The control of edge localized modes (ELMs) is a key issue for the safety operation of ITER and future magnetic confinement fusion reactors. In recent years, extensive theoretical simulations and experimental studies have demonstrated that resonant magnetic perturbation (RMP) is a promising method for controlling edge localized modes (ELMs) in H-mode plasmas.
This study aims to investigate drift kinetic resonant effects of thermal particles on the plasma response to the applied RMP and compare with that of the fluid model for better understanding of ELMs control in HL-2A.
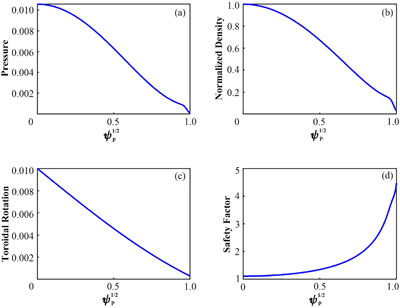
Based on experimental plasma and RMP coil configurations in HL-2A, the MARS-F/K codes were employed to compute the drift dynamic response of plasma to RMP under high constraint mode and compared it with the results of fluid model. Further sensitivity studies were conducted on key parameters including the plasma equilibrium pressure, toroidal flow as well as the thermal particle collision effects.
The fluid response model predicts an initially relatively weak enhancement of the plasma response amplitude with the equilibrium pressure parameter
The importance of considering kinetic effects for high-beta plasma response is emphasized by this study. It is important to include the non-adiabatic resonant contribution of trapped particles to the kinetic response while taking into account the particle collision effect.


 AI Video Guide
AI Video Guide  AI Picture Guide
AI Picture Guide AI One Sentence
AI One Sentence