Xiangnan Zhu, Zongming Tao, Qi Hao. Simulation of Detection and Recognition for Aircraft Wake Vortices in Upper Airspace[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(3): 0328001
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 62, Issue 3, 0328001 (2025)
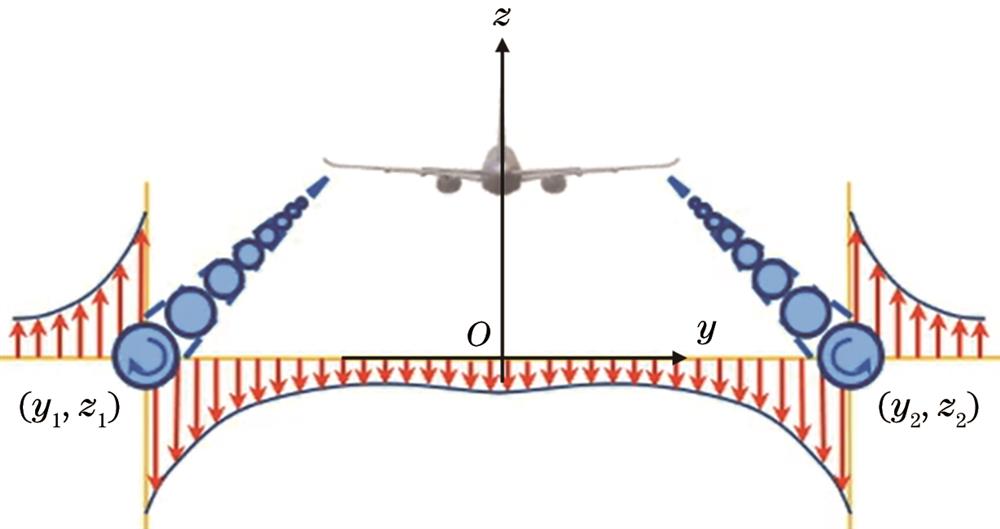
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of aircraft wake vortices field velocity distribution
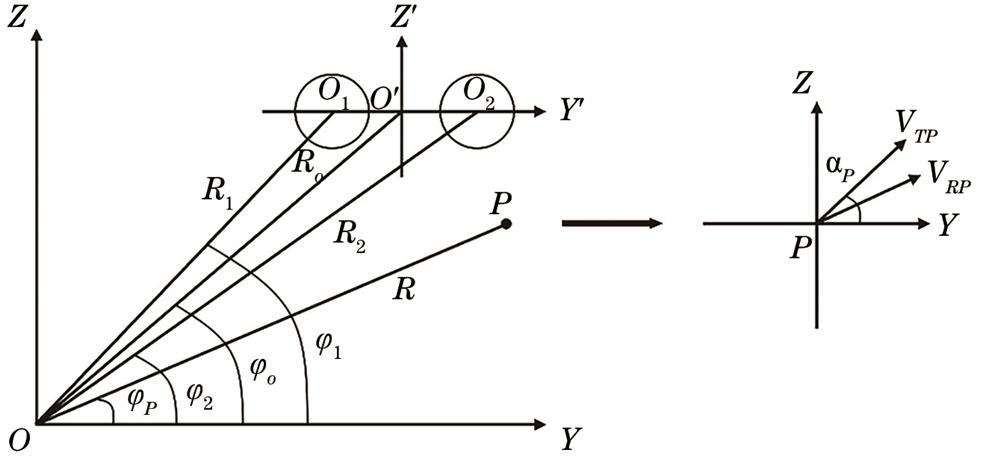
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of radial speed calculation
Fig. 3. Using Doppler spectrum to obtain velocity envelope. (a) Doppler spectrum; (b) schematic diagram of positive and negative velocity envelopes
Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of wake vortices circulation calculation
Fig. 5. Distribution of tangential velocity of a single wake vortex with distance. (a) Left; (b) right
Fig. 6. Velocity distribution diagram of wake vortices field in YOZ section. (a) P2P model; (b) CFD calculation
Fig. 7. Wake vortex dissipation process. (a) Typical wake vortex intensity dissipation process curve; (b) position distribution curve of vortex core of wake vortex in space
Fig. 8. Variations of wake vortices circulation with altitude. (a) Flight speed is fixed at 1000 km/h; (b) flight speed increases linearly with altitude
Fig. 9. Horizontal distribution of maximum tangential velocity and spatial distribution of core position of wake vortex at different altitudes.(a) Horizontal distribution of maximum tangential velocity; (b) spatial distribution of core position
Fig. 10. Comparison of actual observations and model calculations of wake vortex: (a) Dissipation over time; (b) subsidence over time
|
Table 1. Related parameters of Airbus A330-200 model
|
Table 2. Relevant parameters for simulation calculations

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



