Yulong JIN, Xin ZHANG, Jingyuan YAO, Shuai GU, Pu WANG. Low-loss mid-infrared composite hollow core anti-resonant fiber[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2025, 54(2): 20240468
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 54, Issue 2, 20240468 (2025)
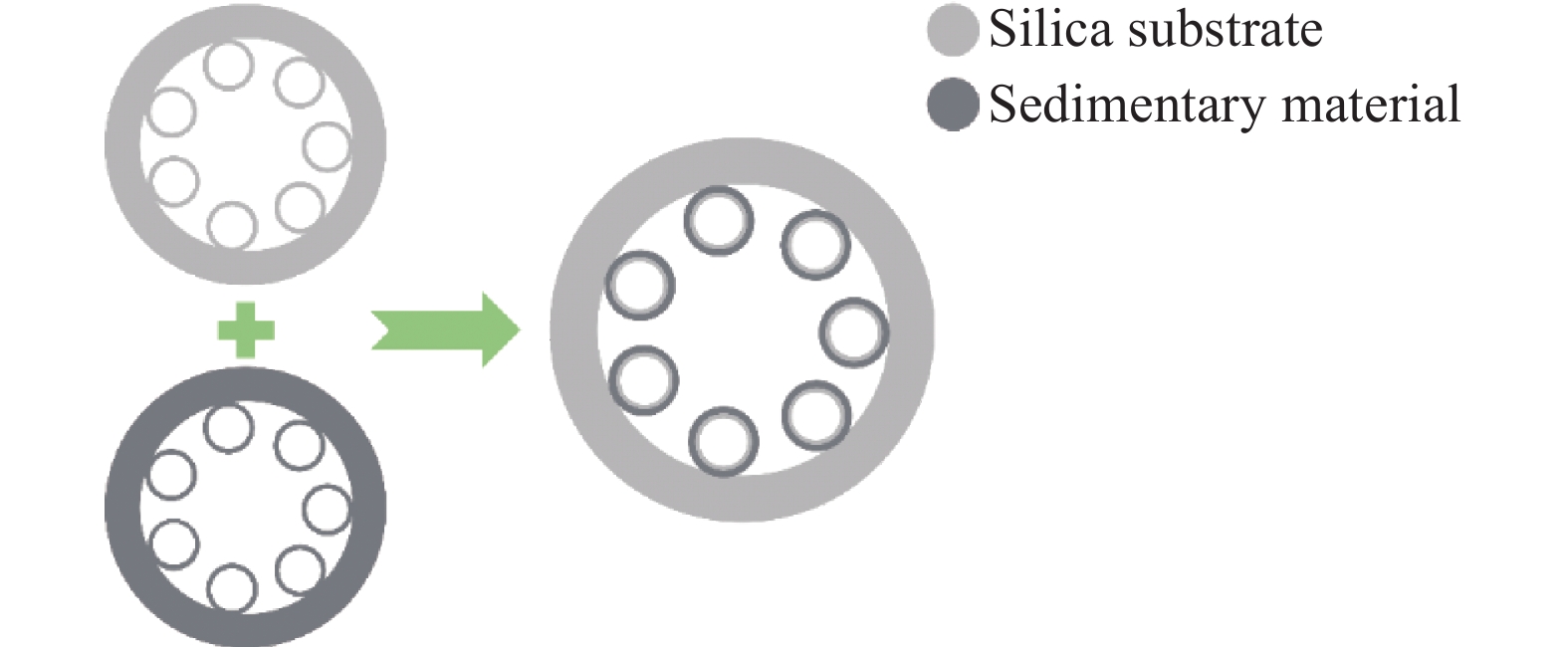
Fig. 1. Design concept of composite hollow core anti-resonant optical fiber

Fig. 2. (a) Structure diagram of hollow core anti-resonant fiber; (b) Back and forth path of light in silica wall
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of structural parameters for composite material hollow core anti-resonant optical fiber
Fig. 4. The loss spectrum of composite material hollow core anti-resonant fibers
Fig. 5. Schematicdiagram of structural parameters for composite optical fiber
Fig. 6. (a) Overlap degree of silica cladding mode field; (b) The degree of overlap of the mode field of the sedimentary layer with different proportions of cladding materials
Fig. 7. (a) Absorption loss; (b) Transmission loss with different proportions of cladding materials
Fig. 8. Mid-infrared optical material absorption loss
Fig. 9. Composite fiber materials of different sedimentary layers. (a) Mode field overlap of silica layers; (b) Mode field overlap of sedimentary layers; (c) Absorption loss; (d) Transmission loss
|
Table 1. Material thickness and corresponding proportion in composite fiber when the first-order resonant wavelength around 3 μm
|
Table 2. Refractive index values of different materials at 3 μm

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



