[27] Scheers J. Charge-state-resolved spectroscopy of multiply-charged tin ions[D], 34-48(2020).
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 62, Issue 3, 0314001 (2025)
References
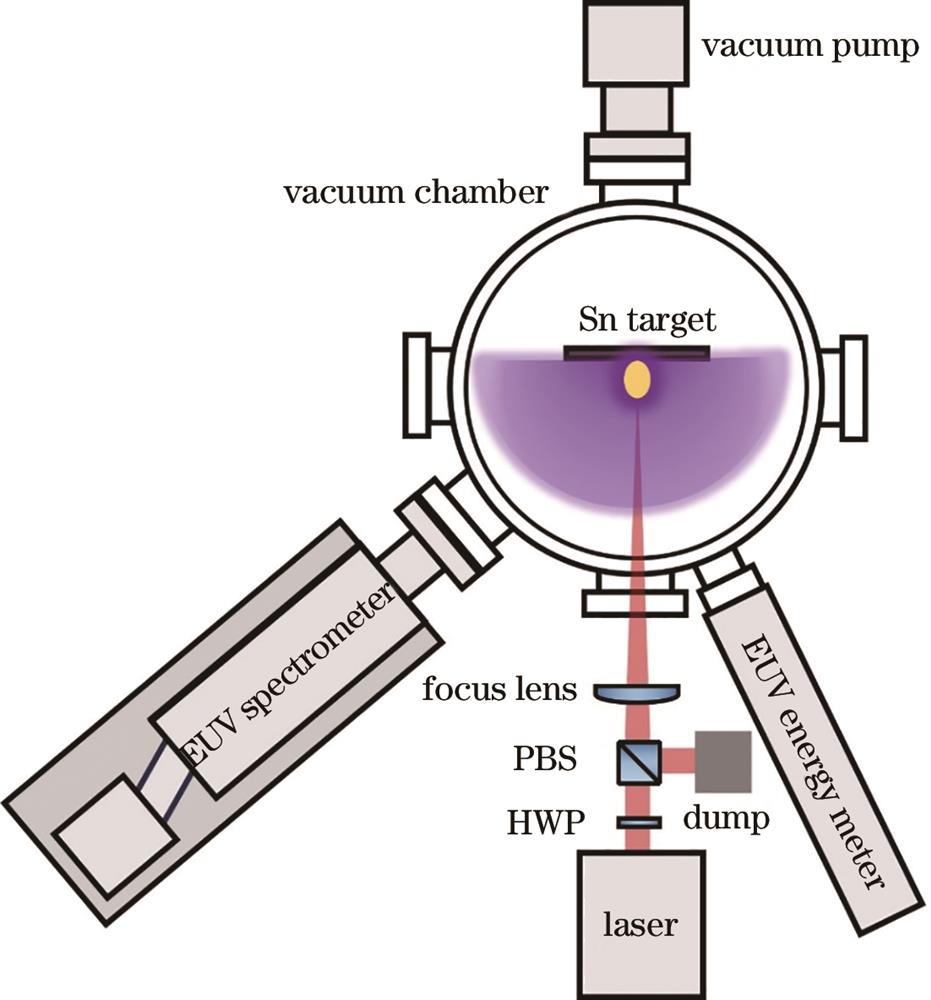
Liang He, Zhenlin Hu, Tianze Wang, Nan Lin, Yuxin Leng. Experimental Study on Highly Effective Broadband Extreme Ultraviolet Light Source by Spatially Confined Plasma[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(3): 0314001
Download Citation
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



