Yuzhu ZHOU, Youkui ZHANG, Li SONG. Noble Metal Phosphide Electrocatalysts and Their Synchrotron-based X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 225
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Inorganic Materials
- Vol. 36, Issue 3, 225 (2021)
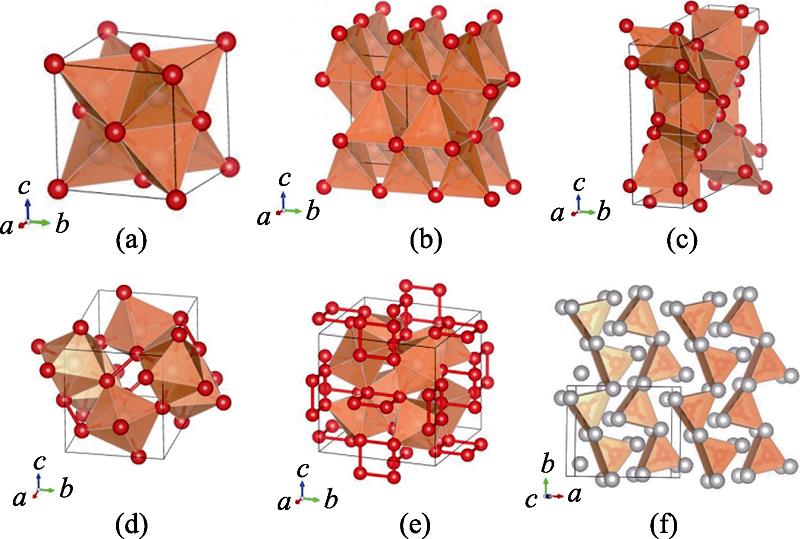
![The structures of selected platinum group metal (PGM) phosphides. The metal atoms displayed in grey and the phosphorus atoms displayed in red[11]](/richHtml/jim/2021/36/3/225/img_1.png)
1. The structures of selected platinum group metal (PGM) phosphides. The metal atoms displayed in grey and the phosphorus atoms displayed in red[11]
![Schematic illustration of the synthetic process for Ru-u2P/PC (a)[40] and RhP/rGO (b)[15]](/richHtml/jim/2021/36/3/225/img_2.png)
3. General synthesis procedure of MPx @NPGC and corresponding XRD patterns (a)[45], schematic illustration of preparation for Ru2P@PNC/CC-900 (b)[53]
4. TEM (a) and HRTEM (b) images of single Rh-P particle of Rh-P/CP, STEM and elemental mapping images for single Rh-P particle Rh (c) and P (d)[56], synthesis diagram of Ru-Ru2PΦNPC and NPC@RuO2 (e)[59]
5. XRD patterns for RhPx @NPC and XPS spectra for the Rh3d and P2p regions of RhPx @NPC catalysts (a)[65], Partial density of states (PDOS) projected on the d orbitals of Rh atoms at the surfaces of Rh(111), Rh2P(200) and RhP2(¯111) (b) (The red dash and yellow solid lines indicate the Fermi level (E F) and the location of d-bands center, respectively), electrocatalytic activities of Pt/C, Rh NS/C, and w-Rh2P NS/C in 0.1 mol/L KOH (c), free energy pathways (∆G ) for HER of P-terminated (PT-Rh2P (200)), Rh-terminated (RhT-Rh2P (200)), and Rh (100) surfaces, respectively, under alkaline condition (d)[71]
6. XPS results (a, b): Ir4f for IrP2/NPC before and after the OER/HER tests[32], schematic of the HER processes by Rux PNFs under alkaline conditions (c)[75], TEM, HR-TEM images of PdP2@CB before durability test in 1 mol/L KOH electrolyte (d) after durability test in 1 mol/L KOH electrolyte (e), and HER performance (f) of PdP2@CB in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4[69]
7. Schematic illustration of the synthesis and structure of the RuPx /NPG electrocatalyst (a)[77], TEM images of NC, NPC, Rh@NC, and RhPx @NPC nanoshells (b)[78], schematic illustration of the synthesis and structure of Rh2P@NPC and RhP2@NPC (c)[65], TEM image and EDS elemental mapping of Rh, P, C and N for RhP2@NPC (d), and SEM image of the PtNiP MNs (e)[73]
8. XRD patterns of RuPx synthesized in different temperatures (a)[44], theoretical models used in DFT calculations and adopted adsorption sites of H* on the surface of these models, calculated free-energy diagram of HER at equilibrium potential for Ru2P, RuP, and RuP2 (b)[46], the calculated water dissociation barrier and water dissociation pathway for RuP (121) and RuP2 (101) surfaces (c)[54]
9. HRTEM (a) and FFT (b) images of Ru-Ru2PΦNPC, HER performance of Ru-Ru2PΦNPC, Ru/C, Ru2P/C, NPC, and 20wt% Pt/C, ∆G H* calculated at the equilibrium potential of different models (c)[59], high-resolution HAADF-STEM(d) and HR-TEM (f) images of a Ru-Ru2P nanoparticle, pH dependences of the Tafel slopes of the Ru-Ru2P/PC and Pt/C catalysts, cyclic stability of the Ru-Ru2P/PC (f)[40], schematic illustration of a formation process for the hollow Ru-Rux P-Cox P polyhedra (g), Gibbs free energy diagram for the OER at different potentials on the surface of Co2P and Ru-RuPx -Cox P models (h)[85]
10. Pt4f core level of BPed Pt/GR with different amounts of BP (a), chemical state contents of the PtNPs as a function of BP adding amount (b), free energy diagram for HER with different Pt-P contents with ΔG H* in each system (c)[88], proposed photocatalytic mechanism of 0.1%-RP/g-CN for H2 evolution (d)[89], kinetics curves of H2 production over Pt/g-C3N4 and RhPx /g-C3N4-5%, cyclic running kinetics curves of H2 production over RhPx /g-C3N4-5% (e1-e2)[90]
11. TEM (a,b), and HRTEM (c) images of Rh2P@NC, polarization curves for Rh2P@NC (initial and after 1000 CV scanning) and time-dependent current density curve for Rh2P@NC under static overpotential of 20 mV for 10 h (d)[51], electrocatalytic properties for the HER in 1.0 mol/L KOH of Ru2P/RGO-20, Ru2P and Pt/C (e), free-energy diagram of the HER for RGO, Ru2P, Pt and Ru2P/RGO-20 (f)[81], band structure of pure RuP2 (left) and RuP2@NPC hybrid (right) (g)[93], HER polarization curves of the pure metal phosphides and the physical mixture of different metal phosphides and graphene in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 and 1 mol/L KOH (h)[45]
12. Schematic illustration of the fabrication of Ru-MnFeP/NF catalysts (a), calculated charge density differences of Fe2P-Ru and Mn2P-Ru structures (b)[98], high-resolution XPS spectra of Ni2p, Fe2p and P2p in the Ru-NiFe-P and the NiFe-P (c), the absorption modeled surfaces of Ru-NiFe-P (d), calculated ΔG H* for Ru-NiFe-P, NiFe-P, Ru-Ni-P, Ni-P, Ru-Fe-P and Fe-P (e), total density of states of Ru-NiFe-P and NiFe-P (f)[99]
13. HRTEM image of PdNP-CN (a), HAADF-STEM images of PdPNP-CN (b) and PdPSA-CN (c), the geometry structures of PdNP-CN (d), PdPNP-CN (e) and PdPSA-CN (f), Pd K-edge XANES spectra (g) and the corresponding k3-weighted FT spectra at R(h) and k(i) space[ 103], EXAFS spectra (j) of RuCl3@HPN and Ru SAs@PN, Wavelet transform (k) of Ru SAs@PN, Ru foil and RuCl3@HPN samples, N K edge (l) and P L edge (m) NEXAFS spectra, 31P solid state MAS NMR spectra at room temperature using a direct acquisition with proton decoupling of PN and RuβSAs@PN (n)[104]
14. In situ silver K-edge XANES (a) and EXAFS spectra (b) of AgP2 NCs, AgO, Ag2O, and Ag foil, Faradaic efficiency of the CO and CO:H2 ratio as a function of Agδ + in AgP2 and Ag (c), linear combination of AgO, Ag2O, and Ag spectra (solid line) compared to the raw Ag K-edge (d), Ag K-edge XANES spectra of AgP2 NCs with respect to CRR time under a constant applied potential of -0.8 V (vs . RHE) (e), Ag K-edge spectra of AgO and Ag2O references before and after CRR at -0.8 V (vs . RHE) for 50 s (f)[38]
15. Schematic illustration of the formation of Ni@Ni2P-Ru HNRs (a), Ni K-edge XANES spectra (b) and Fourier transformed k3-weighted EXAFS spectra of Ni@Ni2P-Ru, Ni@Ni2P, and reference Ni foil (c), Ru K-edge XANES spectra of Ni@Ni2P-Ru and reference Ru foil (d), dependence of the Ru(0) and Ru(IV) atomic fractions of the Ni@Ni2P-Ru HNRs as a function of photon energy (e)[108], Ni2p XPS comparison (f) and Ni L edge XANES comparison between Ni5P4-Ru and Ni5P4 (g), XANES (h) and EXAFS (i) results of Ni5P4-Ru, Ni5P4, Ni foil, and NiO at Ni K edge, respectively, Ru K-edge XAFS spectra (j) and the Ru K-edge k2-weighted EXAFS profiles of Ru foil, Ni5P4-Ru, and RuO2 (k)[97]
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



