Hao Zhao, Jixin Yang, Xiaoqi Hu, Rui Wang, Yunjie Bi. Research on Powder Transport Behavior of Laser Cladding Under Vertical and Inclined Working Conditions[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(13): 1314003
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 13, 1314003 (2023)
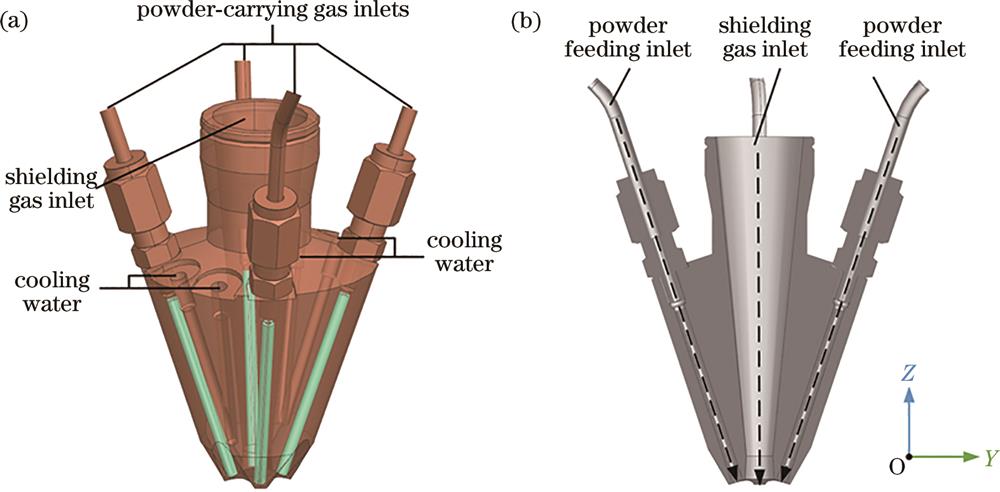
Fig. 1. Geometric model of the coaxial nozzle. (a) Three-dimensional model of the nozzle; (b) section of the nozzle
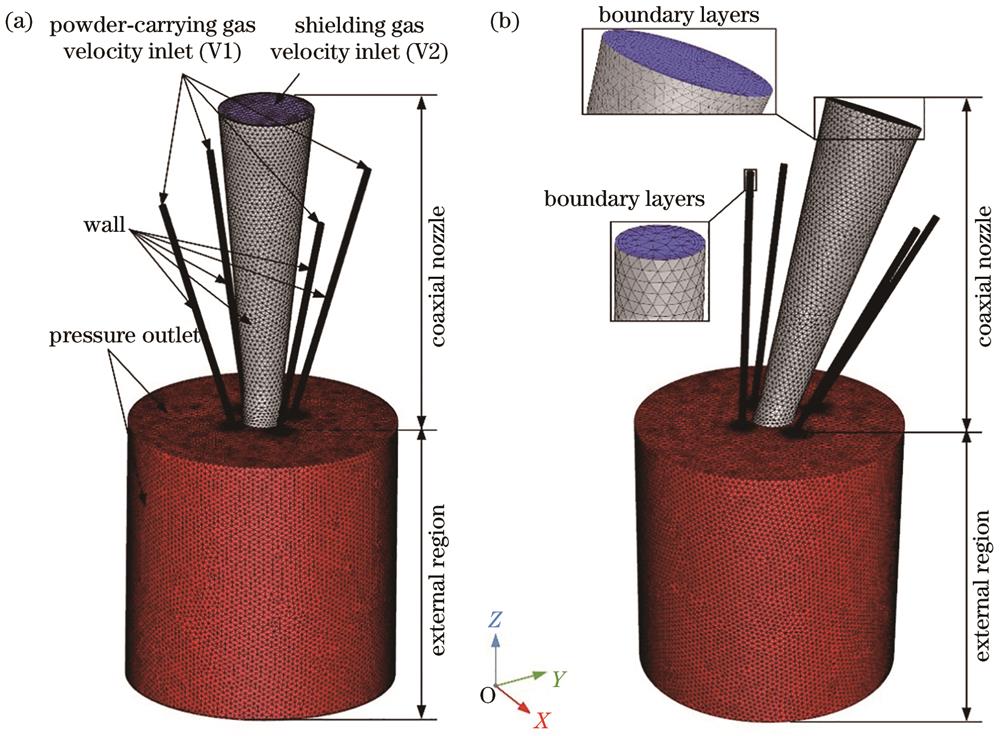
Fig. 2. Computational domain of the coaxial nozzle. (a) Vertical state of nozzle; (b) nozzle at 20° incline
Fig. 3. Distribution of gas flow field at X= 0 mm cross section. (a) Vertical state of nozzle; (b) nozzle at 20° incline
Fig. 4. Powder concentration distributions in different cross sections of the nozzle in vertical state. (a) X= 0 mm; (b) Z= 40 mm; (c) Z= 34 mm; (d) Z= 31 mm; (e) Z= 28 mm; (f) Z= 20 mm
Fig. 5. Powder concentration distributions in different cross sections of the nozzle at 20° incline. (a) X= 0 mm; (b) Z= 40 mm; (c) Z= 32 mm; (d) Z= 29 mm; (e) Z= 26 mm; (f) Z= 20 mm
Fig. 6. Processing methods of the computational domain of the nozzle at 20° incline. (a) Vertical state of nozzle; (b) nozzle at 20° incline
Fig. 7. Effect of carrier gas velocity on powder concentration. (a) Vertical state of nozzle; (b) nozzle at 20° incline
Fig. 8. Effect of powder feeding rate on powder concentration. (a) Vertical state of nozzle; (b) nozzle at 20° incline
Fig. 9. Effect of shielding gas velocity on powder concentration. (a) Vertical state of nozzle; (b) nozzle at 20° incline
Fig. 10. Experiment on powder flow field of nozzle free jet. (a) Measurement of powder focal diameter; (b) measurement of powder focusing height
Fig. 11. Cross section morphology of single pass and four pass samples printed on 316L alloy by laser cladding at different angles. (a)(c) Vertical state of nozzle; (b)(d) nozzle at 20° incline
|
Table 1. Processing parameters of numerical simulation
|
Table 2. Experimental facility

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



