Lei Jiang, Bo Liu, Jianxin Ren, Xiangyu Wu, Rahat Ullah, Yaya Mao, Shuaidong Chen, Yilan Ma, Lilong Zhao, Feng Tian, "High-security multi-constellation shaping modulation with asymmetric encryption," Chin. Opt. Lett. 22, 040602 (2024)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 22, Issue 4, 040602 (2024)
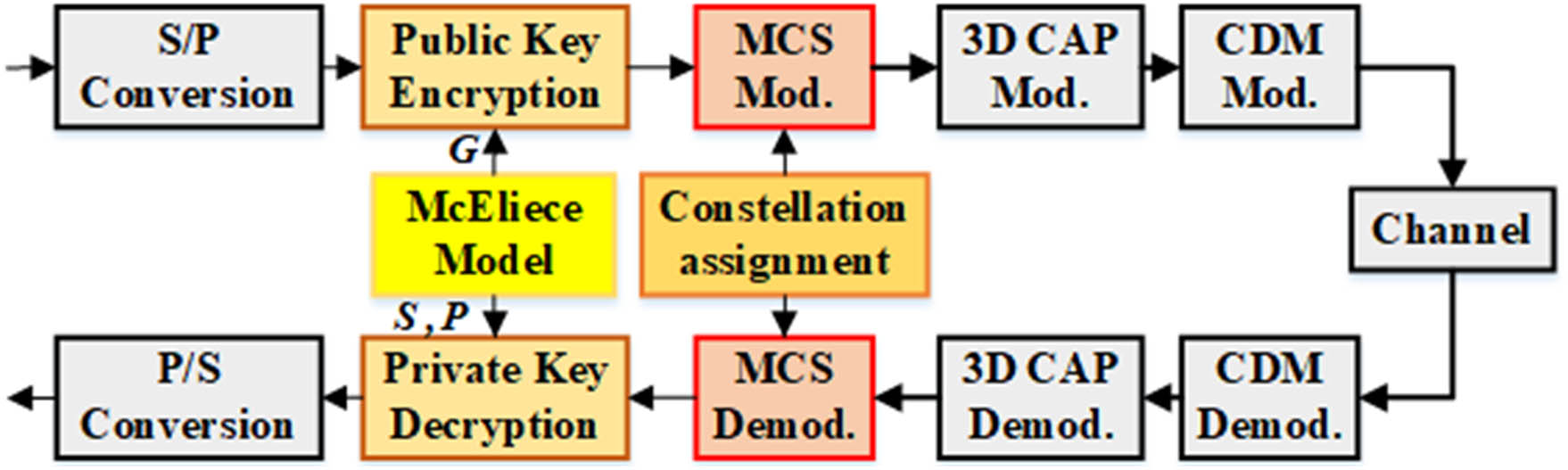
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the proposed scheme.

Fig. 2. Principle of asymmetric encryption.
Fig. 3. Constellation diagram of (a) user_1, (b) user_2, (c) user_3, (d) user_4, and (e) multi-constellation combination. (f) Top view of (e).
Fig. 4. Experimental setup.
Fig. 5. The BER varies with received optical power after back-to-back and multicore fiber transmission.
Fig. 6. The BER varies with received optical power after seven-core fiber transmission.
Fig. 7. (a) BER curves versus received optical power, and (b)–(e) constellation graphs of users_1–4.
Fig. 8. BER curve of the wrong private key.
Fig. 9. Images: (a) before encryption, (b) after illegal reception, (c) after legal reception. Histograms: (d) before encryption, (e) after illegal reception, (f) after legal reception.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Mapping Relationship between Binary Symbols and Each Users’ Constellation Points Coordinates

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



