Author Affiliations
1State Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Application, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, Jilin, China2Daheng College, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China3Jlight Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd., Changchun 130102, Jilin, China4School of Opto-Electronic Engineering, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, Jilin, Chinashow less
Fig. 1. OCT principle
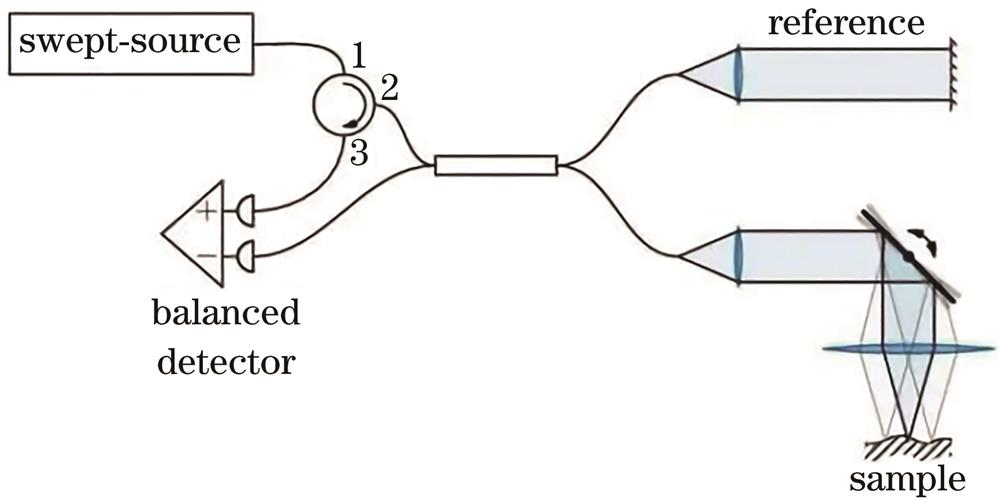
Fig. 2. SS-OCT principle
Fig. 3. Development of SS-OCT and its main frequency swept lasers
Fig. 4. Schematic of polyhedral rotating mirror frequency swept light source
[41] Fig. 5. Structure of blazed grating tunable laser
[42] Fig. 6. Structure of volume Bragg grating tunable laser
[43] Fig. 7. Double-cavity polyhedral rotating mirror swept frequency light source
[45] Fig. 8. Structure comparison between traditional ring cavity frequency swept laser and FDML laser
[51] Fig. 9. Structural diagram of FDML frequency swept light source
[53] Fig. 10. Structure diagram of FFP-TF
[54] Fig. 11. FDML structure with dual SOA
[55] Fig. 12. Output spectrum of FDML fenquency swept laser with DSF and ordinary single-mode fiber
[57] Fig. 13. Schematic of buffer FDML structure
[58] Fig. 14. 4× buffer stage FDML laser
[59] Fig. 15. Structure diagram of harmonic FDML
[60] Fig. 16. FDML laser based on polyhedral rotating mirror filter
[63] Fig. 17. Structure diagram of MEMS-VCSEL
[65] Fig. 18. Process flow chart of InP-based MEMS-VCSEL
[71] Fig. 19. 1050-nm electrically pumped MEMS-VCSEL
[72] Fig. 20. Structural diagram of SG-DBR
[76] Fig. 21. Diagram of vernier tuning principle
Fig. 22. Schematic of simulated SG-DBR structure
[78] Fig. 23. SSG-TTG tunable double guide laser
[80] Fig. 24. Schematic of DS-DBR grating structure
[82] Fig. 25. DCG-DBR tuning current-wavelength diagram
[85] Fig. 26. Structural diagram of SSG-DBR
[87] | Performance index of swept laser | Performance index of SS-OCT | Typical value |
|---|
| Scan rate | Imaging speed | 100 kHz[27] | | Center wavelength | Axial resolution,lateral resolution | 1060 nm[28] | | Tuning range | Axial resolution | 70 nm[29] | | Dynamic coherence length | Imaging depth | 10 mm[30] | | Output power | Signal-to-noise ratio,sensitivity | 11 mW[31] |
|
Table 1. Corresponding relationship between performance index of frequency swept light source and SS-OCT
| Type of swept laser | Tuning range | Scan rate | Output power |
|---|
| External cavity | 330 nm[32] | 50 kHz[33] | 77 W[34] | | FDML | 160 nm[27] | 5.2 MHz[35] | 200 mW[35] | | MEMS-VCSEL | 150 nm[36] | 800 kHz[37] | 30 mW[37] | | VT-DBR | 60 nm[38] | 100 kHz[39] | 30 mW[40] |
|
Table 2. The latest performance index of four swept lasers
| Year | Unit | Method | Performance index | Reference |
|---|
| 2003 | Harvard Medical School & Wellman Laboratories for Photomedicine | Using polygon mirror as filter for the first time | Scan rate:15.7 kHz; tuning range:75 nm | [29] | | 2005 | Harvard Medical School & Wellman Laboratories for Photomedicine | Using dual SOAs to broaden tuning range | Scan rate:20 kHz; tuning range:145 nm | [45] | | 2009 | University of Central Florida | Using blazed grating to achieve tuning | Center wavelength: 2000 nm; tuning range:161 nm | [46] | | 2019 | University of Central Florida | Using volume Bragg grating and lens group | Tuning range:103 nm; output power:48 W | [50] | | 2022 | Fraunhofer IOSB Inst Optron Syst Technol & Image | Using volume Bragg grating and Tm3+∶Ho3+-codoped free-space single-oscillator fiber laser | Center wavelength: 2090 nm; tuning range:200 nm; output power:77 W | [34] |
|
Table 3. Representative research progresses of external cavity frequency swept laser
| Year | Unit | Method | Performance index | Reference |
|---|
| 2006 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | All optical modes are stored in the long cavity up to several kilometers | Scan rate:290 kHz; tuning range:105 nm | [53] | | 2009 | Ludwig Maximilian University | Using faraday rotating mirror to reduce the cavity length | Scan rate:570 kHz; tuning range:95 nm | [60] | | 2012 | LightLab Imaging | Using dispersion compensation module(DCM)to reduce dispersion | Scan rate:200 kHz; tuning range:105 nm; output power:35 mW | [30] | | 2012 | Ludwig Maximilian University | Using four buffer stage to increase scan rate | Scan rate:1.6 MHz; tuning range:100 nm | [59] | | 2018 | Ludwig Maximilian University | Using improved FBG,SOA,and FP cavity | Tuning range:143 nm; scan rate:1.67 MHz | [28] |
|
Table 4. Representative research progresses of FDML frequency swept laser
| Year | Unit | Method | Performance index | Reference |
|---|
| 1999 | Coretek | Using strain compensated multiple quantum wells and using stable cavity to realize low diffraction loss cavity | Tuning range:50 nm; SMSR:50 dB | [67] | | 2003 | Hochschule Darmstadt University of Applied Science | Using electric pumping structure and introducing buried tunnel junction | Tuning range:40 nm; SMSR:32 dB | [70] | | 2009 | Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology,The University of Tokyo | Using movable silicon mirror with a high resonance frequency to increase scan rate | Scan rate:500 kHz; tuning range:55 nm; SMSR:60 dB | [71] | | 2012 | Praevium Research | The thin optical pump active region structure and the wide gain bandwidth InP based multi quantum well active region are combined with the wide bandwidth fully oxidized GaAs based mirrors through wafer bonding | Scan rate:500 kHz; tuning range:150 nm | [36] | | 2020 | Praevium Research | The strain compensated InGaAsP gain region is combined with a fully oxidized back mirror to achieve a wide tuning range | Scan rate:800 kHz; tuning range:100 nm;output power:30 mW | [37] |
|
Table 5. Representative research progresses of MEMS-VCSEL frequency swept laser
| Year | Unit | Method | Performance index | Reference |
|---|
| 1993 | University of California | First using sampling grating as two side grating | Tuning range:57 nm; SMSR:30 dB | [78] | | 1993 | NTT Photoelectric Laboratory | Using super structure grating instead of sampling grating to widen the tuning range | Tuning range:105 nm; SMSR:35 dB | [79] | | 2003 | Bookham | Designing digital supermodel DBR to improve tuning | Tuning range:40 nm; SMSR:40 dB | [82] | | 2004 | Bookham | Designing phase grating DBR to achieve flatness output | Tuning range:35 nm; SMSR:40 dB | [84] | | 2008 | Wuhan National Laboratory of Optoelectronics | Designing digital concatenated grating DBR to achieve flatness output and wide tuning range | Tuning range:54 nm; SMSR:40 dB | [85] | | 2019 | JDSU | SG-DBR produced by JDSU,which represents the SG-DBR with high performance at present | Tuning range:60 nm; SMSR:30 dB; output power:10 mW | [38] |
|
Table 6. Representative research progresses of DBR frequency swept laser
| Type | Technical maturity | Cost | Scan rate | Tuning range | Output power | Swept linearity |
|---|
| External cavity | high | high | low | high | high | middle | | FDML | middle | high | middle | middle | middle | low | | MEMS-VCSEL | high | middle | middle | middle | low | middle | | VT-DBR | low | low | high | low | low | high |
|
Table 7. Performance indexes of different types of swept frequency light sources