Search by keywords or author
Journals >Chinese Optics Letters
Export citation format
Research Articles
Atomic and Molecular Optics
Tunable off-resonant Rydberg microwave frequency comb spectroscopy based on metawaveguide coupled Rydberg atoms | Editors' Pick
Lihua Zhang, Zongkai Liu, Bang Liu, Qifeng Wang... and Baosen Shi|Show fewer author(s)
Studying Rydberg microwave frequency comb (MFC) spectroscopy helps increase the working bandwidth of the Rydberg receiver. This Letter demonstrates off-resonant Rydberg MFC spectroscopy in a meta-waveguide-coupled Rydberg atomic system. An off-resonant MFC field couples with the Rydberg atoms through a meta-waveguide. The system can receive the microwave field in the working band from 0.5 GHz to 13.5 GHz, and the MFC spectroscopy covers a span of 36 MHz at three different arbitrarily-chosen frequencies of 2 GHz, 3 GHz, and 5.8 GHz. The MFC spectrum that covers a wide range of 125 MHz is also verified. This work is significant for tunable wide-band instant microwave signal detection in the Rydberg atomic system, which is useful in microwave frequency metrology, communication, and radar.Studying Rydberg microwave frequency comb (MFC) spectroscopy helps increase the working bandwidth of the Rydberg receiver. This Letter demonstrates off-resonant Rydberg MFC spectroscopy in a meta-waveguide-coupled Rydberg atomic system. An off-resonant MFC field couples with the Rydberg atoms through a meta-waveguide. The system can receive the microwave field in the working band from 0.5 GHz to 13.5 GHz, and the MFC spectroscopy covers a span of 36 MHz at three different arbitrarily-chosen frequencies of 2 GHz, 3 GHz, and 5.8 GHz. The MFC spectrum that covers a wide range of 125 MHz is also verified. This work is significant for tunable wide-band instant microwave signal detection in the Rydberg atomic system, which is useful in microwave frequency metrology, communication, and radar..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 13, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 080201 (2024)
Magnetic field stabilization system designed for the cold-atom coherent population-trapping clock
Chang Zhan, Zhu Ma, Jiatao Wu, Maojie Li... and Chaohong Lee|Show fewer author(s)
Accurate control of magnetic fields is crucial for cold-atom experiments, often necessitating custom-designed control systems due to limitations in commercially available power supplies. Here, we demonstrate precise and flexible control of a static magnetic field by employing a field-programmable gate array and a feedback loop. This setup enables us to maintain exceptionally stable current with a fractional stability of 1 ppm within 30 s. The error signal of the feedback loop exhibited a noise level of 10-5 A·Hz-1/2 for control bandwidths below 10 kHz. Utilizing this precise magnetic field control system, we investigate the second-order Zeeman shift in the context of cold-atom coherent population-trapping (CPT) clocks. Our analysis reveals the second-order Zeeman coefficient to be 574.21 Hz/G2, with an uncertainty of 1.36 Hz/G2. Consequently, the magnetic field stabilization system we developed allows us to achieve a second-order Zeeman shift below 10-14, surpassing the long-term stability of current cold-atom CPT clocks.Accurate control of magnetic fields is crucial for cold-atom experiments, often necessitating custom-designed control systems due to limitations in commercially available power supplies. Here, we demonstrate precise and flexible control of a static magnetic field by employing a field-programmable gate array and a feedback loop. This setup enables us to maintain exceptionally stable current with a fractional stability of 1 ppm within 30 s. The error signal of the feedback loop exhibited a noise level of 10-5 A·Hz-1/2 for control bandwidths below 10 kHz. Utilizing this precise magnetic field control system, we investigate the second-order Zeeman shift in the context of cold-atom coherent population-trapping (CPT) clocks. Our analysis reveals the second-order Zeeman coefficient to be 574.21 Hz/G2, with an uncertainty of 1.36 Hz/G2. Consequently, the magnetic field stabilization system we developed allows us to achieve a second-order Zeeman shift below 10-14, surpassing the long-term stability of current cold-atom CPT clocks..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 13, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 080202 (2024)
Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography
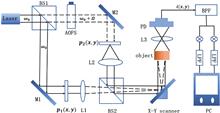
Autofocus by Lissajous scanning in time reversal optical scanning holography
Jie Liu, Haiyan Ou, Hua Wang, Lin Peng, and Wei Shao
In this Letter, an autofocusing method in optical scanning holography (OSH) system is proposed. By introducing Lissajous scanning into multiple signal classification (MUSIC) method in time-reversal (TR) OSH, the axial locations of the targets can be retrieved with better resolution and the peak prominence increases from 0.21 to 0.34. The feasibility of this method is confirmed by simulation as well as experiment.In this Letter, an autofocusing method in optical scanning holography (OSH) system is proposed. By introducing Lissajous scanning into multiple signal classification (MUSIC) method in time-reversal (TR) OSH, the axial locations of the targets can be retrieved with better resolution and the peak prominence increases from 0.21 to 0.34. The feasibility of this method is confirmed by simulation as well as experiment..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 19, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 080501 (2024)
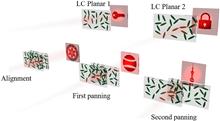
Optical secret sharing by multi-step liquid crystal planar doublet panning and coupling
Zhichang Mo, Yi Chen, Xiangyu Zhu, Zhouhao Zhang... and Jianguo Wang|Show fewer author(s)
The hologram, which is formed by phases coupled through cascade devices for secret information sharing, still carries a cracking risk. We propose a liquid crystal planar doublet as the information carrier, and new holograms generated by the new coupled phases when the relative displacements of the different liquid crystal layers change. The designed geometrical phases are generated by an optimized iterative restoration algorithm, and each holographic image formed by these phases is readable. This scheme achieves an increase in the capacity of the stored secret information and provides more misdirection, which is expected to have potential value in optical steganography and storage.The hologram, which is formed by phases coupled through cascade devices for secret information sharing, still carries a cracking risk. We propose a liquid crystal planar doublet as the information carrier, and new holograms generated by the new coupled phases when the relative displacements of the different liquid crystal layers change. The designed geometrical phases are generated by an optimized iterative restoration algorithm, and each holographic image formed by these phases is readable. This scheme achieves an increase in the capacity of the stored secret information and provides more misdirection, which is expected to have potential value in optical steganography and storage..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 23, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 080502 (2024)
Fiber Optics and Optical Communications
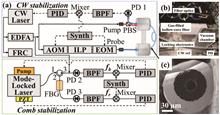
Toward a compact fiber comb with 1.66 × 10−12 instability based on acetylene-filled photonic microcells
Qingqing Chen, Yongqi Li, and Shun Wu
We demonstrated an optical fiber frequency comb stabilized to an acetylene-filled photonic microcell. The short-term instability of the comb at 1 s gate time was 1.66 × 10-12 for a 4.2-h measurement in a laboratory environment with air conditioning. This is the best short-term stability reported for a compact fiber comb stabilized to an acetylene-filled photonic microcell at telecom wavelengths. It is particularly significant in the development of compact fiber combs with target instability of 10-13. Such a device has the potential to serve as an alternative to GPS in areas lacking signal coverage, including remote locations, regions with adverse weather conditions, and military intelligence areas.We demonstrated an optical fiber frequency comb stabilized to an acetylene-filled photonic microcell. The short-term instability of the comb at 1 s gate time was 1.66 × 10-12 for a 4.2-h measurement in a laboratory environment with air conditioning. This is the best short-term stability reported for a compact fiber comb stabilized to an acetylene-filled photonic microcell at telecom wavelengths. It is particularly significant in the development of compact fiber combs with target instability of 10-13. Such a device has the potential to serve as an alternative to GPS in areas lacking signal coverage, including remote locations, regions with adverse weather conditions, and military intelligence areas..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 13, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 080601 (2024)
Demonstration of LDPC-coded PS-64QAM OFDM employing novel bit-class distribution matching in a W-band RoF system
Haitao Zhao, Bangning Xu, Wei Xun, Jianxin Ren... and Bo Liu|Show fewer author(s)
In this work, we proposed and experimentally demonstrated a novel probabilistic shaping (PS) 64-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with low-density parity-check (LDPC)-coded modulation in a W-band radio-over-fiber (RoF) system using envelope detection. The proposed PS scheme has the advantages of no complex multiplication and division operations and low hardware implementation complexity. In our experiments, the two-stage bit weight distribution matching-based PS-64QAM OFDM signals with a rate of 28.13 Gb/s transmission over 4 m wireless + 45-km standard single-mode fiber transmission can be achieved. The system performance is investigated under one LDPC code rate (3/4) and two PS parameter values (k = 3 and 9). The experimental results show that the receiver power sensitivity and the system fiber nonlinear effect tolerance can be significantly improved compared with uniformly distributed OFDM signals.In this work, we proposed and experimentally demonstrated a novel probabilistic shaping (PS) 64-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with low-density parity-check (LDPC)-coded modulation in a W-band radio-over-fiber (RoF) system using envelope detection. The proposed PS scheme has the advantages of no complex multiplication and division operations and low hardware implementation complexity. In our experiments, the two-stage bit weight distribution matching-based PS-64QAM OFDM signals with a rate of 28.13 Gb/s transmission over 4 m wireless + 45-km standard single-mode fiber transmission can be achieved. The system performance is investigated under one LDPC code rate (3/4) and two PS parameter values (k = 3 and 9). The experimental results show that the receiver power sensitivity and the system fiber nonlinear effect tolerance can be significantly improved compared with uniformly distributed OFDM signals..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 080602 (2024)
Imaging Systems and Image Processing
Arbitrary n-step phase-shifting Fourier single-pixel imaging
Zongguo Li, Biao Wang, Zhandong Liu, Kai Xu... and Hongguo Li|Show fewer author(s)
In this Letter, we innovatively present general analytical expressions for arbitrary n-step phase-shifting Fourier single-pixel imaging (FSI). We also design experiments capable of implementing arbitrary n-step phase-shifting FSI and compare the experimental results, including the image quality, for 3- to 6-step phase-shifting cases without loss of generality. These results suggest that, compared to the 4-step method, these FSI approaches with a larger number of steps exhibit enhanced robustness against noise while ensuring no increase in data-acquisition time. These approaches provide us with more strategies to perform FSI for different steps, which could offer guidance in balancing the tradeoff between the image quality and the number of steps encountered in the application of FSI.In this Letter, we innovatively present general analytical expressions for arbitrary n-step phase-shifting Fourier single-pixel imaging (FSI). We also design experiments capable of implementing arbitrary n-step phase-shifting FSI and compare the experimental results, including the image quality, for 3- to 6-step phase-shifting cases without loss of generality. These results suggest that, compared to the 4-step method, these FSI approaches with a larger number of steps exhibit enhanced robustness against noise while ensuring no increase in data-acquisition time. These approaches provide us with more strategies to perform FSI for different steps, which could offer guidance in balancing the tradeoff between the image quality and the number of steps encountered in the application of FSI..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081101 (2024)
Infrared and Terahertz Photonics
Very long wave infrared quantum cascade detector based on modular band structure
Kai Guo, Yu Chen, Yixuan Zhu, Kun Li... and Junqi Liu|Show fewer author(s)
The optoelectronic performance of quantum cascade detectors (QCDs) is highly sensitive to the design of the energy level structure, leading to the inability of a single structure to achieve broad wavelength tuning. To address this issue, we propose and demonstrate a modular concept for very long wave infrared (VLWIR) QCDs based on a miniband diagonal transition scheme. The modular design makes the wavelength tuning only need to be adjusted for the absorption quantum well module rather than for the whole active region. Theoretical simulation shows that the wavelength tuning range is 39.6 meV (∼14–30 μm). To prove the feasibility of the scheme, three samples with different absorption well widths were fabricated and characterized. At 10 K, the response wavelengths of the three QCDs are 14, 16, and 18 μm, respectively, corresponding to responsivities and detectivities exceeding 2 mA/W and 1 × 1010 Jones.The optoelectronic performance of quantum cascade detectors (QCDs) is highly sensitive to the design of the energy level structure, leading to the inability of a single structure to achieve broad wavelength tuning. To address this issue, we propose and demonstrate a modular concept for very long wave infrared (VLWIR) QCDs based on a miniband diagonal transition scheme. The modular design makes the wavelength tuning only need to be adjusted for the absorption quantum well module rather than for the whole active region. Theoretical simulation shows that the wavelength tuning range is 39.6 meV (∼14–30 μm). To prove the feasibility of the scheme, three samples with different absorption well widths were fabricated and characterized. At 10 K, the response wavelengths of the three QCDs are 14, 16, and 18 μm, respectively, corresponding to responsivities and detectivities exceeding 2 mA/W and 1 × 1010 Jones..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 13, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 083701 (2024)
Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing
Common-path illumination in ESPI: enhancing sensitivity for measuring specular deformation
Peizheng Yan, Xiangwei Liu, Xinda Zhou, Rongsheng Ba... and Jie Li|Show fewer author(s)
In this study, an innovative technique is introduced to significantly enhance the sensitivity of electronic speckle pattern interferometry (ESPI) for the dynamic assessment of specular (mirrorlike) object deformations. By utilizing a common-path illumination strategy, wherein illumination and observation beams are precisely aligned, this method effectively doubles the optical path difference, leading to a twofold increase in measurement sensitivity. In addition, this method mitigates the effects of speckle noise on the measurement of minor deformations, expanding the applications of ESPI. Theoretical and experimental evaluations corroborate the efficacy of this approach.In this study, an innovative technique is introduced to significantly enhance the sensitivity of electronic speckle pattern interferometry (ESPI) for the dynamic assessment of specular (mirrorlike) object deformations. By utilizing a common-path illumination strategy, wherein illumination and observation beams are precisely aligned, this method effectively doubles the optical path difference, leading to a twofold increase in measurement sensitivity. In addition, this method mitigates the effects of speckle noise on the measurement of minor deformations, expanding the applications of ESPI. Theoretical and experimental evaluations corroborate the efficacy of this approach..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 19, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081201 (2024)
Chirality discerning and monitoring in a metal cladding optofluidic chip | On the Cover
Qiheng Wei, Xueqian Wang, Hongrui Shan, Yi Lai... and Xianfeng Chen|Show fewer author(s)
The metabolic process of chiral drugs plays a significant role in clinics and in research on drugs. Here, we experimentally demonstrate by all-optical means that the chiral molecules can be quickly discriminated and monitored with the ultrahigh-order modes excited in a metal cladding optofluidic chip, achieving over 5 times sensitivity with a low-dosage sample. We show that the varying concentration of the chiral drugs can be monitored both in cell and animal experiments, presenting a significant difference between chiral enantiomers at the optimal function time and the effect of the reaction. To our knowledge, this approach provides a new way to achieve important chiral discrimination for the pharmacokinetics and the pharmacodynamics and may present opportunities in indicating the health status of humans.The metabolic process of chiral drugs plays a significant role in clinics and in research on drugs. Here, we experimentally demonstrate by all-optical means that the chiral molecules can be quickly discriminated and monitored with the ultrahigh-order modes excited in a metal cladding optofluidic chip, achieving over 5 times sensitivity with a low-dosage sample. We show that the varying concentration of the chiral drugs can be monitored both in cell and animal experiments, presenting a significant difference between chiral enantiomers at the optimal function time and the effect of the reaction. To our knowledge, this approach provides a new way to achieve important chiral discrimination for the pharmacokinetics and the pharmacodynamics and may present opportunities in indicating the health status of humans..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 07, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081202 (2024)
Integrated Optics
Comparative study on pump frequency tuning and self-injection locking in Kerr microcomb generation
Zhuopei Yu, Weihong Hua, Chenxi Zhang, Runlin Miao... and Tian Jiang|Show fewer author(s)
The optical frequency comb has attracted considerable interest due to its diverse applications in optical atomic clocks, ultra-low-noise microwave generation, dual-comb spectroscopy, and optical communications. The merits of large frequency spacing, high integration, and low power consumption have shown that microresonator-based Kerr optical frequency combs will become mainstream in the future. Two methods of pump frequency tuning and self-injection locking were used to obtain Kerr combs in the same silicon nitride microresonators with free spectral ranges of 50 GHz and 100 GHz. Single-soliton combs are realized with both methods. Simplicity, pump power, spectrum bandwidth, conversion efficiency, and linewidth are compared and analyzed. Our results show that the advantages of pump frequency tuning are a wider spectrum and higher soliton power while the advantages of self-injection locking are simplicity, compactness, low cost, significant linewidth narrowing, and high conversion efficiency.The optical frequency comb has attracted considerable interest due to its diverse applications in optical atomic clocks, ultra-low-noise microwave generation, dual-comb spectroscopy, and optical communications. The merits of large frequency spacing, high integration, and low power consumption have shown that microresonator-based Kerr optical frequency combs will become mainstream in the future. Two methods of pump frequency tuning and self-injection locking were used to obtain Kerr combs in the same silicon nitride microresonators with free spectral ranges of 50 GHz and 100 GHz. Single-soliton combs are realized with both methods. Simplicity, pump power, spectrum bandwidth, conversion efficiency, and linewidth are compared and analyzed. Our results show that the advantages of pump frequency tuning are a wider spectrum and higher soliton power while the advantages of self-injection locking are simplicity, compactness, low cost, significant linewidth narrowing, and high conversion efficiency..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081301 (2024)
Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics
Hybrid-integrated 200 Gb/s REC-DML array transmitter based on photonic wire bonding technology
Yuxin Ma, Jie Zhao, Tongtong Yang, Yipeng Mei... and Xiangfei Chen|Show fewer author(s)
An 8-channel hybrid-integrated chip for 200 Gb/s (8 × 25 Gb/s) signal transmission has been demonstrated. The channels are all within the O-band, and with a spacing of 800 GHz. The core of this chip is a monolithic integrated multi-wavelength laser array of 8 directly-modulated distributed feedback (DFB) lasers. By using the reconstruction equivalent chirp technique, multi-wavelength integration and asymmetric phase shift structures are achieved in the laser array. The output laser beams of the array are combined by a planar light-wave circuit, which is hybrid-integrated with the laser array by photonic wire bonding. Experiment results of this transmitter chip show good single-mode working of each unit laser, with a side-mode suppression ratio above 50 dB, and the modulation bandwidth is above 20 GHz. Clear eye diagrams are obtained in the lasers for 25 Gb/s non-return-to-zero modulation, which implies a total 200 Gb/s transmission rate for the whole chip.An 8-channel hybrid-integrated chip for 200 Gb/s (8 × 25 Gb/s) signal transmission has been demonstrated. The channels are all within the O-band, and with a spacing of 800 GHz. The core of this chip is a monolithic integrated multi-wavelength laser array of 8 directly-modulated distributed feedback (DFB) lasers. By using the reconstruction equivalent chirp technique, multi-wavelength integration and asymmetric phase shift structures are achieved in the laser array. The output laser beams of the array are combined by a planar light-wave circuit, which is hybrid-integrated with the laser array by photonic wire bonding. Experiment results of this transmitter chip show good single-mode working of each unit laser, with a side-mode suppression ratio above 50 dB, and the modulation bandwidth is above 20 GHz. Clear eye diagrams are obtained in the lasers for 25 Gb/s non-return-to-zero modulation, which implies a total 200 Gb/s transmission rate for the whole chip..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081401 (2024)
Detection of transient mode-locking dynamics for a femtosecond Yb:KGW laser
Huimin Liu, Jinrong Tian, Zexin Zhang, Haiyan Liu... and Yanrong Song|Show fewer author(s)
The evolution dynamics of mode locking for a solid-state femtosecond Yb:KGW laser is demonstrated and detected with time-stretch dispersive Fourier transform (DFT) technique for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The Yb:KGW laser is constructed first with a classical X-shaped cavity, and SESAM-assisted Kerr lens mode locking is obtained. Then, a DFT device is built to record the buildup and extinction dynamics of the mode-locked laser. The results suggest that the time of extinction is slightly shorter than the buildup time and both of them experience complex transitions. The results indicate that DFT could also be suitable to detect the transient buildup and extinction process in solid-state lasers, which would help investigate both the evolution of mode locking and characteristics determination for solid-state lasers.The evolution dynamics of mode locking for a solid-state femtosecond Yb:KGW laser is demonstrated and detected with time-stretch dispersive Fourier transform (DFT) technique for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The Yb:KGW laser is constructed first with a classical X-shaped cavity, and SESAM-assisted Kerr lens mode locking is obtained. Then, a DFT device is built to record the buildup and extinction dynamics of the mode-locked laser. The results suggest that the time of extinction is slightly shorter than the buildup time and both of them experience complex transitions. The results indicate that DFT could also be suitable to detect the transient buildup and extinction process in solid-state lasers, which would help investigate both the evolution of mode locking and characteristics determination for solid-state lasers..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081402 (2024)
LD-pumped acousto-optic Q-switched Pr:YLF pulsed laser at 604 nm
Wei Yuan, Canlin Jiang, Huiying Xu, and Zhiping Cai
We demonstrated an actively acousto-optic Q-switched pulsed laser based on Pr:YLF at 604 nm. A 604 nm continuous-wave (CW) laser with a maximum output power of 3.84 W was achieved for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The Q-switched laser with a maximum average output power of 0.384 W, a narrowest pulse duration of 44.5 ns, a maximum single pulse energy of ∼64.1 µJ, and a maximum peak power of ∼1.44 kW was obtained at a repetition rate of 6 kHz. As far as we know, this was the first report of such a narrow pulse duration, high-power, and high-energy Q-switched pulsed laser at 604 nm. The beam quality factors Mx2 and My2 were measured to be 2.87 and 2.40, respectively. The results show that acousto-optic Q-switching is a promising method for obtaining pulsed lasers.We demonstrated an actively acousto-optic Q-switched pulsed laser based on Pr:YLF at 604 nm. A 604 nm continuous-wave (CW) laser with a maximum output power of 3.84 W was achieved for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The Q-switched laser with a maximum average output power of 0.384 W, a narrowest pulse duration of 44.5 ns, a maximum single pulse energy of ∼64.1 µJ, and a maximum peak power of ∼1.44 kW was obtained at a repetition rate of 6 kHz. As far as we know, this was the first report of such a narrow pulse duration, high-power, and high-energy Q-switched pulsed laser at 604 nm. The beam quality factors Mx2 and My2 were measured to be 2.87 and 2.40, respectively. The results show that acousto-optic Q-switching is a promising method for obtaining pulsed lasers..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 19, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081403 (2024)
High-power Pr3+:YLF continuous wave lasers at 691.7 nm, 701.4 nm, 705.0 nm, and 708.7 nm
Run Fang, Rongbin Dai, Huiying Xu, and Zhiping Cai
Lasers from 1I6 to 3F4 transitions were first demonstrated in a Pr3+:YLF crystal by inserting a birefringent filter. Output powers up to 2.44 W, 2.10 W, 2.01 W, and 2.42 W were obtained at 691.7 nm, 701.4 nm, 705.0 nm, and 708.7 nm, respectively. Their slope efficiencies were 19.8%, 16.5%, 15.8%, and 19.4%, respectively. The Mx2 and My2 factors were measured to be 2.29 and 2.03 at 691.7 nm, 2.23 and 1.86 at 701.4 nm, 2.31 and 2.08 at 705.0 nm, and 2.41 and 2.04 at 708.7 nm, with corresponding power fluctuations of less than 5.3%, 5.6%, 5.8%, and 2.9%.Lasers from 1I6 to 3F4 transitions were first demonstrated in a Pr3+:YLF crystal by inserting a birefringent filter. Output powers up to 2.44 W, 2.10 W, 2.01 W, and 2.42 W were obtained at 691.7 nm, 701.4 nm, 705.0 nm, and 708.7 nm, respectively. Their slope efficiencies were 19.8%, 16.5%, 15.8%, and 19.4%, respectively. The Mx2 and My2 factors were measured to be 2.29 and 2.03 at 691.7 nm, 2.23 and 1.86 at 701.4 nm, 2.31 and 2.08 at 705.0 nm, and 2.41 and 2.04 at 708.7 nm, with corresponding power fluctuations of less than 5.3%, 5.6%, 5.8%, and 2.9%..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081404 (2024)
High-power compact continuous-wave Fe:ZnSe laser at 4 µm with >50% overall conversion efficiency | Editors' Pick
Yanlong Shen, Yingchao Wan, Feng Zhu, Tongxing Chai... and Ke Huang|Show fewer author(s)
We report on a compact, high-efficiency mid-infrared continuous-wave (CW) Fe:ZnSe laser pumped by a 2.9 µm fiber laser under liquid nitrogen cooling. A maximum output power of 5.5 W and a slope efficiency of up to 66.3% with respect to the launched pump power were obtained. The overall optical-to-optical (OTO) conversion efficiency, calculated from the output of the 2.9 µm fiber laser to the 4 µm laser, was as high as ∼54.5%. The OTO efficiency and the slope efficiency are, to the best of our knowledge, the highest ever reported in Fe:ZnSe lasers. A rate-equation-based numerical model of CW operation was established, and the simulation agreed well with the experiment, identifying the routes used in the experiment for such high efficiency.We report on a compact, high-efficiency mid-infrared continuous-wave (CW) Fe:ZnSe laser pumped by a 2.9 µm fiber laser under liquid nitrogen cooling. A maximum output power of 5.5 W and a slope efficiency of up to 66.3% with respect to the launched pump power were obtained. The overall optical-to-optical (OTO) conversion efficiency, calculated from the output of the 2.9 µm fiber laser to the 4 µm laser, was as high as ∼54.5%. The OTO efficiency and the slope efficiency are, to the best of our knowledge, the highest ever reported in Fe:ZnSe lasers. A rate-equation-based numerical model of CW operation was established, and the simulation agreed well with the experiment, identifying the routes used in the experiment for such high efficiency..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 20, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081405 (2024)
Field stabilization of pulse duration in a hundred-femtosecond level
Runmin Liu, Yong Wu, Guoqing Pu, Jiayang Cheng... and Minglie Hu|Show fewer author(s)
Pulse duration is considered as one of the most important characteristics of high-power femtosecond lasers. However, pulses output from the laser system are susceptible to ambient changes and manifest the instability of pulse durations in an open environment. In this paper, incorporating the algorithmic framework of the improved stochastic hill-climbing search and incremental proportional-integral controller, temperature-induced fluctuations of pulse duration can be effectively compensated by an automatic feedback control in an all-fiber chirped-pulse amplification system. In the experiment, sub-hundred femtosecond fluctuation of pulse duration is introduced to verify the performance robustness of the proposed pulse-duration feedback control (PDFC). The stability of pulse duration is obviously higher than the case without the feedback control, and the peak-to-peak fluctuation of pulse duration is reduced to 6.5%. Furthermore, the robust switching between different pulse durations proves the versatility of the PDFC. We expect that the proposed feedback control method could provide a novel insight into high-power femtosecond lasers widely applied in fundamental researches and industrial fields.Pulse duration is considered as one of the most important characteristics of high-power femtosecond lasers. However, pulses output from the laser system are susceptible to ambient changes and manifest the instability of pulse durations in an open environment. In this paper, incorporating the algorithmic framework of the improved stochastic hill-climbing search and incremental proportional-integral controller, temperature-induced fluctuations of pulse duration can be effectively compensated by an automatic feedback control in an all-fiber chirped-pulse amplification system. In the experiment, sub-hundred femtosecond fluctuation of pulse duration is introduced to verify the performance robustness of the proposed pulse-duration feedback control (PDFC). The stability of pulse duration is obviously higher than the case without the feedback control, and the peak-to-peak fluctuation of pulse duration is reduced to 6.5%. Furthermore, the robust switching between different pulse durations proves the versatility of the PDFC. We expect that the proposed feedback control method could provide a novel insight into high-power femtosecond lasers widely applied in fundamental researches and industrial fields..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081406 (2024)
Optical Materials
Slicing of large-size single crystals by ultrafast laser with external stress assistance
Lifeng Wang, Lili Liu, Yinan Wang, Xun Li... and Ming Li|Show fewer author(s)
The existing single-crystal slicing techniques result in significant material wastage and elevate the production cost of premium-quality thin slices of crystals. Here we report (for the first time, to our knowledge) an approach for vertical slicing of large-size single-crystal gain materials by ultrafast laser. By employing aberration correction techniques, the optimization of the optical field distribution within the high-refractive-index crystal enables the achievement of a continuous laser-modified layer with a thickness of less than 10 µm, oriented perpendicular to the direction of the laser direction. The compressed focal spot facilitates crack initiation, enabling propagation under external forces, ultimately achieving the successful slicing of a Φ12 mm crystal. The surface roughness of the sliced Yb:YAG is less than 2.5 µm. The results illustrate the potential of low-loss slicing strategy for single-crystal fabrication and pave the way for the future development of thin disk lasers.The existing single-crystal slicing techniques result in significant material wastage and elevate the production cost of premium-quality thin slices of crystals. Here we report (for the first time, to our knowledge) an approach for vertical slicing of large-size single-crystal gain materials by ultrafast laser. By employing aberration correction techniques, the optimization of the optical field distribution within the high-refractive-index crystal enables the achievement of a continuous laser-modified layer with a thickness of less than 10 µm, oriented perpendicular to the direction of the laser direction. The compressed focal spot facilitates crack initiation, enabling propagation under external forces, ultimately achieving the successful slicing of a Φ12 mm crystal. The surface roughness of the sliced Yb:YAG is less than 2.5 µm. The results illustrate the potential of low-loss slicing strategy for single-crystal fabrication and pave the way for the future development of thin disk lasers..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 081601 (2024)
Optoelectronics
4 × 112 Gb/s hybrid integrated silicon receiver based on photonic-electronic co-design
Ye Jin, Yujun Xie, Zhihan Zhang, Donglai Lu... and Ming Li|Show fewer author(s)
A 4 × 112 Gb/s hybrid-integrated optical receiver is demonstrated based on the silicon-photonic vertical p-i-n photodetector and silicon–germanium transimpedance amplifier. We propose a photonic-electronic co-design technique to optimize both the device-level and system-level performance, based on the end-to-end equivalent circuit model of the receiver. Continuous-time linear equalization and shunt peaking are employed to enhance the frequency response. Experimental results reveal that the optical-to-electrical 3-dB bandwidth of the receiver is 48 GHz. Clear open NRZ eye diagrams at 56 Gb/s and PAM-4 eye diagrams at 112 Gb/s are achieved without an equalizer in the oscilloscope. The measured bit error rates for 56 Gb/s in NRZ and 112 Gb/s in PAM-4 reach 1 × 10-12 and 2.4 × 10-4 (KP4-FEC: forward error correction) thresholds under -4 dBm input power, respectively. Furthermore, the proposed receiver boasts a power consumption of approximately 2.2 pJ/bit, indicating an energy efficient solution for data center traffic growth.A 4 × 112 Gb/s hybrid-integrated optical receiver is demonstrated based on the silicon-photonic vertical p-i-n photodetector and silicon–germanium transimpedance amplifier. We propose a photonic-electronic co-design technique to optimize both the device-level and system-level performance, based on the end-to-end equivalent circuit model of the receiver. Continuous-time linear equalization and shunt peaking are employed to enhance the frequency response. Experimental results reveal that the optical-to-electrical 3-dB bandwidth of the receiver is 48 GHz. Clear open NRZ eye diagrams at 56 Gb/s and PAM-4 eye diagrams at 112 Gb/s are achieved without an equalizer in the oscilloscope. The measured bit error rates for 56 Gb/s in NRZ and 112 Gb/s in PAM-4 reach 1 × 10-12 and 2.4 × 10-4 (KP4-FEC: forward error correction) thresholds under -4 dBm input power, respectively. Furthermore, the proposed receiver boasts a power consumption of approximately 2.2 pJ/bit, indicating an energy efficient solution for data center traffic growth..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 13, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 082501 (2024)
Physical Optics
Wide-color-gamut, high-purity, and high-brightness thin film structural colors based on modified Fano resonant structure
Weijie Chen, Zexiang He, Zhenzhen Duan, Jian Yang... and Yikun Bu|Show fewer author(s)
Recently, the Fano resonance has played an increasingly important role in improving the color performance of structural colors. In this study, we further elucidate the asymmetric spectral shape generated by Fano resonance from a phase perspective and explore four distinct continuum state structures. By integrating the proposed cavity-like structure with a metal–dielectric–metal discrete state, multilayered thin-film structural colors with minimal background reflection, as low as 8%, were successfully achieved. The reflection peak of this structure exhibits a bandwidth of approximately 50 nm and reaches up to 80%, indicating heightened saturation and color brightness. Moreover, by adjusting the thickness, we effortlessly obtained a broader color gamut compared to Adobe RGB (45.2%), covering 56.7% of the CIE color space. Even adjusting a single layer can achieve a color gamut of 47.1%. In experiments, by deliberately choosing low oxygen-dependent materials, excellent RGB colors with high brightness and in high consistency with simulation results were successfully achieved. Therefore, the scheme’s simple process for structural color creation, along with its excellent color performance and the ability to effectively replicate simulation characteristics makes it highly valuable in fields like anticounterfeiting, decoration, display devices, and solar cell panels.Recently, the Fano resonance has played an increasingly important role in improving the color performance of structural colors. In this study, we further elucidate the asymmetric spectral shape generated by Fano resonance from a phase perspective and explore four distinct continuum state structures. By integrating the proposed cavity-like structure with a metal–dielectric–metal discrete state, multilayered thin-film structural colors with minimal background reflection, as low as 8%, were successfully achieved. The reflection peak of this structure exhibits a bandwidth of approximately 50 nm and reaches up to 80%, indicating heightened saturation and color brightness. Moreover, by adjusting the thickness, we effortlessly obtained a broader color gamut compared to Adobe RGB (45.2%), covering 56.7% of the CIE color space. Even adjusting a single layer can achieve a color gamut of 47.1%. In experiments, by deliberately choosing low oxygen-dependent materials, excellent RGB colors with high brightness and in high consistency with simulation results were successfully achieved. Therefore, the scheme’s simple process for structural color creation, along with its excellent color performance and the ability to effectively replicate simulation characteristics makes it highly valuable in fields like anticounterfeiting, decoration, display devices, and solar cell panels..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 21, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 082601 (2024)
Solar Energy and Photovoltaics
Time-resolved photoluminescence: a precision tool for shallow trap density determination in perovskite films
Wei Chen, Yifeng Shi, Pengxiang Wang, Guodong Zhang... and Yuchuan Shao|Show fewer author(s)
Determining the trap density in the absorbing layer thin film of perovskite solar cells is a critically important task, as it directly influences the efficiency of the devices. Here, we proposed time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) as a nondestructive method to assess trap density. A model was constructed to investigate carrier recombination and transition in perovskite materials. The model was utilized for numerical calculations and successfully fitted TRPL signals of perovskite materials. Furthermore, a genetic algorithm was employed to optimize the parameters. Finally, statistical methods were applied to obtain the parameters associated with the trap states of the material. This approach facilitates the successful determination of trap densities for different samples with clear differentiation.Determining the trap density in the absorbing layer thin film of perovskite solar cells is a critically important task, as it directly influences the efficiency of the devices. Here, we proposed time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) as a nondestructive method to assess trap density. A model was constructed to investigate carrier recombination and transition in perovskite materials. The model was utilized for numerical calculations and successfully fitted TRPL signals of perovskite materials. Furthermore, a genetic algorithm was employed to optimize the parameters. Finally, statistical methods were applied to obtain the parameters associated with the trap states of the material. This approach facilitates the successful determination of trap densities for different samples with clear differentiation..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Aug. 19, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 8, 084001 (2024)