Author Affiliations
1Faculty of Information Engineering and Automation, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, Yunan, China2Key Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence in Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, Yunan, Chinashow less
Fig. 1. Framework of proposed method
Fig. 2. Example diagram of triband decomposition. (a) Input images; (b) high-frequency subbands; (c) low-frequency subbands; (d) low-frequency structures; (e) low-frequency textures
Fig. 3. Flow chart of high-frequency subband fusion
Fig. 4. Fusion results of “Camp” source image. (a) Infrared images; (b) visible image; (c) CBF; (d) JSR; (e) JSRSD; (f) DRTV; (g) CVT-SR; (h) GTF; (i) MISF; (j) proposed method
Fig. 5. Fusion results of “Street” source image. (a) Infrared images; (b) visible image; (c) CBF; (d) JSR; (e) JSRSD; (f) DRTV; (g) CVT-SR; (h) GTF; (i) MISF; (j) proposed method
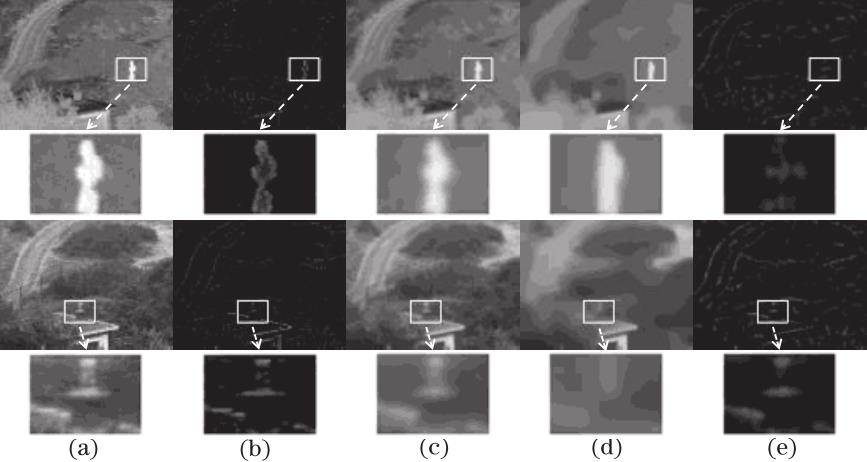
Fig. 6. Fusion results of “Gate” source image. (a) Infrared images; (b) visible image; (c) CBF; (d) JSR; (e) JSRSD; (f) DRTV; (g) CVT-SR; (h) GTF; (i) MISF; (j) proposed method
Fig. 7. Fusion results of “Car” source image. (a) Infrared images; (b) visible image; (c) CBF; (d) JSR; (e) JSRSD; (f) DRTV; (g) CVT-SR; (h) GTF; (i) MISF; (j) proposed method
Fig. 8. Fusion results of “House” source image. (a) Infrared images; (b) visible image; (c) CBF; (d) JSR; (e) JSRSD; (f) DRTV; (g) CVT-SR; (h) GTF; (i) MISF; (j) proposed method
Fig. 9. Three-band decomposition model verification. (a) Infrared images; (b) visible images; (c) dual-band decomposition; (d) triband decomposition
Fig. 10. Histogram of objective indexes of 21 fusion images
| Convolution group | Convolution | Pooling | Channel number | Output |
|---|
| 1(1_1,1_2) | | Max,22 | 64 | | | 2(2_1,2_2) | | Max,22 | 128 | | | 3(3_1,3_2,3_3) | | Max,22 | 256 | | | 4(4_1,4_2,4_3) | | Max,22 | 512 | | | 5(5_1,5_2,5_3) | | Max,22 | 512 | |
|
Table 1. Structural parameters of VGG-16
| Input:infrared and visible image and . Output:fused image |
|---|
| Step 1: and are decomposed by means of mean filtering | | Step 2:Low-frequency subbands and are decomposed by ST decomposition to obtain low-frequency structure and low-frequency texture | | Step 3:Low-frequency structure-texture fusion | | Step 3.1:Low-frequency structures are fused using average rule | | Step 3.2:Low frequency textures are fused using NSF rules | | Step 4:High-frequency subband fusion | | Step 4.1:Input image are fed into VGG-16 network to extract multi-channel feature map | | Step 4.2:L1 regularization and convolution smoothing are performed on multi-channel feature map to obtain single channel feature map | | Step 4.3:Single channel feature map is up sampled and corresponding weight map is calculated | | Step 4.4:Five-dimensional weight map is normalized by sigmoid average normalization strategy to obtain normalized weight to guide fusion of high-frequency subbands,and pre-fused high-frequency image is obtained | | Step 5:Final fusion image is reconstructed from three pre-fusion subbands(,,) |
|
Table 2. Concrete implementation of proposed method
| Image | Algorithm | CBF | JSR | JSRSD | DRTV | CVT-SR | GTF | MISF | Proposed |
|---|
| Group 1 “Camp” | NABF | 0.2436 | 0.2319 | 0.3137 | 0.0946 | 0.1537 | 0.0754 | 0.0467 | 0.0261 | | SSIM | 0.6009 | 0.6024 | 0.5505 | 0.6802 | 0.6920 | 0.6776 | 0.6977 | 0.7452 | | MS-SSIM | 0.7369 | 0.8720 | 0.7530 | 0.6990 | 0.8637 | 0.7733 | 0.8334 | 0.8807 | | CC | 0.5466 | 0.6299 | 0.5618 | 0.4561 | 0.5726 | 0.4622 | 0.4978 | 0.6349 | | MSE | 0.0136 | 0.0478 | 0.0237 | 0.0199 | 0.0145 | 0.0192 | 0.0183 | 0.0109 | | PSNR | 66.7992 | 61.3336 | 64.3766 | 65.1374 | 66.5115 | 65.3087 | 65.5095 | 67.7416 | | Group 2 “Street” | NABF | 0.4870 | 0.1804 | 0.1908 | 0.1437 | 0.2142 | 0.0803 | 0.0762 | 0.0284 | | SSIM | 0.4986 | 0.6299 | 0.6237 | 0.6245 | 0.6337 | 0.6172 | 0.6391 | 0.6741 | | MS-SSIM | 0.6986 | 0.9688 | 0.9471 | 0.9177 | 0.9214 | 0.8953 | 0.9124 | 0.9162 | | CC | 0.5267 | 0.6476 | 0.6172 | 0.4948 | 0.5438 | 0.5024 | 0.5280 | 0.6740 | | MSE | 0.0310 | 0.0462 | 0.0437 | 0.0400 | 0.0347 | 0.0381 | 0.0378 | 0.0207 | | PSNR | 63.2231 | 61.4825 | 61.7211 | 62.1136 | 62.7326 | 62.3177 | 62.3572 | 64.9705 | | Group 3 “Gate” | NABF | 0.2554 | 0.2430 | 0.3419 | 0.0686 | 0.1729 | 0.0365 | 0.0582 | 0.0128 | | SSIM | 0.6497 | 0.6281 | 0.5665 | 0.6871 | 0.7229 | 0.7008 | 0.7042 | 0.7775 | | MS-SSIM | 0.7333 | 0.9037 | 0.8329 | 0.7589 | 0.8806 | 0.7979 | 0.8135 | 0.9162 | | CC | 0.4937 | 0.5862 | 0.5637 | 0.3905 | 0.5005 | 0.3910 | 0.4325 | 0.6073 | | MSE | 0.0331 | 0.0714 | 0.0545 | 0.0453 | 0.0401 | 0.0448 | 0.0405 | 0.0232 | | PSNR | 62.9376 | 59.5965 | 60.7645 | 61.5729 | 62.1037 | 61.6147 | 62.0529 | 64.478 | | Group 4 “Car” | NABF | 0.2393 | 0.2692 | 0.3807 | 0.1351 | 0.1835 | 0.0771 | 0.0660 | 0.0209 | | SSIM | 0.6172 | 0.5692 | 0.4990 | 0.7117 | 0.6980 | 0.7195 | 0.6962 | 0.7643 | | MS-SSIM | 0.6986 | 0.8146 | 0.7746 | 0.7532 | 0.8576 | 0.8260 | 0.7998 | 0.8929 | | CC | 0.2303 | 0.3659 | 0.3336 | 0.2227 | 0.2517 | 0.2234 | 0.2460 | 0.3865 | | MSE | 0.0416 | 0.1115 | 0.0726 | 0.0506 | 0.0416 | 0.0508 | 0.0466 | 0.0262 | | PSNR | 61.9382 | 57.6584 | 59.5217 | 61.0862 | 61.9404 | 61.0695 | 61.4480 | 63.9461 | | Group 5 “House” | NABF | 0.5278 | 0.2109 | 0.2801 | 0.1100 | 0.2216 | 0.0829 | 0.1595 | 0.0218 | | SSIM | 0.4575 | 0.6253 | 0.5808 | 0.6486 | 0.6537 | 0.6606 | 0.6492 | 0.7248 | | MS-SSIM | 0.5105 | 0.8873 | 0.7446 | 0.8055 | 0.8668 | 0.8267 | 0.7668 | 0.9105 | | CC | 0.2624 | 0.3556 | 0.2722 | 0.1519 | 0.2062 | 0.1647 | 0.1903 | 0.3794 | | MSE | 0.0483 | 0.0992 | 0.0845 | 0.0668 | 0.0657 | 0.0734 | 0.0659 | 0.0374 | | PSNR | 61.2878 | 58.1652 | 58.8630 | 59.8834 | 59.9580 | 59.4746 | 59.9426 | 62.4026 |
|
Table 3. Comparison of objective indexes of fusion results
| Scheme | NABF | SSIM | MS-SSIM | CC | MSE | PSNR |
|---|
| Max+ST | 0.0371 | 0.7477 | 0.8958 | 0.4869 | 0.0244 | 64.6999 | | VGG_Max+ST | 0.0186 | 0.7629 | 0.9028 | 0.4904 | 0.0241 | 64.7542 | | VGG_Sigmiod+ST | 0.0177 | 0.7659 | 0.9096 | 0.4995 | 0.0241 | 64.7526 |
|
Table 4. Ablation experiment