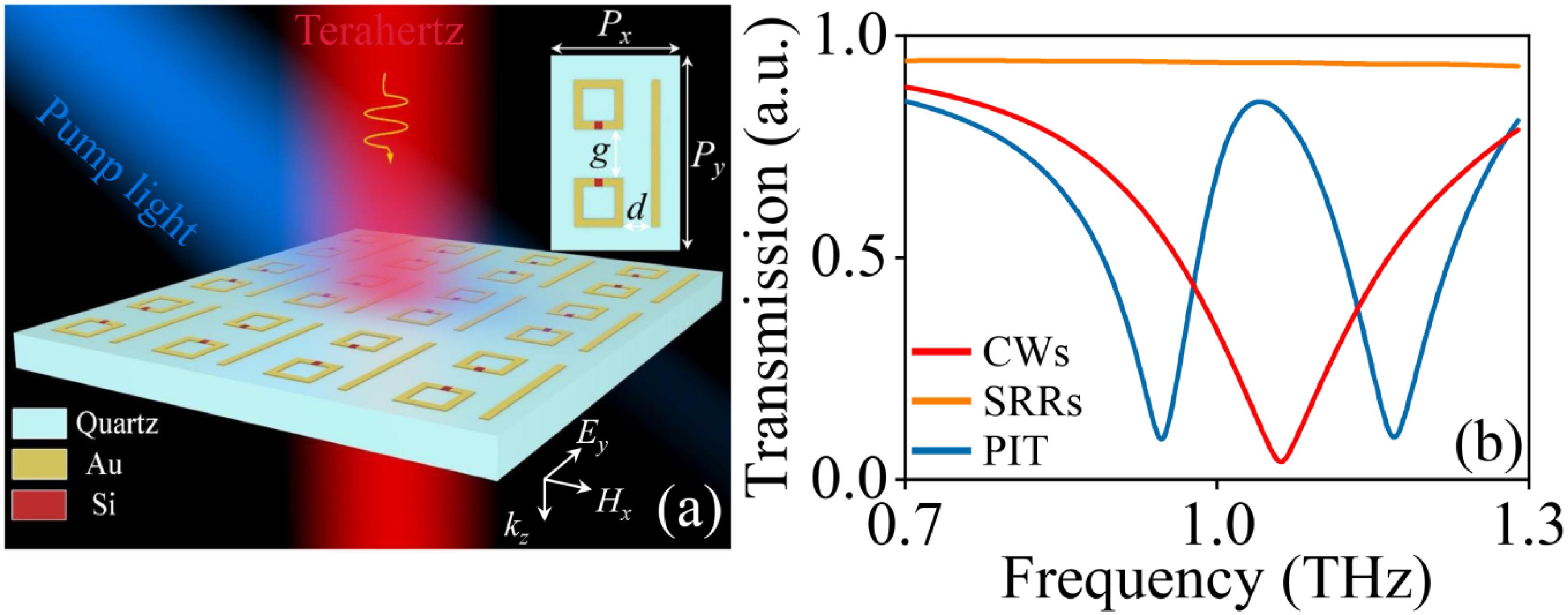
[1] S. E. Harris. Electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Today, 50, 36(1997).
[21] N. I. Zheludev, Y. S. Kivshar. From metamaterials to metadevices. Nat. Mater., 11, 917(2012).
[22] T. F. Krauss. Why do we need slow light?. Nat. Photon., 2, 448(2008).