Dechun Zou, Lü Zhibin. Advancement of All-Solid-State Fiber-Shaped Photovoltaic Cells[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(13): 1316007
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 13, 1316007 (2023)
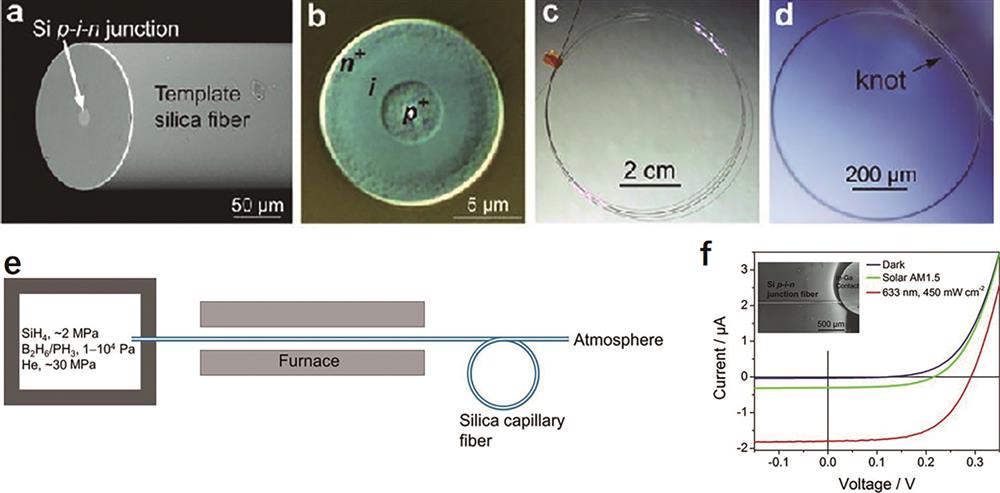
![Structure, preparation and performance of silicon-based fibrous photovoltaic cells[2,38-39]. (a) P-i-n junction on the fiber; (b) p-i-n junction section on the fiber; (c) silicon-based fiber solar cell; (d) preparation of the p-i-n junction on the fiber by vapor deposition; (e) current-voltage curve](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/13/1316007/img_01.jpg)
Fig. 1. Structure, preparation and performance of silicon-based fibrous photovoltaic cells[2,38-39]. (a) P-i-n junction on the fiber; (b) p-i-n junction section on the fiber; (c) silicon-based fiber solar cell; (d) preparation of the p-i-n junction on the fiber by vapor deposition; (e) current-voltage curve
![Preparation and performance of optical fiber micro-radial junction solar cell[40]. (a) Selectively etched with hydrogen fluoride; (b) exposed fiber core cavity structure; (c) p-i-n junctions formed by PEVCD; (d) ITO layer and aluminum electrode; (e) current density-voltage curve](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/13/1316007/img_02.jpg)
Fig. 2. Preparation and performance of optical fiber micro-radial junction solar cell[40]. (a) Selectively etched with hydrogen fluoride; (b) exposed fiber core cavity structure; (c) p-i-n junctions formed by PEVCD; (d) ITO layer and aluminum electrode; (e) current density-voltage curve
Fig. 3. ITO-based fibrous photovoltaic cells[9,41]. (a)(b) Structure of fibrous organic photovoltaic cells; (c) structure of fiber-based dye-sensitized cells; (d) current density-voltage curve of fiber-based dye-sensitized cells; (e) structure of CIS fibrous photovoltaic cells; (f) current density-voltage curve of CIS fibrous photovoltaic cells
Fig. 4. Structural design of fiber-based photovoltaic cells without transparent conductive oxides[24-26,31,42-43]. (a) Stainless steel wire mesh photoanode; (b) two-electrode wound structure based liquid state dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells; (c) two-electrode wound structure based all-solid state dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells; (d) two-electrode wound organic photovoltaic fiber cells; (e) liquid dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells of counter electrode wound photoanode type; (f) perovskite photovoltaic cells of counter electrode wound photoanode type; (g) organic photovoltaic cells of counter electrode wound photoanode type
Fig. 5. Organic fiber photovoltaic cells[31]. (a) Surface morphology of functional layers; (b) full-view image of the multilayer film coating; (c) cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy(SEM) image; (d) SEM image of the complete organic fiber photovoltaic cells; (e) enlarged view of the CNT yarn counter electrode; (f) current intensity-voltage curve of organic photovoltaic cells; (g) box plot of statistical efficiency
Fig. 6. Fiber perovskite photovoltaic cells[32]. (a) Structure of battery active layer; (b) physical image of battery; (c) SEM image of optical active layers; (d) SEM image of perovskite by dip-coating method; (e) SEM image of perovskite active layer prepared by vapor-assisted deposition method
Fig. 7. Fiber perovskite photovoltaic cells[33]. (a) Electrospinning preparation of photovoltaic active layer and cell winding process; (b) comparison of CH3NH3PbI3-PVP fibers obtained by electrospinning before and after annealing; (c) schematic diagram of the battery structure; (d) working-function relationship of functional layers; (e) CH3NH3PbI3-PVP fiber SEM images; (f) current density-voltage curve; (g) bending resistance test results
Fig. 8. Encapsulation and modularization of fiber solar cells[9,31,33]. (a) (b) Encapsulation and modularization of liquid fiber solar cells; (c) (d) modularity of organic fiber solar cells; (e) (f) modular schematic and physical diagram of a perovskite fiber solar cells obtained by electrospinning
|
Table 1. Performance comparison of representative devices of fiber perovskite photovoltaic cells
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



