Lingfei Liu, Daocheng Yuan, Lianxin Zhang. Binocular Vision Method for Measuring Shaft-in-Hole Assembly Parameters[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(16): 1615003
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 16, 1615003 (2023)

Fig. 1. Intersection line of hole plane and shaft. (a) Actual location of the intersection line; (b) relationship between the intersection line and the hole edge
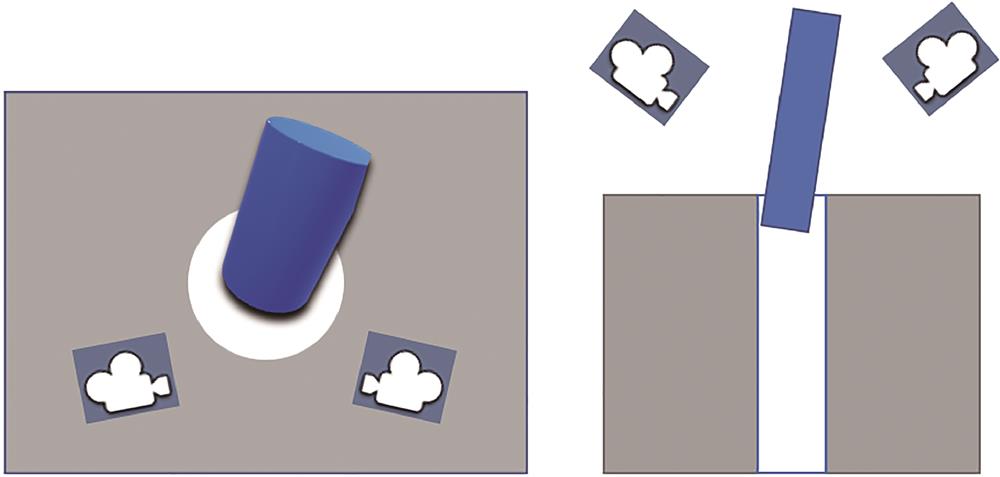
Fig. 2. Overall schematic of the assembly system
Fig. 3. Coordinate relationship of the system
Fig. 4. Imaging projection. (a) Imaging projection process of the outermost bus of the shaft; (b) top view; (c) imaging map
Fig. 5. Calculation process of the center position of the shaft
Fig. 6. Reprojection error analysis
Fig. 7. Calibration area division
Fig. 8. Overall experimental procedure
Fig. 9. Experimental setup
Fig. 10. Original image captured by the two cameras. (a) Image before assembly; (b) image after shaft placement
Fig. 11. Recognition result. (a) Intersection line before calibration; (b) calibration diagram; (c) calibrated intersection line, which is also the final result
Fig. 12. Hole and shaft condition under extreme condition
Fig. 13. Comparison of data before and after calibration. (a) Comparison of measured values; (b) comparison of mean relative errors
Fig. 14. Vertical shot of the experimental equipment and original image
|
Table 1. Measurement results and relative error before error calibration
|
Table 2. Measurement results and relative error after error calibration
|
Table 3. Measurement results and relative error of extended experiment after calibration

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



