Search by keywords or author
Journals >Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
Export citation format
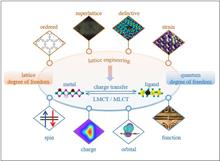
Lattice engineering for electronic state control research
ZHANG Dantong, and XUE Dongfeng
Lattice engineering plays a crucial role in the fields of material science and device design. By precisely constructing lattice-ordered states, superlattice states, lattice defect states, etc., it becomes possible to effectively build materials with topological order and customize the macroscopic lattice architecture tLattice engineering plays a crucial role in the fields of material science and device design. By precisely constructing lattice-ordered states, superlattice states, lattice defect states, etc., it becomes possible to effectively build materials with topological order and customize the macroscopic lattice architecture to enhance their functionality in areas such as optics, electronics, and magnetism. Specifically, materials with topological order based on the intrinsic periodicity of the lattice exhibit unique band structures that result in high conductivity, lower energy loss, and special quantum Hall effect during electron transport. And superlattice materials assembled through spatial organization and longitudinal rotation, such as the Moiré pattern series, can provide new avenues for improving the performance of optoelectronic sensors and photonic devices. While lattice defects enable the realization of localized electronic states, defect spin states, and other special effects, facilitating the design of magnetic control and magnetic storage devices..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 839 (2024)
Design and research of Cs atomic concentration detection system based on laser absorption spectroscopy
SONG Zeyang, LIANG Lizhen, LIU Shanhu, TIAN Zhenhu... and HU Chundong|Show fewer author(s)
It is well known that in magnetic confinement fusion research, the extraction current density of negative hydrogen ion source depends on the negative hydrogen ion density formed on the metal surface with low work function. Therefore, the formation of negative hydrogen ions is largely dependent on the dynamics of cesiumIt is well known that in magnetic confinement fusion research, the extraction current density of negative hydrogen ion source depends on the negative hydrogen ion density formed on the metal surface with low work function. Therefore, the formation of negative hydrogen ions is largely dependent on the dynamics of cesium in the source, and optimizing the performance of ion source to improve the extraction current density is a prerequisite. Based on the tunable semiconductor laser absorption spectroscopy, a new system for detecting cesium concentration in discharge chamber was designed and established to achieve rapid and real-time detection of trace Cs. The system design mainly focused on four aspects: light source generation unit, optical transmission testing unit, signal processing acquisition unit, and spectral display and analysis unit. And then an off-line testing system was established and system testing experiments were conducted. The curve of cesium concentration with temperature was obtained. As the temperature of the vapor cell increases, the detected Cs atom concentration exhibits a nonlinear positive correlation with temperature, demonstrating that the system enables quantitative detection of Cs atom concentration..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 852 (2024)
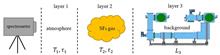
Research on infrared spectra simulation of sulfur hexafluoride in confined space
ZHAO Yue, MA Fengxiang, WANG Anjing, LI Dacheng... and DONG Wangchao|Show fewer author(s)
In response to the demand for infrared remote sensing of trace leakage of sulfur hexafluoride gas in power confined space and the lack of measured data in different scenarios and different environmental parameters required for the high-precision identification algorithm modeling of sulfur hexafluoride infrared spectra,In response to the demand for infrared remote sensing of trace leakage of sulfur hexafluoride gas in power confined space and the lack of measured data in different scenarios and different environmental parameters required for the high-precision identification algorithm modeling of sulfur hexafluoride infrared spectra, the simulation of sulfur hexafluoride infrared spectra in confined space has been conducted. On the one hand, an infrared radiation transmission model of sulfur hexafluoride was established, and the influences of background radiation, atmospheric interference radiation and background temperature difference on the infrared signal of sulfur hexafluoride were analyzed theoretically. On the other hand, in order to solve the problem of insufficient on-site acquisition or measurement conditions for background radiation in some confined space scenarios, a laboratory detection device for sulfur hexafluoride infrared radiation simulation transmission was built, which not only helped to realize the background radiation simulations in different confined spaces by controlling and adjusting influencing factors, but also to validate the infrared spectra simulation results. The infrared spectra of sulfur hexafluoride under two typical backgrounds (cement wall and equipment metal shell) of confined spaces were experimentally simulated and collected at different temperatures, and at the same time, the infrared spectra under different atmospheric interference and sulfur hexafluoride concentrations were also simulated. As a verification, the whole transmission process of sulfur hexafluoride infrared radiation in a confined space was simulated, and the measured spectra were obtained and compared with the simulated spectra. The comparison results showed that the simulation brightness error was0.11-0.45 K, which preliminarily verified the feasibility of the proposed method, and provided a reference for constructing and improving the infrared identification algorithm of sulfur hexafluoride gas leakage in confined space in the future..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 861 (2024)
Research on calibration method of large‐aperture meter‐scale laser beam quality measuring device
ZHU Fei, HOU Zaihong, WANG Gangyu, QIN Laian... and WU Decheng|Show fewer author(s)
With the increasing application of laser, the quality measurement of laser beams with meter-sacle large-aperture is of important research value. To avoid the influence of atmosphere, the wavefront measurement method is gernerally used to directly measure the quality of laser beams with meter-scale large-aperture at theWith the increasing application of laser, the quality measurement of laser beams with meter-sacle large-aperture is of important research value. To avoid the influence of atmosphere, the wavefront measurement method is gernerally used to directly measure the quality of laser beams with meter-scale large-aperture at the outlet of laser systems. In order to achieve accurate measurement, it is necessary to calibrate the zero point of the meter-scale large-aperture measurement system first. A scanning calibration method for the large-aperture measurement system is proposed in this work using a small aperture calibration light source. The errors of the beam spot centroid shift caused by residual errors of the parallelism of the calibration light source under different scanning mode are analyzed, and the influence of residual errors of the parallelism of the calibration light source on the measurement accuracy in different scanning mode is simulated and analyzed. According to the wavefront restoration results, the unidirectional scanning mode is selected, and it is specified that the residual error of the parallelism of the calibration light source is not greater than 5 μrad when the aperture of scale validation model system is 127 mm, while the residual error of the parallelism of the calibrated light source for the actual measurement system with 1.27 m aperture is not greater than 0.5 μrad..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 872 (2024)
Reliability design of detector array target circuit system
YUAN Lichao, TAN Fengfu, HUANG Zhigang, CHENG Yilun, and HOU Zaihong
Detector array target is a common equipment for measuring the spatiotemporal distribution of laser intensity, and as an important part of detector array target, circuit system's reliability is the key to the efficient and stable operation of detector array target. Firstly, the failure mode and effect analysis (FMEADetector array target is a common equipment for measuring the spatiotemporal distribution of laser intensity, and as an important part of detector array target, circuit system's reliability is the key to the efficient and stable operation of detector array target. Firstly, the failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) of the circuit system is carried out to obtain the influence of different modules on the reliability of the overall system. In order to calculate the reliability of the circuit system, the importance of each module is introduced, and the importance of the traditional AGREE allocation method is improved when analyzing the importance of each module. Subsequently, according to the improved AGREE allocation method, reliability indexes are assigned, and redundancy design is used to improve the reliability of the modules that do not meet the reliability index, so that the reliability of the circuit system operating for 5 h is increased from 0.99931830 to 0.99996730. This study provides a method and basis for the reliability design and distribution of detector array target circuit systems..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 881 (2024)
Analysis of light source errors of no⁃phase⁃postselection twin⁃field type quantum key distribution protocal
LU Wenhao, WU Zihan, MA Junyao, YU Yang, and ZHAO Shengmei
No-phase-postselection twin-field quantum key distribution (NPP TF-QKD) protocal is a variant of twin-field quantum key distribution (TF-QKD) protocal. It not only inherits TF-QKD's advantage of overcoming the constraint of a point-to-point QKD link, but also simplifies its security proof. Its practical feasibilityNo-phase-postselection twin-field quantum key distribution (NPP TF-QKD) protocal is a variant of twin-field quantum key distribution (TF-QKD) protocal. It not only inherits TF-QKD's advantage of overcoming the constraint of a point-to-point QKD link, but also simplifies its security proof. Its practical feasibility has been demonstrated in experiments. However, it has been assumed that the protocol's light source is precisely controllable, but that is unavailable in practical applications due to the drawbacks of practical devices and environmental noises. In this paper, the influence of the light source intensity fluctuation, an example of light source errors, on NPP TF-QKD protocol's performance is discussed both for the symmetrical and asymmetrical channels. The simulation results show that light source errors can decrease the protocol's secure key rate and shorten the transmission distance of NPPTF-QKD protocal..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 891 (2024)
Decentralized quantum anonymous one⁃vote veto scheme
XU Xiaotong, SHI Runhua, KE Weiyang, and YU Hui
To remove any trusted third party from the voting scheme, a new concept of secure multiparty computations is defined, i.e., secure multiparty disjunction(SMD), and then a quantum SMD protocol is presented by using local operators and entanglement swapping of Bell states. Based on this primitive protocol of secure multiTo remove any trusted third party from the voting scheme, a new concept of secure multiparty computations is defined, i.e., secure multiparty disjunction(SMD), and then a quantum SMD protocol is presented by using local operators and entanglement swapping of Bell states. Based on this primitive protocol of secure multiparty computations, a novel quantum anonymous one-vote veto scheme is constructed, which can meet complete security attributes. Expecially, this scheme does not need any third party to count the votes, while all voters can calculate the voting results together. At the same time, BlockChain is introduced for supervision, so that the voters can verify the validity of the voting content under extreme circumstances. The voting scheme takes Bell states as quantum resource and only performs local single-particle Pauli operators and Bell measurements, so it is feasible to implement this scheme with the present quantum information processing technology. Finally, the proposed voting scheme is simulated in IBM Qiskit, and the simulation results show that this scheme is correct and feasible..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 901 (2024)
Perfect optomechanically induced transparency in Bose⁃Einstein condensate cavity
XIA Changchao, and SONG Liwei
Optomechanically induced transparency and slow light effect have always been the hotspots in the field of quantum optics. Here, the necessary conditions for perfect optomechanically induced transparency in Bose-Einstein condensed cavity are investigated, and the influence of frequency detuning of driving field on perfeOptomechanically induced transparency and slow light effect have always been the hotspots in the field of quantum optics. Here, the necessary conditions for perfect optomechanically induced transparency in Bose-Einstein condensed cavity are investigated, and the influence of frequency detuning of driving field on perfect optomechanically induced transparency is discussed. In particular, it is found that the perfect optomechanically induced transparency phenomenon can still be achieved even when the decay rate of Bogoliubov mode is very large, which is one of the advantages of the perfect optomechanically induced transparency theory. In addition, the slow light effect at the perfect transparent window is discussed, and it is found that both the decay rate of the cavity and the decay rate of the Bogoliubov mode have significant influence on the slow light effect. Especially, ultra-slow light effect can be realized in the unresolved sideband region of system parameters. The results in this work can be applied to the construction of modern optical networks and quantum information processing in the future.Key words: quantum optics; cavity optomechanics; perfect optomechanically induced transparency; slow light effect; Bose-Einstein condensation.
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 914 (2024)
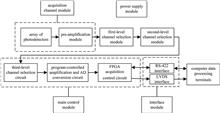
A miniaturized quantum random number generator device based on CMOS
WANG Qibing, WANG Linsong, WANG Yaqi, LI Li... and WANG Shaohua|Show fewer author(s)
To meet the miniaturization and integrated application of quantum random number generator (QRNG), a QRNG based on light emitting diode (LED) light source and complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) detection is designed. Quantum random numbers ensure the high security of random numbers based on the inherent charTo meet the miniaturization and integrated application of quantum random number generator (QRNG), a QRNG based on light emitting diode (LED) light source and complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) detection is designed. Quantum random numbers ensure the high security of random numbers based on the inherent characteristics of optical quantum, and their low cost and high speed processing methods also have high application value. However, traditional data sampling methods based on high-speed analog-to-digital converter (ADC) have the problems of high cost, complex system, and high post-processing requirements. In addition, the imperfection of ADC sampling also introduces pseudo-random characteristics, reducing the random number characteristics of the system, thus limiting its further commercial application and promotion. In the QRNG proposed in this paper, a binary method based on voltage comparison is proposed, which utilizes the randomness of the detection voltage between pixels, and uses the voltage difference between adjacent pulses in the output voltage sequence detected with CMOS pixels as a random number entropy source to obtain a quantum random number sequence. This method has the advantages of simplicity, reliability and easy realization, which is more conducive to the industrial promotion of products..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 924 (2024)
Time synchronization method for quantum communication based on time⁃frequency domain
SHEN Wei, and LIU Weiyue
Time synchronization is crucial for satellite-to-ground quantum key distribution (QKD). To overcome the noise interference and the loss of quantum light signal in satellite-to-ground QKD, previous schemes used global positioning system (GPS) equipment to assist synchronous light mapping. In order to reduce the complexiTime synchronization is crucial for satellite-to-ground quantum key distribution (QKD). To overcome the noise interference and the loss of quantum light signal in satellite-to-ground QKD, previous schemes used global positioning system (GPS) equipment to assist synchronous light mapping. In order to reduce the complexity and cost of the system, a time synchronization method combining time domain and frequency domain is proposed in this paper. The method utilizes the spectral characteristics of quantum light and linear fitting method to achieve high precision time synchronization. The method is tested with the experimental data of satellite-to-ground QKD, a synchronization accuracy of 1.03 ns can be achieved, and a full width at half maximum of the histogram is 1.4 ns. The method does not require the use of GPS and synchronous light, and can be widely used in satellite-to-ground QKD..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 933 (2024)
Quantum designated verifier signature scheme based on quantum walk
LOU Xiaoping, FAN Zhou, and GE Qiyue
Given that the existing quantum designated verifier signature schemes require the preparation of entanglement resources in advance and pose a risk of being attacked, a new quantum designated verifier signature scheme is designed in this work based on the quantum walk principle. The new protocol uses two coins quantum wGiven that the existing quantum designated verifier signature schemes require the preparation of entanglement resources in advance and pose a risk of being attacked, a new quantum designated verifier signature scheme is designed in this work based on the quantum walk principle. The new protocol uses two coins quantum walking system on the complete graph,achieving quantum key generation and transmission of signature information. With the help of the trust center, the key generated by quantum walk is shared between the signer and the designated verifier in the new scheme, without the require to share the pre-keys and the entangled states. In the signature phase, the signer encrypts the message by using a key to perform controlled unitary operations, and the generated signature is sent to a designated verifier through quantum teleportation for verification, ensuring the integrity of the message and the correctness of the source. Furthermore, through the theoretical derivation of the examples and the simulation experiments on IBM quantum cloud platform, the correctness of the designed scheme is verified. The final security analysis shows that this scheme not only meets the requirements of designated verification, unforgeability, non-transferability and hiding source, but also is secure under entanglement attacks and intercept-and-resend attacks..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 942 (2024)
Image encryption based on one⁃dimensional quantum walks on a circle
LIU Wenjing, LIU Jun, CAO Yuan, WANG Pengyue, and ZHANG Rong
With the development of the fifth generation (5G) mobile communication technology, images are widely used in key fields such as internet, medical diagnosis and satellite observation, and the security of picture information is becoming increasingly important. For the secure transfer of image data in the internet, a new With the development of the fifth generation (5G) mobile communication technology, images are widely used in key fields such as internet, medical diagnosis and satellite observation, and the security of picture information is becoming increasingly important. For the secure transfer of image data in the internet, a new image encryption scheme based on one-dimensional quantum walks on a circle is proposed in this work. The scheme utilizes the power of quantum walks to construct permutation boxes and generates exclusive or (xor) numbers for encryption, and innovatively introduces the generation of control matrix to control the image encryption after image blocking. The simulation and numerical analyses show that the proposed encryption algorithm has good performance and security, the histograms of images after encryption tend to uniform distribution, the pixel correlation coefficient approaches 0, and the key space reaches 2212, the information entropy reaches 7.99, which can effectively resist brute force attacks,statistical attacks and other attack methods. In addtion, the scheme also shows good performance in sensitivity and anti-noise..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 956 (2024)
Optical Material
Spontaneous radiation properties of graphene⁃based core⁃shell structure
SHI Shenxi, WANG Zuohong, SUN Mengran, and ZHENG Gaige
To study the scattering properties of core-shell structure containing graphene, expecially electric field distribution, energy density, and radiative/nonradiative decay rate properties, the transfer matrix method (TMM) is used to evaluate the effects of wavelength of the incident ray and dipole emitter location on the To study the scattering properties of core-shell structure containing graphene, expecially electric field distribution, energy density, and radiative/nonradiative decay rate properties, the transfer matrix method (TMM) is used to evaluate the effects of wavelength of the incident ray and dipole emitter location on the spontaneous radiation of Au@SiO2@Graphene. It is found that when the core size and shell thickness remain constant, the Purcell factor in the near-field region of the core-shell structure increases with the increase of the thickness of the intermediate SiO2 dielectric layer. And the Purcell factor of the core-shell structure decreases with the distance of the dipole emitter from the center of the sphere, realizing the regulation of spontaneous radiation. On the other hand, by optimizing the structural parameters of graphene-based core-shell structure, the maximum value of the Purcell factor in the visible light range is achieved at about 633 nm. When the thickness of the dielectric layer is fixed, increasing the radius of the model will lead to a decrease of the Purcell factor. And changing the size parameters of the model can effectively strengthen the interaction between the graphene-based core-shell structure with light wave. The research can provide a reference for the solar thermal field..
Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics
- Publication Date: Nov. 28, 2024
- Vol. 41, Issue 6, 970 (2024)