Weiming WANG, Weide WANG, Yi SU, Qingsong MA, Dongxu YAO, Yuping ZENG. Research Progress of High Thermal Conductivity Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared by Non-oxide Sintering Additives [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 634
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Inorganic Materials
- Vol. 39, Issue 6, 634 (2024)
![Schematic of typical packaging of power semiconductor device[1]](/richHtml/jim/2024/39/6/634/img_1.png)
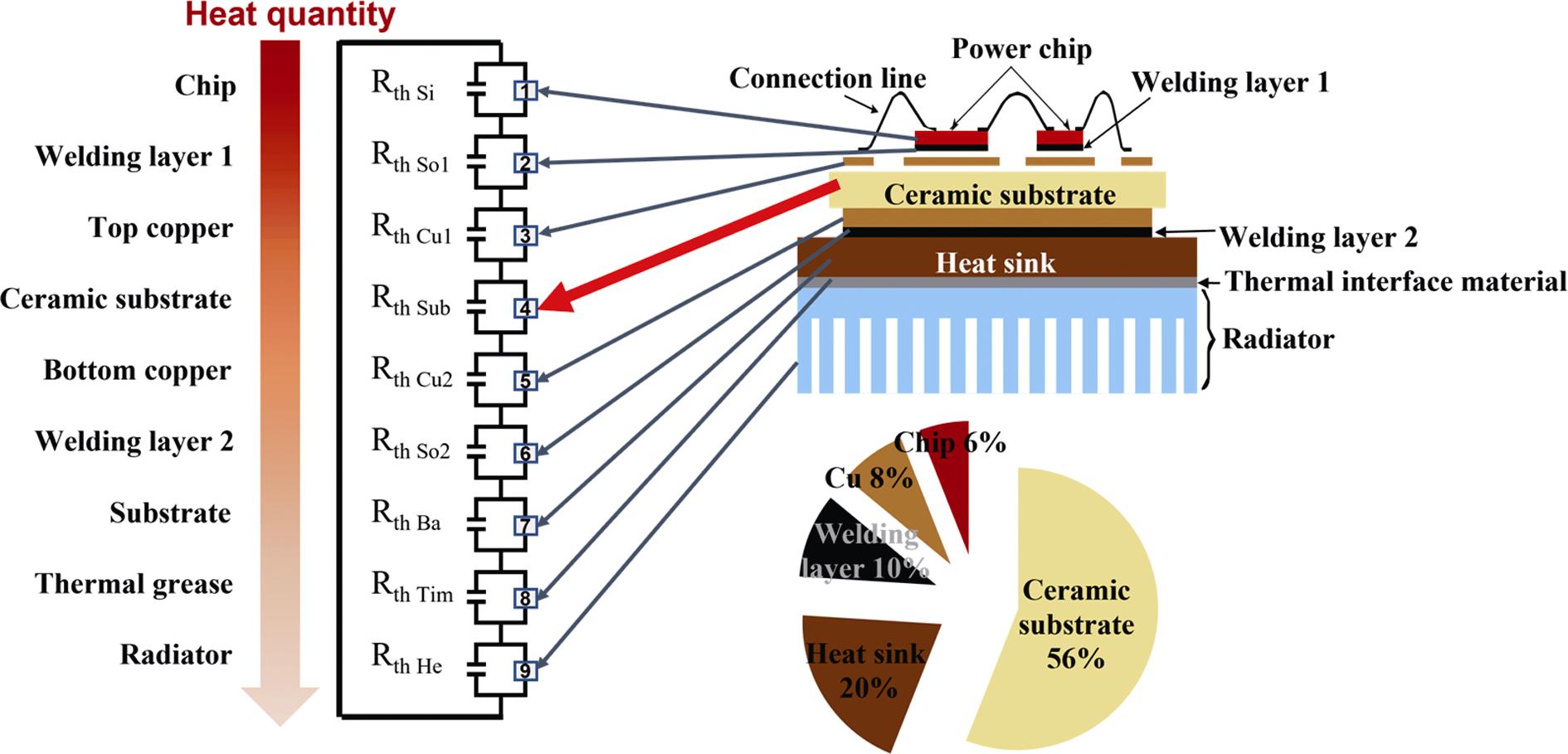
1. Schematic of typical packaging of power semiconductor device[1]
![Schematic of the liquid phase sintering mechanism for Si3N4 ceramics[10]](/richHtml/jim/2024/39/6/634/img_2.png)
2. Schematic of the liquid phase sintering mechanism for Si3N4 ceramics[10]
3. Effects of volume fraction of glassy phase, grain- boundary film thickness(δ ), and grain size on the thermal conductivity of β -Si3N4[13]
4. Effect of lattice oxygen content on the thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics[17]
5. Displacement-temperature curves of Si3N4 ceramics with MgF2 or MgO as sintering additives[19]
6. XRD patterns of Si3N4 samples prepared with different LiF contents[20]
7. Depolymerization mechanism of F atom in silicate melts[22]
8. SEM morphologies of the polished surfaces of Si3N4 ceramics after gas pressure sintering (GPS) with different additives added[24]
9. Typical HRTEM images of Si3N4 ceramics added with Y2O3 (a) and Y2Si4N6C (b) as additives[31]
10. Curves of relative displacement of the as-pressed specimens with temperature variation[32]
11. Densification mechanism of Si3N4 ceramics with ZrSi2-MgO additive[36]
12. Shrinkage curves of the Si3N4 ceramics[10]
13. Schematic illustration of Si3N4-Y2O3-SiO2 phase at 1900 ℃[10]
14. STEM-EDS characterizations of Si3N4 ceramics with the addition of ZrO2 and ZrH2[47]
15. SEM images on the fracture surfaces of nitrided samples (a, b) and post-sintered samples (c, d) without (a, c) and with (b, d) graphite powder bed addition[57]
17. (a) Shrinkage behaviors and densification mechanism of Si3N4 ceramics during sintering, and (b) relationship between β phase ratio and relative density[62]
18. Evolution of microstructure and diameter of Si3N4 ceramics[10]
|
Table 1. Properties of ceramic substrate materials[2]
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



