Search by keywords or author
- Photonics Research
- Vol. 13, Issue 4, 1021 (2025)
References
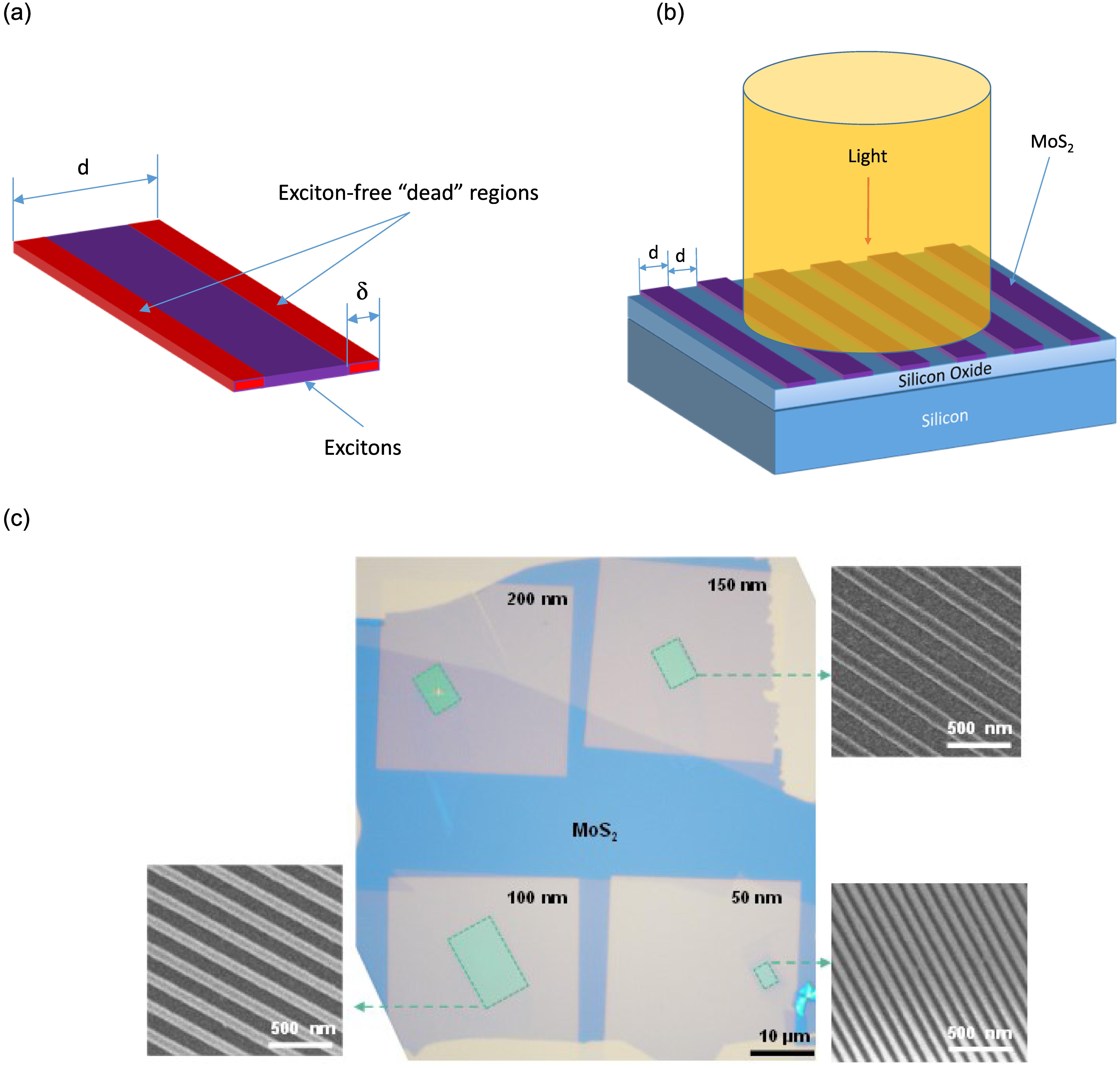
V. G. Kravets, Zhaolong Chen, Yashar Mayamei, K. S. Novoselov, A. N. Grigorenko, "Bilayer MoS2 nanoribbons: observation of optically inactive “exciton-free” regions and electrical gating of optical response," Photonics Res. 13, 1021 (2025)
Download Citation
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



