Lixia ZHENG, Wangqiao YOU, Kang HU, Jin WU, Weifeng SUN, Xingye ZHOU. Fast active-passive mixed quenching circuit applied to SPAD array[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(7): 20240136
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 53, Issue 7, 20240136 (2024)
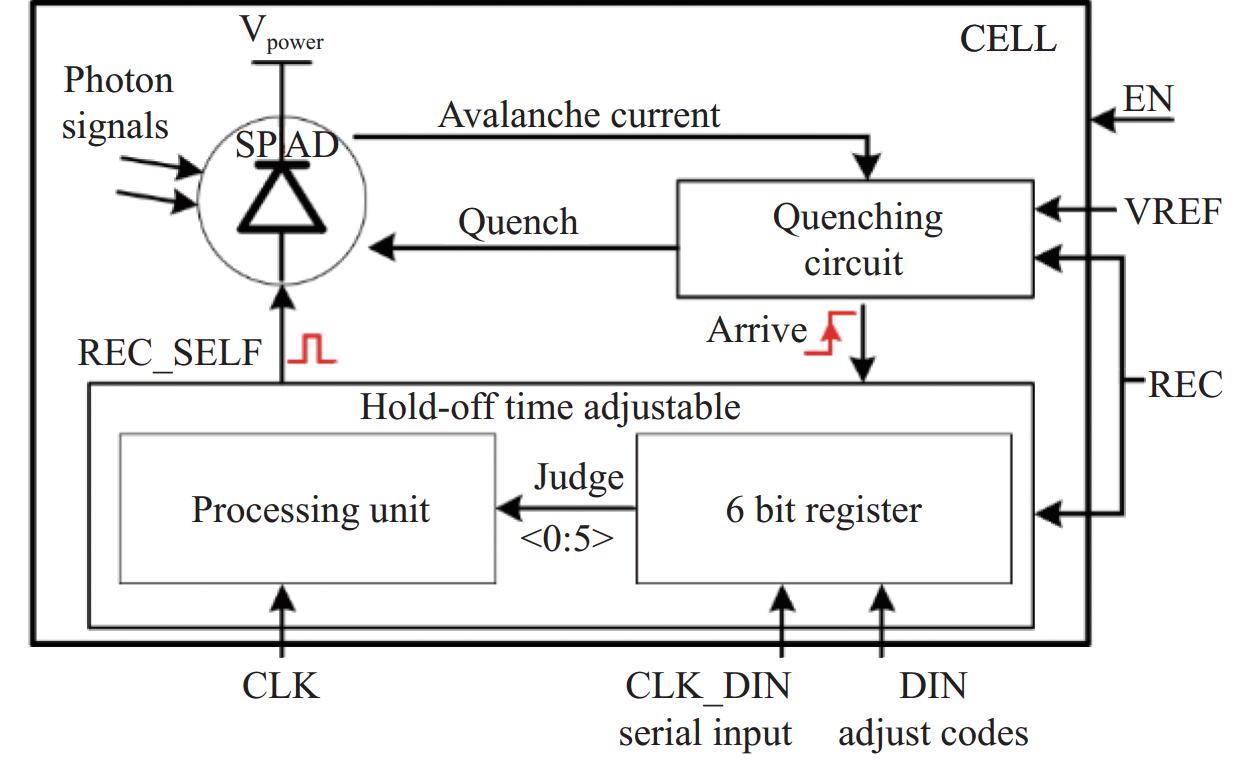
Fig. 1. Circuit architecture diagram

Fig. 2. Timing diagram of the circuit nodes
Fig. 3. (a) Passive quenching circuit structure; (b) Active-passive mixed quenching circuit structure
Fig. 4. Transient response of the mixed quenched SPAD
Fig. 5. (a) Equivalent circuit diagram of the quenching circuit with
Fig. 6. Simulated dependence of the induction delay time on inductive resistance k
Fig. 7. Simulated dependence of the normalized delay improvement on inductive resistance k =k 2
Fig. 8. Simulated dependence of the “cost performance” on inductive resistance k
Fig. 9. Quenching circuit structure
Fig. 10. (a) Layout of the proposed circuit; (b) Chip diagram of the detector and circuit connection
Fig. 11. (a) Measured resetting time of the proposed circuit; (b) Measured quenching time of the proposed circuit
|
Table 1. Comparison of proposed quenching circuit with state-of-art

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



