Yongli Bai, Xinguo Huang, Shanshan Zhang, Xian Leng, Yunfei Zhong, Nan Peng, Xiaochun Xie, Nan Peng. Type Identification and Concentration Quantitative Analysis of Water-Based Ink Additives Based on Visible/Near-Infrared Spectroscopy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(23): 2330003
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 23, 2330003 (2022)

Fig. 1. Normalized reflectance spectra of experimental samples
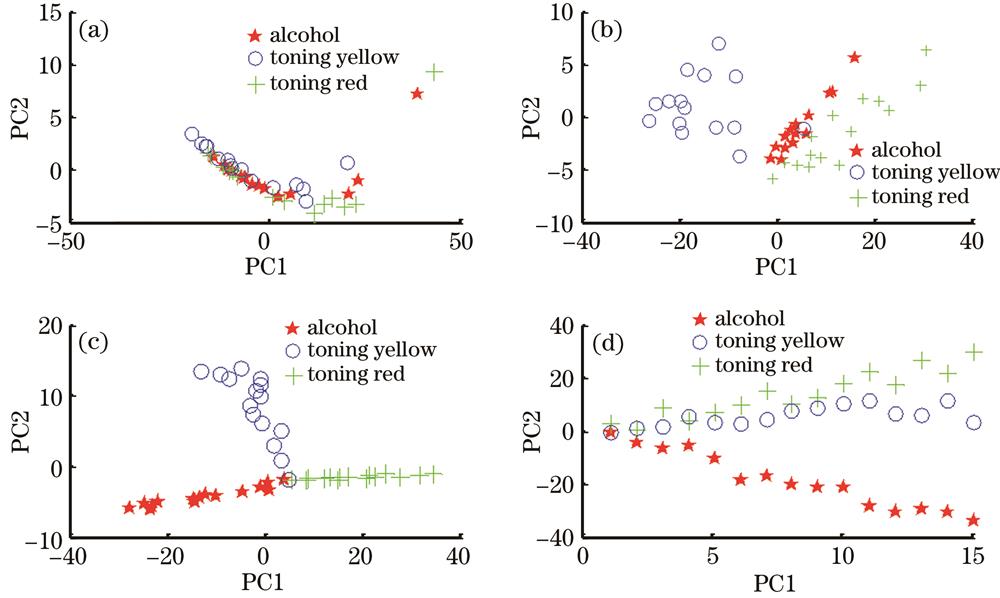
Fig. 2. Principal component score distributions of each spectrum interval of different additives. (a) 380-500 nm; (b) 501-616 nm; (c) 617-726 nm; (d) 727-831 nm
Fig. 3. Correlation between measured value and predicted value of concentration of alcohol additives
Fig. 4. Correlation between measured value and predicted value of concentration of toning yellow additives
Fig. 5. Correlation between measured value and predicted value of concentration of toning red additive
|
Table 1. Mass fraction of additives added in ink
|
Table 2. Principal component analysis cumulative variance contribution rate
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Comparison of quantitative cross-validation of PLS under different pretreatment methods
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Comparison of iPLS modeling results in different bands

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



