Search by keywords or author
Journals >Remote Sensing Technology and Application
Export citation format
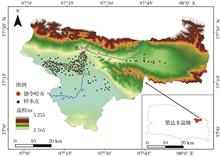
Irrigation Grass Space Distribution Data Set in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Bayin River
Li ZHENG, Xin JIN, Yanxiang JIN, Kai DU... and Yanhong QIN|Show fewer author(s)
Grassland is crucial to the ecosystem stability and agricultural development. In semi-arid or arid areas, the problem of insufficient water for grass growth is mainly solved by irrigation, but grasslands with irrigation conditions are limited. At present, there are few researches on the monitoring of irrigation and raiGrassland is crucial to the ecosystem stability and agricultural development. In semi-arid or arid areas, the problem of insufficient water for grass growth is mainly solved by irrigation, but grasslands with irrigation conditions are limited. At present, there are few researches on the monitoring of irrigation and rain-fed grassland resources and their spatial-temporal distribution using remote sensing techniques, and the relevant datasets are extremely lacking, which brings inconvenience to the assessment of water resources in areas where irrigation and rain-fed grasslands coexist and land surface process simulation. Therefore, this study used the Google Earth Engine Calculation Cloud Platform (Google Earth Engine, GEE), called the Sentinel-2 satellite remote sensing image of 2020, selected random forest classification method (Random Forest, RF), added vegetation moisture index, extracted irrigated and rain fed grassland in the middle and lower reaches of the Bayin River in the northeast of the Qaidam Basin, and formed a dataset. After verification, the overall accuracy of this data set was 99%, and the Kappa coefficient was 0.84. The area of irrigated grass was 74.23 km2, accounting for 4.1% of the total grassland area in the middle and upper reaches of the Bayin River. This data set accurately reflected the interlaced distribution characteristics of irrigated grassland, cultivated land, wetland and other types of land. This study can support the water resources planning and evaluation, land surface process simulation, etc. in the Bayin River Basin..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 777 (2024)
Daytime Land Fog Detection based on H8/AHI Satellite Data
Huiyun MA, Yanan LI, Xiaojing WU, Zengwei LIU, and Junjie YAN
Fog is a kind of disastrous weather, which seriously affects traffic order and causes serious loss of life and property. The Himawari-8/AHI (H8/AHI) image with 10-minute time resolution, which provides the possibility for near-real-time fog detection, but the reflectivity of the image is greatly affected by the sun altFog is a kind of disastrous weather, which seriously affects traffic order and causes serious loss of life and property. The Himawari-8/AHI (H8/AHI) image with 10-minute time resolution, which provides the possibility for near-real-time fog detection, but the reflectivity of the image is greatly affected by the sun altitude angle during the day, and the conventional fog detection algorithms are difficult to adapt. This paper takes the differences in spectral characteristics and motion characteristics of clouds, fog and the surface between time series images as the starting point, uses time series images to synthesize clear sky surface, uses the background difference method to remove the surface, and uses the ratio of adjacent time series images to remove the fast-moving and rough-textured clouds in images, finally combined with the traditional cloud and fog separation algorithm to remove scattered and unseparated clouds in the image, realized the rapid detection of land fog in the daytime. The test results show that the algorithm can realize near real-time automatic daytime fog detection. The algorithm is applicable in the daytime from 9:00 to 15:00. The algorithm has high quantitative verification accuracy.The average probability of detection for 6 consecutive days in winter is 96.6%,the false alarm ratio is 9.4%,and the critical success index is 87.9%.The advantage of this algorithm is that the detection threshold is not affected by the angle of the sun's altitude. Compared with the existing detection algorithms of daytime land fog, this algorithm has higher detection accuracy. The false alarm ratio of fog detection results for 120 days from February to May in winter and spring is 3.6%,which proves that the algorithm has certain reliability and stability..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 784 (2024)
Advances of Satellite Remote Sensing Retrieval on Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gases
Xiyuan MI, and Ronghai HU
Non-carbon dioxide greenhouse gases such as methane (CH4), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3) also have a huge impact on the climate in addition to carbon dioxide. For example, methane is the second most important greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide (CO2) in radiative forcing, and ozone has becNon-carbon dioxide greenhouse gases such as methane (CH4), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3) also have a huge impact on the climate in addition to carbon dioxide. For example, methane is the second most important greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide (CO2) in radiative forcing, and ozone has become the primary pollutant in many places in China after PM2.5. Rapidly locating emission sources, quantitatively monitoring non-carbon dioxide emissions, and accurately estimating the distribution of global and regional non-carbon dioxide sources and sinks is of great practical significance for formulating, implementing, and evaluating emission reduction measures. This study reviews the development of satellite-based greenhouse gas retrieval, starting from the principle of algorithm, then the current state of methane, nitrogen dioxide, Nitrous Oxide, and ozone retrieval, and identify gaps in existing studies for potential future research. The study on satellite-based non-CO2 gas concentration is undergoing rapid growth. The optimal estimation method and DOAS-based algorithm are used as mainstream methods for estimating non-CO2 greenhouse gas concentration using satellite observation. The overall column concentration accuracy of CH4, NO2, N2O, and O3 can be up to 1%, 10%, 1%, 1%, respectively. To better provide reliable data products for monitoring and practical applications, we should: (1) further improve the accuracy and efficiency of Non-CO2 gas concentration retrieval; (2) further investigate data assimilation issues based on multiple sensors, algorithms, and products; (3) further optimize the retrieval models for different land surface types; (4) introduce refined spatial resolution, spectral resolution and more accurate auxiliary data; (5) further coordinate global multi-satellite network resources; (6) further study the Interrelationships between multiple gases..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 793 (2024)
Sensitivity Analysis and Inversion Wavelength Selection for Atmospheric Methane Detection based on HIRAS
Weifang FANG, Xiaoying LI, Yapeng WANG, Tianhai CHENG... and Wenjing LU|Show fewer author(s)
Methane contributes about one quarter to global warming and can affect the concentration of ozone, water vapor, hydroxyl groups and other components in the atmosphere. The inversion of vertical methane concentration is of great significance, and the sensitivity analysis of remote sensing detection and the selection of Methane contributes about one quarter to global warming and can affect the concentration of ozone, water vapor, hydroxyl groups and other components in the atmosphere. The inversion of vertical methane concentration is of great significance, and the sensitivity analysis of remote sensing detection and the selection of inversion wavelength are the basis of methane inversion. In this paper, based on the characteristics of the infrared Hyperspectral Vertical Atmospheric Sounder (HIRAS) on the Fengyun-3E star, we carry out forward simulation of atmospheric methane detection on the basis of the infrared atmospheric radiative transfer mechanism, and conduct detection sensitivity analysis and inversion wavelength selection. Firstly, the main absorption window of CH4 and the main interference components are analyzed based on the high-resolution transmittance spectral line library (HITRAN), and then based on the atmospheric profile background library and the instrumental parameters of HIRAS, the 1 200~1 400 cm-1 band CH4 and its interference elements (atmospheric temperature, surface temperature, surface emissivity,H2O,N2O,CO2, F14, HNO3 and O3) detection sensitivity. The results show that the atmospheric temperature, surface temperature, surface emissivity, H2O, and N2O have a strong interfering effect on the irradiance brightness as well as the brightness temperature in the 1 200~1 400 cm-1 band range. Finally, the information entropy principle based on the Jacobian matrix is used for the initial selection of CH4 detection wavelengths, and combined with the results of detection sensitivity analysis, the selection of CH4 inversion wavelengths for HIRAS detection is completed..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 809 (2024)
Full-coverage Reconstruction of XCO2 at 100 × 100 m Spatial Resolution in Beijing Using 4 Carbon Satellite Products
Chen ZHAO, Jing ZHAO, Naixia MOU, and Qunqun ZHAO
The application of carbon satellite observation data urgently needs to solve the problems of spatiotemporal discontinuity and low spatiotemporal resolution. Among them, the high spatial and temporal resolution reanalysis data reconstructed from XCO2 product data will provide a solution to the lack of real-time observatThe application of carbon satellite observation data urgently needs to solve the problems of spatiotemporal discontinuity and low spatiotemporal resolution. Among them, the high spatial and temporal resolution reanalysis data reconstructed from XCO2 product data will provide a solution to the lack of real-time observation data in regional and industrial CO2 source and sink research. Based on 4 sets of XCO2 product data, DataCube multi-dimensional data modeling can integrate the spatio-temporal information of different product data, thus realize the unified storage, correlation and gridding of spatio-temporal information of 4 sets of XCO2 product data. An XCO2 reconstruction method is proposed that can realize dynamic mapping, interaction, correlation analysis and feature fusion of multiple XCO2 product data, and finally the XCO2 reconstruction product of the 100 m full coverage grid in Beijing is obtained. The results show: the reconstruction results are highly consistent with the TCCON Xianghe station observation values (R2=0.90, RMSE=0.89), and are consistent with the time change trend of the CarbonTracker simulation results and TCCON observation results; in 2020, XCO2 in Beijing generally displayed a spatial distribution of lower in the north, higher in the central north and south, and highest in the central part; and dynamically reveals the regularity of the high and low value spatio-temporal variations and the vertical and horizontal transportation characteristics between "ecological conservation areas" and "development areas" in the Beijing area due to the influence of surface carbon sources and sinks..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 821 (2024)
Atmospheric Temperature Detection Performance and Airborne Test Data Analysis of V-band Spectrometer
Wenming HE, Jingyi LIU, Hao LU, Wenyu WANG... and Zhenzhan WANG|Show fewer author(s)
To verify the performance of the microwave spectrometer for temperature detection and better design and apply the microwave spectrometer on the new generation of Fengyun satellite, the National Space Science Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences successfully developed the Atmospheric Microwave Comprehensive SounderTo verify the performance of the microwave spectrometer for temperature detection and better design and apply the microwave spectrometer on the new generation of Fengyun satellite, the National Space Science Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences successfully developed the Atmospheric Microwave Comprehensive Sounder (AMCS) and carried out the first airborne test in China. The test was conducted on September 17 and 21, 2022 in the Sanjiangyuan area. The altitude of the observation area remains basically above 4 km, and the cruising altitude of the drone is 7~7.5 kilometers. A normal-temperature blackbody thermal calibration source and a high-temperature noise calibration source are used to calibrate the flight data at five moments on September 17 and 21, 2022, and the optimal estimation method in the Atmospheric Radiation Transmission Simulator (ARTS) is used for retrieval analysis. The results show that the brightness temperature data after calibration at the same time have good consistency, which are basically consistent with the simulated brightness temperature. The retrieval data of the three moments on September 17, 2022 are affected by clouds, rain and snow, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) remain within 1.5 K, while the retrieval results of the traditional channel microwave radiometer at different times are quite different. The RMSEs at the two moments on September 21, 2022 are basically maintained within 1 K, and the RMSE at most heights was kept within 0.7 K, which are significantly better than the traditional channel radiometer. This airborne test preliminarily verifies the performance of the AMCS within 400~520 hPa and lays a foundation for the subsequent design and application of spaceborne microwave spectrometers. More detailed V-band spectrometer test analysis of the higher atmosphere will be carried out..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 832 (2024)
Analysis of Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Methane in China in 2003~ 2018
Yuqi PENG, Hongke CAI, and Zhaonan CAI
In order to better understanding the distribution of CH4 concentration in China, this study analyzed the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of CH4 concentration in China from 2003 to 2018 using CH4 concentration data provided by C3C. The results show that:(1)In terms of spatial distribution, the CH4 concIn order to better understanding the distribution of CH4 concentration in China, this study analyzed the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of CH4 concentration in China from 2003 to 2018 using CH4 concentration data provided by C3C. The results show that:(1)In terms of spatial distribution, the CH4 concentration features a pattern of high concentration in the southeast and low concentration in the northwest, with high values mainly distributed in Hunan, Hubei, and Guangxi, and low values in Qinghai and Tibet.The interannual variation of CH4 concentration in China showed an increasing trend over time. The methane concentration remained relatively stable from 2003 to 2006, and increased significantly from 2007 to 2018.(2)The CH4 concentration exhibits a significant seasonal variation, with higher concentrations in summer and autumn and lower concentrations in spring and winter. The highest concentration was 1 781 ppbv in autumn, while the lowest concentration was 1 748 ppbv in spring. The peak concentration occurred in August and September, and the low point occurred in March and April.(3) In order to better analyze methane concentration in China, China is divided into six geographical regions, which are Northeast China, South Central China, East China, North China, Northwest China, Southwest China.Methane concentrations are higher in East China, South Central China, and lowest in the Northwest China, Southwest China..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 841 (2024)
Hyperspectral Infrared Atmospheric Vertical Sounder-II Atmospheric Product Inversion System Design
Yuhang GUO, Xiaoying LI, Tianhai CHENG, Shenshen LI... and Weifang FANG|Show fewer author(s)
With the intensification of global climate change, the monitoring of atmospheric trace gases has received increasing attention. The column concentrations and profiles distributions of trace gases become the data basis for atmospheric environmental monitoring and global climate change research. The Hyperspectral InfrareWith the intensification of global climate change, the monitoring of atmospheric trace gases has received increasing attention. The column concentrations and profiles distributions of trace gases become the data basis for atmospheric environmental monitoring and global climate change research. The Hyperspectral Infrared Atmospheric Vertical Sounder II (HIRAS-II) on board the Fengyun-3E and Fengyun-3F satellites provides high spectral resolution infrared radiometric observations of the Earth-gas system, which can be used to invert high-precision atmospheric compositional profiles and column concentrations. In this study, we have developed an operational inversion system based on HIRAS-II. This system incorporates a modular design and parallel computing framework, integrating a global reference atmospheric profile database and surface emissivity database. Leveraging the optimal estimation methods and the RFM forward model, this system inverts the CH4, O3 profiles and column concentrations products as well as CO2 column concentrations products. The inversion system was tested and the accuracy of the 12 products obtained by the inversion system is verified. The results show that the inversion system operated stably and the products had high accuracy. The inversion system can provide algorithmic and technical support for atmospheric environment monitoring in China and global climate change research..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 850 (2024)
Relative Radiometric Normalization Method of High-resolution Optical Satellite Image based on An Improved IR-MAD Algorithm
Denghui FAN, Liwei LI, Qian SHEN, Hao ZHANG, and Gang CHENG
Relative radiometric normalization is one of the main means of producing surface reflectance products from high-definition optical satellite images, the relative radiometric normalization method based on Iteratively Reweighted multivariate alteration detection is currently the most widely used method for high-resolutioRelative radiometric normalization is one of the main means of producing surface reflectance products from high-definition optical satellite images, the relative radiometric normalization method based on Iteratively Reweighted multivariate alteration detection is currently the most widely used method for high-resolution optical satellite image. However, the classical IR-MAD method is only applicable when there is little change in features between the reference image and the image to be corrected, and the method fails when there is a large change in features. In this paper, an improved IR-MAD algorithm is proposed by introducing a pseudo-invariant region constraint mechanism. The main idea is to use a Gaussian mixture model to extract the invariant regions between images, thus improving the quality of the pseudo-invariant points, so that effective radiometric normalization results can still be output when the feature changes a lot. The experiment was conducted using three representative sets of images, with GF-2 as the image to be corrected and Sentinel-2 as the reference image. The results show that compared to the classical IR-MAD method,(1) The pseudo-invariant points extracted by our method are mainly concentrated in the invariant regions, and the spatial distribution is more reasonable; (2) In dataset 1 representing general changes, the average coefficient of determination of our method is increased by 8.8%, while in dataset 2 and 3 representing strong changes, the average coefficient of determination of our method is 95% and 89%, respectively, while the traditional method is lower than 50% or even negative; (3) The spectral reflectance information of typical features in the processed image by our method is closer to the reference image. Therefore, our method provides a new and effective approach for relative radiometric normalization of high-resolution optical satellite images in complex situations..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 859 (2024)
Dynamic Monitoring Ability of Passive Microwave-based Vegetation Index for Different Vegetation Types
Xueying WANG, and Zhenzhan WANG
Global vegetation dynamic monitoring has great significance in regional and global ecological environment protection. Optical vegetation indexes such as Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) have been used as important tools for vegetation monitoring for a long time. While, mGlobal vegetation dynamic monitoring has great significance in regional and global ecological environment protection. Optical vegetation indexes such as Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) have been used as important tools for vegetation monitoring for a long time. While, microwave-based vegetation index, which can detect the woody parts of vegetation and be sensitive to vegetation water content, can provide a possible complementary dataset for monitoring global vegetation. With NDVI and EVI as the reference, the changes of MPDI, MVI_B and EDVI in the microwave band in the past three years were analyzed, and the correlation coefficients between other vegetation indexes and NDVI were calculated. The results show that EDVI has a strong ability to monitor the dynamic changes of vegetation. Compared with NDVI, EDVI has a higher sensitivity to vegetation growth and water content changes, contributing to a wider dynamic range and more details. MVI_B is insensitive to seasonal changes for most vegetation types, and MPDI is suitable for monitoring medium- and low-biomass vegetation with distinct growth cycles..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 867 (2024)
Research on UAV Hyperspectral of Tree Species Classification based on Machine Learning Algorithms and Spatial Resolution Adjustment
Xiangshan ZHOU, Wunian YANG, Ke LUO, Hongyi PIAO... and Xiaolu TANG|Show fewer author(s)
This study proposes a method based on machine learning algorithms to improve the accuracy of hyperspectral tree species classification by changing spatial resolution at the regional scale, providing a new approach for tree species classification research in terrestrial surveys. This study used drones to obtain hyperspeThis study proposes a method based on machine learning algorithms to improve the accuracy of hyperspectral tree species classification by changing spatial resolution at the regional scale, providing a new approach for tree species classification research in terrestrial surveys. This study used drones to obtain hyperspectral images of the entire Chengdu Botanical Garden, and collected 1 249 samples of 140 tree species in the garden. By constructing 32 vegetation indices and 176 original bands for variable screening, a classification model was established using two algorithms: random forest and support vector machine. Based on the forest stand types and canopy sizes of typical tree species in the study area, 10, 15, and 20 tree species were selected at 9 different spatial resolutions to explore the accuracy of tree species classification. The results showed that when the spatial resolution gradually decreased from 0.12 m to 4 m, the classification accuracy of the models for 10, 15, and 20 tree species reached the highest level at a resolution of 3 m, and the overall accuracy of the support vector machine classification results was relatively high. This indicates that methods based on support vector machine algorithm, feature variable extraction and selection, and determining the optimal observation scale can effectively capture canopy information of different tree species and improve tree classification accuracy..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 880 (2024)
High Spatial-Hyperspectral Tree Species Classification based on 3D-Octave Convolution
Mingming WANG, Yunzhi CHEN, Yan DONG, Lei LIU, and Yu Ke WANG
The application of 3D Octave convolution model in high spatial-hyperspectral image classification can improve the accuracy of multi-tree species classification tasks, which is of great significance to improve the refinement level of forest management. A 3DOC-SSAM model combining 3D Octave convolution and attention mechThe application of 3D Octave convolution model in high spatial-hyperspectral image classification can improve the accuracy of multi-tree species classification tasks, which is of great significance to improve the refinement level of forest management. A 3DOC-SSAM model combining 3D Octave convolution and attention mechanism is designed. Through 3D Octave convolution and spatial-spectral attention mechanism, the operation efficiency and classification performance of the model are improved. The results show that : ( 1 ) The overall accuracy of the 3DOC-SSAM model reaches 99.53 %, which is 13.86 %, 18.49 %, 12.90 % and 5.36 % higher than that of SVM, ELM, 2D-CNN and 3D-CNN, respectively. The average accuracy AA reached 99.38 %, and the Kappa coefficient reached 0.994 7. ( 2 ) In the case of small sample training, the overall accuracy and average accuracy can still reach 96.9 % and 95.52 %, which is higher than the comparison model. The research results provide an efficient and high-precision solution for multi-tree classification tasks, and have broad application prospects in forestry remote sensing, which is helpful to improve the scientificity and sustainability of forest resource management..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 897 (2024)
Research on Fire Detection Method based on Deep Neural Network MODIS Data
Jinpeng CHEN, Lin SUN, Feifei XIE, Huijuan GAO, and Shuai GE
The observation characteristics of MODIS data with high temporal resolution and medium spatial resolution can play an important role in fire detection. However, MODIS fire detection is currently in areas with high heterogeneity, and there are many false detections of fire, and cold fire are easily missed. To solve thisThe observation characteristics of MODIS data with high temporal resolution and medium spatial resolution can play an important role in fire detection. However, MODIS fire detection is currently in areas with high heterogeneity, and there are many false detections of fire, and cold fire are easily missed. To solve this problem, in order to fully mine the relevant information in MODIS data, realize the high-precision identification of fire points. A MODIS fire detection algorithm using deep learning technology is proposed. Acquisition of a large number of samples with high quality and broad representation is the prerequisite for deep learning to achieve accurate detection of fire. In order to increase the number of fire samples and ensure the quality of wildfire samples, use the American ground wildfire data set as real fire samples to accurately match them with MODIS data in time and space, and build a fire detection sample library based on deep learning methods . According to the analysis of the radiation transfer process, the wave band and band combination with good identification for fire detection are determined as the input source. Based on the constructed sample data set and information source, build a DNN (Deep Neural Network) fire detection model. Application experiments were carried out in three typical scenarios and compared with MODIS fire products. The results show that the improved method reduces the average brightness temperature of 4um by 2 K in the extraction of cold fire in agricultural areas, and the ratio of correct to wrong changes is positive. Compared with MODIS products, the false fire points extracted in the suburban area are significantly reduced, and the false fire points near the 4um brightness temperature of 325 K are excluded, and the false detection rate is reduced by 19.89%..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 905 (2024)
Sensitivity of Black Soil Organic Matter Content Prediction to the Spectral Resolution and Signal-to-Noise Ratio of Space-based Remote Sensing Loads
Zexin LI, Shuang GAO, Denghui HU, Changkun WANG, and Guohua LIU
The high precision monitoring of the organic matter content of space-based black soil is of great significance to the utilization and conservation of black soil resources. Soil organic matter content prediction based on space-based hyperspectral data is an effective means to achieve high spatial and temporal soil coverThe high precision monitoring of the organic matter content of space-based black soil is of great significance to the utilization and conservation of black soil resources. Soil organic matter content prediction based on space-based hyperspectral data is an effective means to achieve high spatial and temporal soil coverage monitoring in large regions. The core parameters such as spectral resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of satellite-based hyperspectral instruments have a significant impact on the accuracy of soil organic matter content prediction. This paper aims to improve the level of soil organic matter monitoring in the black soil region of China. In this paper, to improve the level of soil organic matter monitoring in the black soil region of China, we conducted a study on the influence of spectral resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of satellite optical payload on soil organic matter content inversion, and constructed a hyperspectral satellite "instrument-observation-inversion" model for black soil monitoring based on MODTRAN atmospheric transmission model, instrument signal-to-noise ratio analysis model and partial least squares regression soil organic matter inversion model. And using the actual soil measurement data of Sanjiang Plain, a typical black soil area in northeast China, as model input, the soil spectral data measured in the laboratory in the black soil area is simulated into simulated data incorporating atmospheric effects and the characteristics of real space-based remote sensing instruments, and the inversion results are compared and analyzed for changing the spectral resolution and signal-to-noise ratio parameters, and the results show that: (1) The inversion performance of space-based remote sensing load spectral resolution parameter for black soil organic matter content prediction is better in the interval less than 40 nm, with RMSE<0.60% and R2>0.75; (2) When the spectral resolution is 15nm and the weighted signal-to-noise ratio is greater than or equal to 477.31, the inversion performance of black soil organic matter is optimal, with RMSE<0.535%;(3) The smaller the spectral resolution, the more significant the effect of noise, and the smaller the spectral interval, the higher the signal-to-noise ratio requirement. the best weighted signal-to-noise ratios at 10 nm and 20 nm resolution correspond to 494.07 and 462.16, and the minimum weighted signal-to-noise ratio requirements at 60 nm and 100 nm are 358.84 and 275.63, respectively..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 917 (2024)
Estimation of Leaf Nitrogen Content in Maize based on UAV Hyperspectral Image
Xingyu ZHANG, Yue ZHANG, Chenzhen XIA, Xiaoyan ZHANG... and Xiaoyu LI|Show fewer author(s)
The estimation of crop nitrogen content at the field scale by using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV) images has attracted increasing attention due to their nondestructiveness and time-effectiveness. The black soil region of Northeast China is the main agricultural production base in China, and accurately obtaining crop nitThe estimation of crop nitrogen content at the field scale by using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV) images has attracted increasing attention due to their nondestructiveness and time-effectiveness. The black soil region of Northeast China is the main agricultural production base in China, and accurately obtaining crop nitrogen content is of great significance for national food security. In this study, the Leaf Nitrogen Content(LNC) of maize was estimated by the stepwise regression method using UAV hyperspectral images and 22 narrowband spectral indices at the jointing, silking, and maturity growth stages of maize. The results showed that the maize LNC estimation models at the three growth stages all had good performance. Moreover, the estimation accuracy of the model at the maturity stage was slightly higher than those from the other two stages, with R2, RMSE, and nRMSE values of 0.76, 0.31%, and 0.15%, respectively. The estimation model at the silking stage had the lowest accuracy, with R2, RMSE, and nRMSE values of 0.33, 0.27%, and 0.19%, respectively. At the same time, the spectral indices that can indicate maize LNC were obtained. They were VARI (Vegetation Atmospherically Resistant Index), DDI (Desertification Difference Index) and EVI (Enhanced Vegetation Index) at the jointing stage; MTCI (MERIS Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index) and SIPI (Simple Insensitive Pigment Index) at the silking stage; and EVI (Enhanced Vegetation Index), CCI (Canopy Chlorophyll Index) and NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) at the maturity stage. Finally, the spatial distribution map of maize LNC was obtained using the model with the highest estimation accuracy at each growth stage, and its spatial distribution characteristics were consistent with the actual maize LNC conditions. However, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer had a greater impact on the maize LNC among the microplots with different treatments. The results of this study can provide a database and decision support for the nondestructive, rapid and dynamic monitoring of maize leaf nitrogen content in the black soil region of Northeast China..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 927 (2024)
Research on Long-term Gap-Free Land Surface Temperature Reconstruction Method
Yao BAO, and Yingbao YANG
Land Surface Temperature (LST) is a key parameter in the study of global climate change. Thermal infrared remote sensing LST products are an ideal data source for obtaining LST. However, at present, LST products suffer from large-area deletions caused by clouds, and the limited time series cannot meet the needs of climLand Surface Temperature (LST) is a key parameter in the study of global climate change. Thermal infrared remote sensing LST products are an ideal data source for obtaining LST. However, at present, LST products suffer from large-area deletions caused by clouds, and the limited time series cannot meet the needs of climate change research in historical periods, which limit the in-depth application of LST products. In this paper, the cumulative solar radiation SOA of ERA5 is used to characterize the change of LST under cloud, and three factors (radiative factor, terrain factor and spectral factor) used for LST reconstruction are combined to construct a random forest reconstruction model of Gap-Free LST, and the model is discussed. Reconstruction effects in cloudy sky, and time-series migration. The research results show that: (1) the factors used for LST reconstruction are ranked by importance, and the topographic and radiative factors show high importance.and the topographic and radiative factors show high importance. The LST reconstruction model constructed has a high degree of fit, R2 is 0.97, RMSE is 1.27 K. (2) The reconstructed cloud-air Gap-Free LST fixes the fragmentation of the original LST distribution. Verified by ground station LST, R2 is above 0.90. RMSE is between 2.67 K and 3.15 K. Comparing the change trend of SOA and ground station LST, it is found that the two show good coherence, indicating that SOA can fully reflect the change of LST under the cloud. (3) The seamless LST with sequential migration is reconstructed. For the LST with monthly sequential migration, R2 ranges from 0.77~0.96 and RMSE ranges from 1.35 K~4.02 K. For LST with annual sequential migration, R2 is above 0.86 and RMSE is between 2.73 K and 3.25 K. combined with the statistical map of predictor variables, it is found that the radiation factor is less affected by time migration, and the spectral factor NDVI migrates with time A change occurs, when the range of the NDVI used for LST reconstruction and the NDVI used for LST reconstruction model training is greatly different, the accuracy of the reconstructed LST will be reduced.This study can provide some theoretical support for long-time and seamless LST reconstruction..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 940 (2024)
Evaluating the Detection Efficiency of MODIS Data for Low-density Green Tides in the Yellow Sea
Liu YANG, Mingxiu WANG, Xiaobo ZHU, Jun TANG... and Yingcheng LU|Show fewer author(s)
InThe movement characteristics of floating green tides are strongly influenced by wind and flow fields, making it challenging to conduct a synchronous comparison analysis. Following an analysis of data from 2015 to 2021 in the Yellow Sea of China, two quasi-synchronous high-precision data pairs from Sentinel-2 MSI and InThe movement characteristics of floating green tides are strongly influenced by wind and flow fields, making it challenging to conduct a synchronous comparison analysis. Following an analysis of data from 2015 to 2021 in the Yellow Sea of China, two quasi-synchronous high-precision data pairs from Sentinel-2 MSI and MODIS, with imaging intervals of less than 10 minutes, were identified. These exhibited algae drift deviations of less than one MODIS pixel. In order to examine the authenticity of the 10 m MSI identification results and the detection efficiency of MODIS data , this study employs a simulation in which the Algae-containing Pixel Ratio (APR) is calculated within a coverage area of 25×25 MSI pixels (equivalent to one MODIS pixel) as an aggregation parameter of green tides. The results demonstrated that the majority of green tide patches can be detected by MODIS when the APR in the simulated images is greater than 13%. In contrast, algae with an APR of less than 13%, which are primarily composed of dispersed low-aggregation green tide patches, are difficult to detect and are particularly concentrated around the Jiangsu offshore region. The uncertainty in green tide detection by MODIS data with its coarse spatial resolution is primarily due to differences in its ability to monitor low-aggregation patches. Additionally, fine monitoring of small algae patches using high-resolution images is valuable for the timely detection of the generation, extinction, and convergence of green tide evolution with better accuracy..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 952 (2024)
Discovery of Lithological Anomaly Belt in the Western Region of Junggar Basin Using Multi-source Remote Sensing Images
Ziyong ZHOU
Accurate identification and classification of lithology are the basis of mineral exploration. Xinjiang region is rich in minerals with great exploration potential. Due to its vast territory and sparse population, conducting field surveys of lithology is challenging, thus using remote sensing images to extract lithologiAccurate identification and classification of lithology are the basis of mineral exploration. Xinjiang region is rich in minerals with great exploration potential. Due to its vast territory and sparse population, conducting field surveys of lithology is challenging, thus using remote sensing images to extract lithological information has become an important method. Furthermore, the region has minimal surface vegetation coverage, making it easier to identify rock types using remote sensing images effectively. Additionally, the increasing availability of open-source remote sensing data provides a rich data source for extracting lithological information. However, there are still many issues that need further research on how to comprehensively utilize these open-source remote sensing data for lithological identification. This study focuses on the western part of the Junggar Basin in Xinjiang, and Landsat 8 OLI, Sentinel-2 MSI, and ASTER data of different temporal phase are obtained. Firstly, various image band ratios, principal components, and other variables are extracted and selected for color composition to highlight different rock types. Subsequently, based on geological map, training samples are obtained from the known Darbut ophiolite belt. Then, SVM, maximum likelihood, and random forest methods are used to classify the Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI images. Results of both methods indicate the presence of lithological anomaly belt in the northern part of the Darbut ophiolite belt in the western Junggar Basin, with remote sensing image characteristics similar to those of the Darbut ophiolite belt. The anomaly belt extends in a northeast-southwest direction for over 20 km, with a maximum width of approximately 1 km. However, there exist different opinions on the lithological characteristics of this anomaly belt, and further verification through field survey is needed to confirm the final results..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 961 (2024)
Numerical Simulation and Risk Evaluation of Urban Flooding based on High-resolution Remote Sensing
Xiaomeng XUE, Hongga LI, Xiaoxia HUANG, and Kai WEI
One of the difficulties and challenges in research on urban safety disaster mitigation and prevention is the risk assessment of urban storm waterlogging. The numerical simulation evaluation model of urban flooding by high-resolution remote sensing is useful for determining pre-disaster risk, simulating mid-disaster sceOne of the difficulties and challenges in research on urban safety disaster mitigation and prevention is the risk assessment of urban storm waterlogging. The numerical simulation evaluation model of urban flooding by high-resolution remote sensing is useful for determining pre-disaster risk, simulating mid-disaster scenario, and determining post-disaster loss of flooding. It also has significant application value for assisting in urban planning and managing flooding emergencies. A numerical simulation model of urban flooding is constructed using the GF-7 satellite stereo photogrammetry, object-oriented classification, and hydrodynamic coupling technique, and the risk evaluation is constructed by combining water depth, flow velocity, impact area, storm frequency, and other characteristics. The model accuracy is better than 82% after testing on the middle and lower reaches of the Dasha River in Shenzhen, and when compared to historical measured data for verification, the flooding risk area is decreased by 3.36% in 2021 compared to 2017. According to the study, a high-precision DEM is essential for increasing the precision of an examination of urban storm waterlogging. The waterlogging depth accuracy of the 2.5 m resolution DEM is 5.31%,23.88%, and 58.09% higher than that of the 5 m,10 m, and 20 m, respectively, based on the results of the 1h simulation. The research results have been applied to the evaluation of sponge city in Shenzhen and achieved better effects, providing scientific means and basis for urban flood disaster risk management..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 971 (2024)
Temporal and Spatial Variation Analysis of Vegetation Coverage in Tianshui City based on MOD13Q1 Data
Runke WANG, Jian WANG, Zebin ZHAO, and Liting NIU
Fractional Vegetation Cover (FVC) is an important parameter to describe the change of land surface vegetation. It plays an important role in surface process simulation, climate modeling and global change research. It is of great significance to study the change of vegetation coverage. Based on the reconstruction of MODFractional Vegetation Cover (FVC) is an important parameter to describe the change of land surface vegetation. It plays an important role in surface process simulation, climate modeling and global change research. It is of great significance to study the change of vegetation coverage. Based on the reconstruction of MOD13Q1 NDVI data from 2005 to 2020, the temporal and spatial variation characteristics of vegetation cover in Tianshui City were studied and analyzed by using dimidiate pixel model and maximum value composite method. The results show that the vegetation coverage of Tianshui city shows an increasing trend from 2005 to 2020. The increasing areas mainly include the two sides of Xihe River, the middle, East and northeast of Tianshui city; The low vegetation coverage of the whole city has shifted to medium and low vegetation coverage and medium vegetation coverage. The vegetation coverage on both sides of the Xihe River Basin has increased significantly, especially in the north of the Xihe River; The vegetation coverage in the west of Qinzhou District, the middle and west of Gangu County and the west of Wushan County showed an increasing trend, and the ecological environment improved significantly; The change of high vegetation coverage area is small and basically remains stable. The results reasonably explain the spatial change of vegetation cover in Tianshui City, which can provide an important theoretical basis for ecosystem protection and environmental governance..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 987 (2024)
Research on a Real-time Precipitation Recognition Method based on Geostationary Satellite Observation Data
Mengyuan CUI, Dabin JI, Li JIA, Chaolei ZHENG, and Weiguo JIANG
Accurate and real-time monitoring of extreme precipitation is of great significance for improving flood forecasting, however, the current geostationary satellite-based precipitation products are generally characterized by low precipitation recognition accuracy, which seriously affects their application in flood warningAccurate and real-time monitoring of extreme precipitation is of great significance for improving flood forecasting, however, the current geostationary satellite-based precipitation products are generally characterized by low precipitation recognition accuracy, which seriously affects their application in flood warning. Based on the infrared band brightness temperature data observed by Himawari-8 geostationary meteorological satellite, ERA5 reanalysis atmospheric profile data and ground rain gauge observation data, this study developed a set of real-time precipitation recognition method suitable for geostationary meteorological satellites by establishing a real-time and dynamic precipitation recognition model based on random forest. On the one hand, this method solves the problem that the precipitation recognition accuracy of the static training machine learning models decays with time by introducing real-time hourly precipitation data of the surface rain gauge for real-time training of the precipitation recognition model. On the other hand, it effectively improves the accuracy of precipitation recognition based on the infrared data of the geostationary meteorological satellite by adding the atmospheric environmental condition data closely related to the formation and development of precipitation. The hourly precipitation observation data of 2 157 surface rain gauge stations in Chinese Mainland are used for verification. The proposed precipitation recognition algorithm has a POD of 0.73, a FAR of 0.49, and a CSI of 0.43 on an hourly scale. All indicators are better than the real-time precipitation product GSMaP_NOW and the official real-time precipitation estimation product QPE of FY4A..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 1000 (2024)
Simulation of High-resolution Population Spatial Distribution based on Ensemble Learning
Xintong WU, Dawei GAO, Feixiang LI, Chenming YAO... and Xuchao YANG|Show fewer author(s)
Readily available and accurate maps of population distribution are of critical importance in decision-making. In this study, a new methodology based on ensemble learning technology is introduced that leverages geospatial big data and multi-source remote sensing data for high-resolution and high precision population mapReadily available and accurate maps of population distribution are of critical importance in decision-making. In this study, a new methodology based on ensemble learning technology is introduced that leverages geospatial big data and multi-source remote sensing data for high-resolution and high precision population mapping. Population predictor variables were extracted from Tencent location big data, points of interest and remote sensing data. Using three individual machine learning algorithms (i.e. XGBoost, neural network, and random forest) and the Stacking ensemble learning method, four population prediction models were established to disaggregate the 2020 census population data of Zhejiang Province to grids with 100 m resolution. The results show that: (1) Among three machine learning algorithms, random forest has the best prediction performance. Compared to individual machine learning algorithms, the Stacking ensemble learning strategy has good generalization performance, alleviates the high-value overflow issue, and reduces prediction errors; (2) The results from the ensemble show that the high population density in Zhejiang Province located in the city's core region, with a peak value of 500 people/grid. Population density decreases in steps with increasing distance from urban centers; (3) The gridded population data from the stacking ensemble outperform the WorldPop dataset in terms of higher population density in urban centers and data integrity. This study provides new methods and technical means for rapidly and accurately population mapping in the era of big data..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 1013 (2024)
Spatial and Temporal Variation of Qinghai Lake in Two Seasons Monitored by Remote Sensing
Xingsheng XIA, Jianjun CAI, Lingang WANG, Yuxi ZHONG, and Yaozhong PAN
Qinghai Lake is an important water body that maintains the ecological integrity of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and is also a natural barrier to control the spread of the western desertification to the east. And the study of the changes Qinghai Lake area is of great significance to regional ecological securitQinghai Lake is an important water body that maintains the ecological integrity of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and is also a natural barrier to control the spread of the western desertification to the east. And the study of the changes Qinghai Lake area is of great significance to regional ecological security and economic development. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the trends and causes of the changes of Qinghai Lake area from 1990 to 2020. With the support of Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, Landsat data were used to monitor the dynamic changes of Qinghai Lake for winter-spring and summer-autumn in the past 30a, and the reasons for the changes were analyzed in combination with meteorological and hydrologic data. The results show that:(1) With 2004 as the inflection point, the area of Qinghai Lake showed a trend of decreasing first and then increasing during 1990 to 2020. In recent years, the area increase is most obvious. During 1990~2004, the area of Qinghai Lake decreased by 140.36 km2 in winter-spring, about 3.19% of the area in 1990; and decreased by 157.547 km2 in summer-autumn, about 3.56% of the area in 1990. During the period 2004~2020, the area of Qinghai Lake increased by 336.59 km2 in winter-spring, about 7.89% of the area in 2004; and increased by 349.3814 km2 in summer-autumn, about 8.18% of the area in 2004. (2) In terms of intra-annual variation, the change in area from winter-spring to summer-autumn was large from 1990 to 2000, with an average change value of 26.09 km2/a, and the intra-annual variation was small after 2000, with an average change value of 5.87 km2/a. (3) From 1990 to 2004, the instability of precipitation and runoff and high steady evaporation in Qinghai Lake area were the important reasons affecting the area of Qinghai Lake. High evaporation, low precipitation and low runoff together led to the decline of the area of Qinghai Lake. From 2004 to 2020, the simultaneous increase of precipitation and runoff makes the area of Qinghai Lake increase significantly, assisted by the weak decreasing trend of evapotranspiration. (4) The shoreline morphology of Qinghai Lake is constantly changing, and the most obvious changes are in Shadao Island on the east bank, Niaodao Island and Tiebuka Bay on the west bank, and the entrance of Shaliu River on the north bank. It may be caused by the sediment of runoff soil and the dynamic mechanism of lake water. The specific reasons need to be further discussed. This study has certain value for the study of lake hydrology and the response of lakes to climate change at different scales..
Remote Sensing Technology and Application
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 39, Issue 4, 1026 (2024)