2 | -2 | -1 | 3 | -2 | 3 | 2 | | Actual distance L /cm | 54.8 | 57.2 | 62.7 | 58.4 | 56.8 | 60.2 | 54.4 | 61.7 | 59.6 | 57.3 | 65.2 | 60.3 | | Measured distance L' /cm | 63.33 | 61.77 | 60.22 | 56 | 57.67 | 62.07 | 58.24 | 60.66 | 57.47 | 59.78 | 63.22 | 52.76 | | Distance error ΔL /cm | 8.53 | 4.57 | -2.48 | -2.4 | 0.87 | 1.87 | 3.84 | -1.04 | -2.13 | 2.48 | -1.98 | -7.54 | | Success rate /% | 85.7(6/7) | 100(7/7) | 100(7/7) | | Algorithm running time /s | 0.9027 | 0.8294 | 0.7518 | 0.8082 | 0.6831 | 0.7432 | 0.8384 | 0.6678 | 0.6831 | 0.8105 | 0.7457 | 0.8018 | | Grasping quality(Excellent is E,Good is G) | ‒ | E | E | G | G | G | E | G | G | E | G | ‒ |
|
Table 4. Grasping results for electric equipments
| Parameter | Box | Cola can | Stapler | Screwdriver | Combination |
|---|
| Average angle error | -0.857 | 1.428 | -2.429 | -1.285 | 1.519 | | Average distance error | 1.257 | 1.357 | 2.871 | 1.585 | 1.943 | | Success rate /% | 85.7(6/7) | 85.7(6/7) | 71.4(5/7) | 71.4(5/7) | 85.7(6/7) | | Average running time /s | 1.259 |
|
Table 5. Grasping results for multi objects
| Algorithm | Average angle error | Average distance relative error /% | Success rate /% | Average running time /s |
|---|
| Linemod | - | 35.6 | 0(0/7) | 0.7651 | | Algorithm in Ref.[6] | 1.647 | 2.14 | 71.4(5/7) | 0.7613 | | Proposed algorithm | 1.428 | 1.96 | 85.7(6/7) | 0.7494 |
|
Table 6. Comparative experimental results of three algorithms
Algorithm Parameter | Wood block | Box | Coke can | Connector | Stapler | Screwdriver | Umbrella |
|---|
Linemod | SA /% | 14.3 | 28.5 | 0 | 14.3 | 28.5 | 0 | 14.3 | AAS /s | 0.8455 | 0.8030 | 0.7651 | 0.8965 | 0.8343 | 0.8437 | 0.7846 | Algorithm in Ref.[6] | SA /% | 86 | 100 | 71.40 | 57.10 | 85.70 | 57.10 | 71.40 | AAS /s | 0.8248 | 0.7782 | 0.7601 | 0.8053 | 0.8142 | 0.7819 | 0.7671 | Proposed algorithm | SA /% | 100 | 100 | 85.7 | 71.4 | 71.4 | 57.1 | 85.7 | AAS /s | 0.8060 | 0.7671 | 0.7494 | 0.7903 | 0.7993 | 0.7727 | 0.7583 |
|
Table 7. Comparison results of three algorithms for different targets
| Method | Single object | Multi objects |
|---|
| Total time /s | IoU /% | Total time /s | IoU /% |
|---|
| K-means | 0.098 | 92.4 | 0.105 | 93.5 | | K-means+OTSU | 0.258 | 96.3 | 0.324 | 96.8 | | OTSU | 0.076 | 95.6 | 0.086 | 94.2 | | Improved OTSU | 0.023 | 99.1 | 0.034 | 98.9 |
|
Table 8. Target segmentation ablation experiment results
| Method | Centroid shift /% | Invalid region percentage /% |
|---|
| Without CD | - | 84.3 | | CD | 3.21 | 3.42 | | CD+MSC | 0.42 | 0.36 |
|
Table 9. Connected domain ablation experiment results