Runmin Liu, Yong Wu, Guoqing Pu, Jiayang Cheng, Huan Mu, Bowen Liu, Lilin Yi, Minglie Hu, "Field stabilization of pulse duration in a hundred-femtosecond level," Chin. Opt. Lett. 22, 081406 (2024)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081406 (2024)
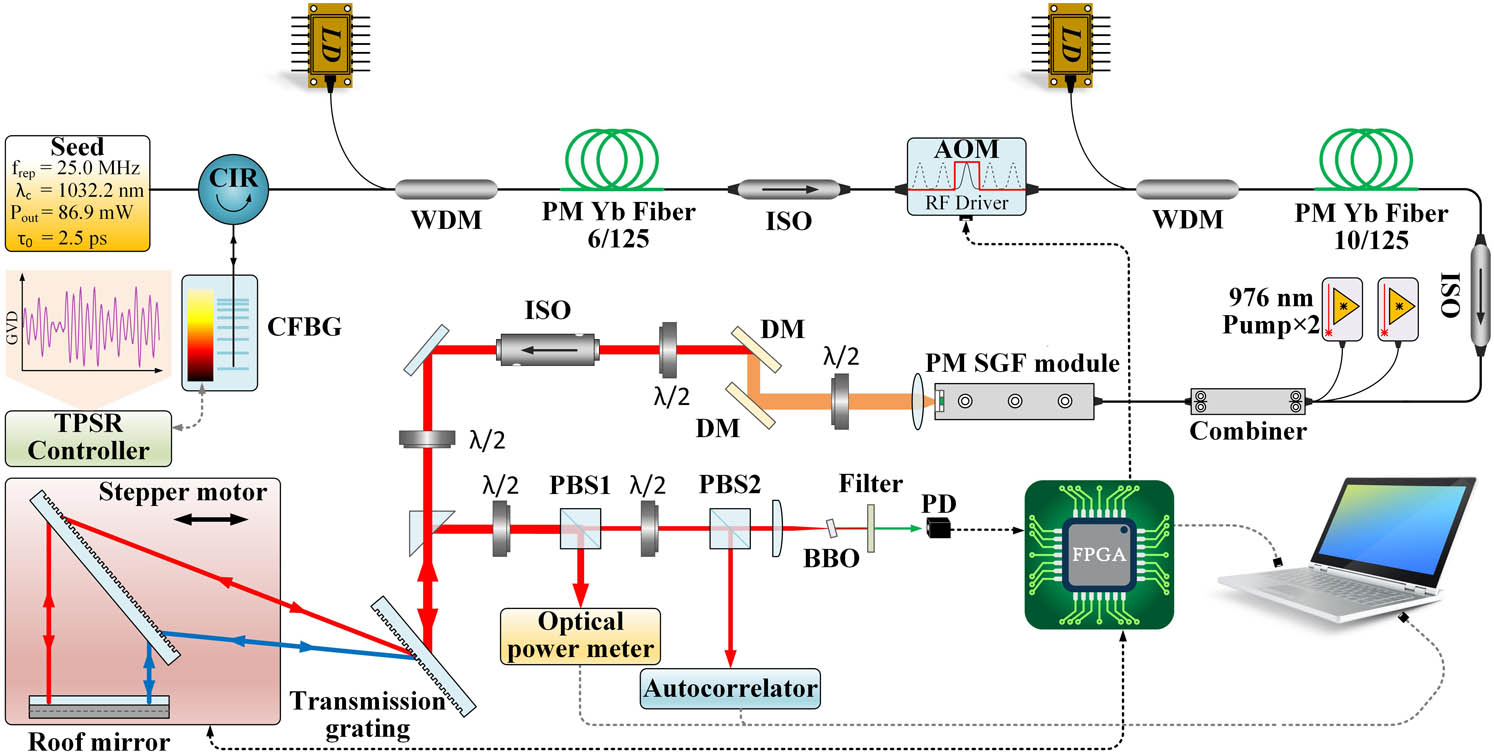
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the all-fiber femtosecond CPA system with the PDFC. CIR, circulator; CFBG, chirped fiber Bragg grating; LD, laser diode; WDM, wavelength division multiplexer; ISO, isolator; AOM, acoustic optical modulator; PM, polarization-maintaining; λ/2, half wave plate; DM, dichroic mirror; PBS, polarizing beam splitter; FPGA, field programmable gate array.

Fig. 2. Output characteristics of (a), (b) the seed laser and (c), (d) the CPA system: (a), (c) optical spectrum; (b), (d) autocorrelation trace. The red dashed curve in (d) refers to the autocorrelation trace of the Fourier transform limited (FTL) pulse.
Fig. 3. Variations of the pulse duration (red) and PD response (blue) with the scanned absolute positions of the stepper motor.
Fig. 4. 60-min stability test of the free-running CPA system: (a) output average power; (b) PD response; (c) pulse duration.
Fig. 5. (a) Framework of improved stochastic hill-climbing search; (b)–(d) characteristics of the minimum pulse-duration searching process: (b) motor position; (c) PD response; (d) pulse duration.
Fig. 6. Performances of the incremental PI controller. (a)–(c) Initial stage of the incremental PI controller: (a) motor position; (b) PD response; (c) pulse duration. (d) Random amplitude perturbance of GVD; (e) variations of the pulse duration without the control algorithm; (f) variations of the pulse duration and motor position with the incremental PI control.
Fig. 7. (a), (b) 60-min pulse-duration stability test: (a) random amplitude perturbance of GVD; (b) evolution of the pulse duration with the PDFC. (c), (d) Robust switching between different pulse durations: evolutions of different pulse durations without (c) and with (d) the PDFC.

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



