Qingge Li, Xiaogang Yang, Ruitao Lu, Siyu Wang, Jiwei Fan, Hai Xia. Cross-modal geo-localization method based on GCI-CycleGAN style translation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(7): 20220875
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 52, Issue 7, 20220875 (2023)
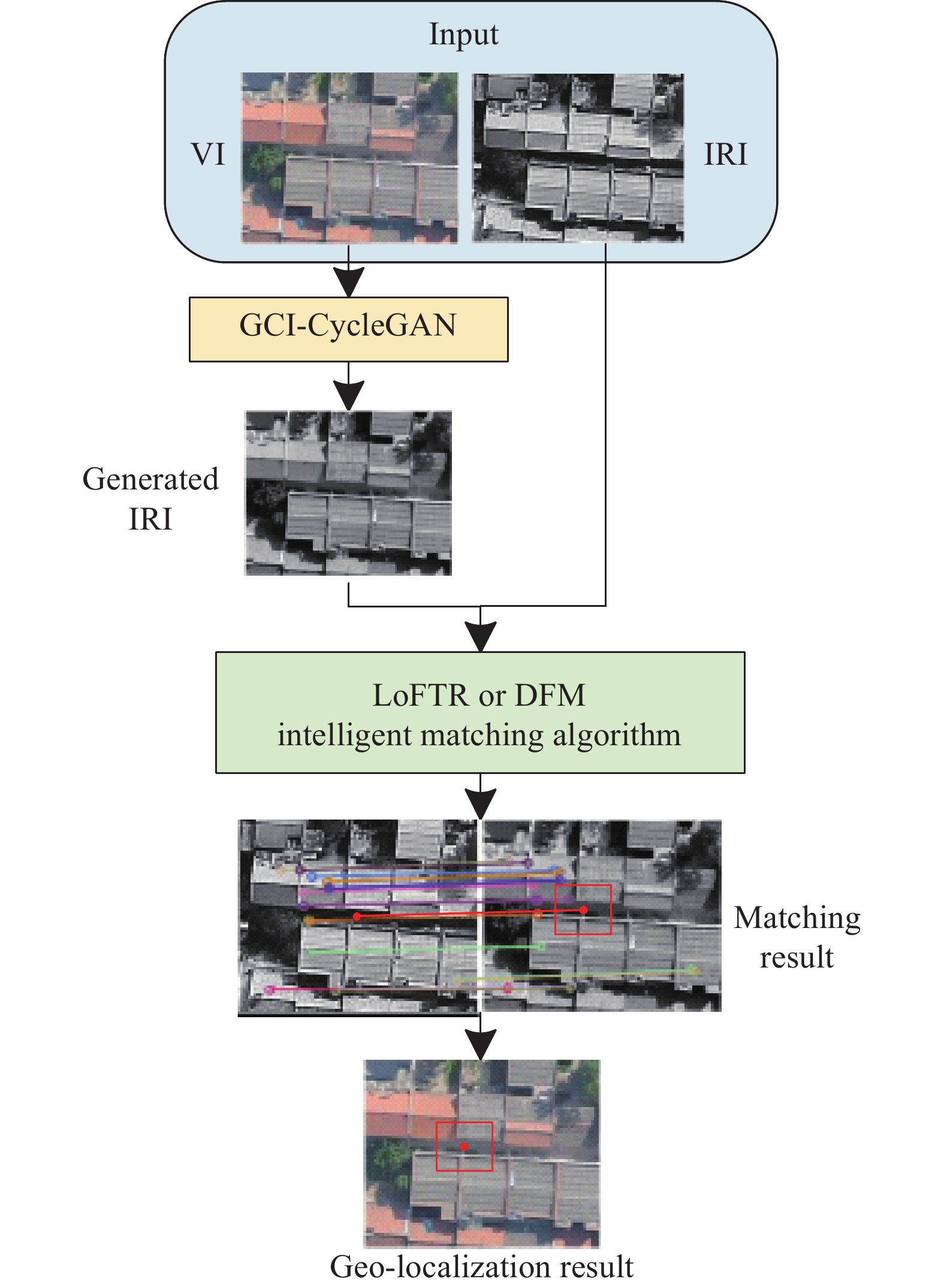
Fig. 1. Framework of the cross-modal geo-localization method

Fig. 2. Principle of the cross-modal images style translation
Fig. 3. Diagram of the GCI-CycleGAN model structure
Fig. 4. Example of training samples. (a) VIs; (b) IRIs
Fig. 5. Loss function curve. (a) CycleGAN; (b) GCI-CycleGAN
Fig. 6. Diagram of the LoFTR model structure
Fig. 7. Diagram of the DFM model structure
Fig. 8. (a) VIs to be converted; (b) IRIs converted by CycleGAN; (c) IRIs converted by GCI-CycleGAN; (d) Real IRIs
Fig. 9. Comparison of the matching methods results
Fig. 10. Example images of the geo-location dataset. (a) Visible images; (b) Real-time infrared images; (c) Generated infrared images
Fig. 11. Diagram of the matching and geo-location results
Fig. 12. Comparison between actual flight trajectory and location results
|
Table 1. Performance comparison of different models
|
Table 2. Performance comparison of matching methods
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. The performance of geo-location

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



