Author Affiliations
1State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 611731, China2DTU Electro, Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby, 2800, Denmarkshow less
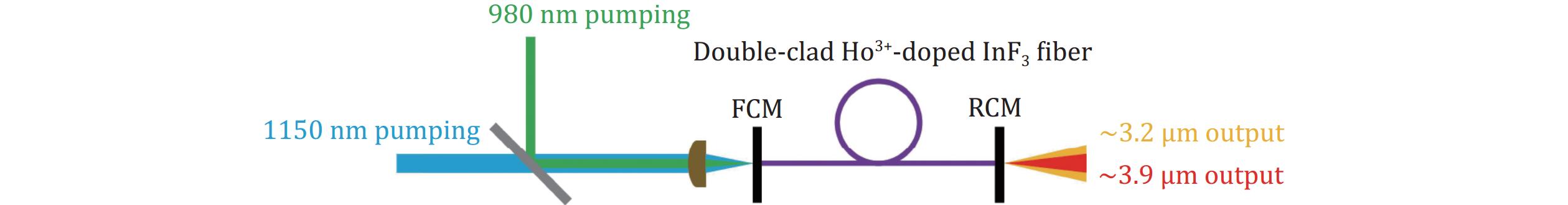
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the setup in simulations. FCM and RCM indicate the front and rear cavity mirrors, respectively.
Fig. 2. Energy level diagram of Ho3+-doped InF3 fiber pumped at 1150 nm and 980 nm with the relevant transitions processes. GSA: Ground state absorption; VGSA: Visual ground state absorption; ESA: Excited state absorption; ETU1 and ETU2: Energy transfer upconversion 1 and 2; CR1 and CR2: Cross relaxation 1 and 2.
Fig. 3. Power distribution with the varied and L (P1 = 5 W and P2 = 20 W).
Fig. 4. Power evolutions with (a) P1 and (b) P2 (= 0.11 and L = 1.85 m).
Fig. 5. Effects of the interionic processes (i.e., ETU1, ETU2, CR1, and CR2) and ESA on the laser performance (P1 = 5 W, = 0.11, and L = 1.85 m).
Fig. 6. Comparison of the ~3.2 μm output power evolutions with the different 5I5 lifetimes (P1 = 5 W, = 0.11, and L = 1.85 m).
Fig. 7. ~3.9 μm laser power evolution with (P1 = 5 W, P2 = 20 W, = 0.11, and L = 1.85 m).
Fig. 8. Dual-wavelength laser power and heat load evolutions with P2, where the ~3.2 μm power evolution under the single transition operation is added as a comparison (P1 = 5 W, = 0.11, = 0.1, and L = 1.85 m).
| Parameter | Value | Source | | NHo | 2×1026 m–3 | Manufacturer | | rcore | 5.5 μm | Manufacturer | | rclad | 50.0 μm | Manufacturer | | NA | 0.3 | Manufacturer | | L | To be optimized | / | | ${\lambda _{{s_1}}}$ | 3260 nm | Set | | ${\lambda _{{s_2}}}$ | 3920 nm | Set | | ${\lambda _{{p_1}}}$ | 1150 nm | Set | | ${\lambda _{{p_2}}}$ | 980 nm | Set | | ${\alpha _{{s_1}}}$ | 0.22 dB/m | [25] | | ${\alpha _{{s_2}}}$ | 0.20 dB/m | [25] | | ${\alpha _{{p_1}}}$ | 0.60 dB/m | Manufacturer | | ${\alpha _{{p_2}}}$ | 0.96 dB/m | [25] | | ${\Gamma _{{p_1}}}$ | 0.0110 | Calculated | | ${\Gamma _{{p_2}}}$ | 0.9271 | Calculated | | ${\Gamma _{{s_1}}}$ | 0.8859 | Calculated | | ${\Gamma _{{s_2}}}$ | 0.8287 | Calculated | | ${R_{{p_{11}}}}$ | 0.01 | Set | | ${R_{{p_{12}}}}$ | 0.99 | Set | | ${R_{{p_{21}}}}$ | 0.01 | Set | | ${R_{{p_{22}}}}$ | 0.99 | Set | | ${R_{{s_{11}}}}$ | 0.99 | Set | | ${R_{{s_{21}}}}$ | 0.99 | Set | | ${R_{{s_{12}}}}$ | To be optimized | / | | ${R_{{s_{22}}}}$ | To be optimized | / | | ${\sigma _{{\text{ab}}{{\text{s}}_{{\text{02}}}}}}$ | 2.35×1025 m2 | [32] | | ${\sigma _{{\text{em}}{{\text{i}}_{20}}}}$ | 1.80×1025 m2 | Calculated | | ${\sigma _{{\text{ab}}{{\text{s}}_{25}}}}$ | 3.29×1025 m2 | [33] | | ${\sigma _{{\text{em}}{{\text{i}}_{52}}}}$ | 4.81×1025 m2 | [33] | | ${\sigma _{{\text{ab}}{{\text{s}}_{14}}}}$ | 1.58×1025 m2 | [34] | | ${\sigma _{{\text{em}}{{\text{i}}_{41}}}}$ | 6.35×1025 m2 | Calculated | | ${\sigma _{{\text{em}}{{\text{i}}_{54}}}}$ | 1.92×1025 m2 | [22] | | ${\sigma _{{\text{ab}}{{\text{s}}_{45}}}}$ | 2.65×1025 m2 | Calculated | | ${\sigma _{{\text{em}}{{\text{i}}_{32}}}}$ | 3.40×1025 m2 | [25] | | ${\sigma _{{\text{ab}}{{\text{s}}_{23}}}}$ | 2.49×1025 m2 | Calculated | | W1,1 | 7.15×10–25 m3/s | Calculated | | W2,2 | 1.58×10–23 m3/s | Calculated | | W3,0 | 3.77×10–24 m3/s | Calculated | | W5,0 | 1.19×10–24 m3/s | Calculated |
|
Table 1. Cavity, absorption/emission, and interionic parameters.
| Parameter | Value | | τ1 | 16.2 ms | | τ2 | 6.2 ms | | τ3 | 135 μs | | τ4 | 16.3 μs | | τ5 | 312 μs | | β1,0 | 1 | | β2,0, β2,1 | 0.9420, 0.0580 | | β3,0, β3,1, β3,2 | 0.0110, 0.0085, 0.9800 | | β4,0, β4,1, β4,2, β4,3 | 0.0385, 0.0097, 0.0023, 0.9490 | | β5,0, β5,1, β5,2 | 0.5000, 0.4000, 0.1000 |
|
Table 2. Spectrum parameters of Ho3+-doped InF3 glass.
| Parameter | Value | | ${W_{{\text{MP}}{{\text{R}}_{5{\mathrm{,}}4}}}}$ | 0 | | ${W_{{\text{MP}}{{\text{R}}_{4{\mathrm{,}}3}}}}$ | 58234 s–1 | | ${W_{{\text{MP}}{{\text{R}}_{3{\mathrm{,}}2}}}}$ | 7260 s–1 | | ${W_{{\text{MP}}{{\text{R}}_{2{\mathrm{,}}1}}}}$ | 0 | | ${W_{{\text{MP}}{{\text{R}}_{1{\mathrm{,}}0}}}}$ | 0 | | E5,4 | 3056 cm–1 | | E4,3 | 4353 cm–1 | | E3,2 | 2586 cm–1 | | E2,1 | 3510 cm–1 | | E1,0 | 5090 cm–1 | | E5,3 | 7409 cm–1 | | E4,2 | 6939 cm–1 | | E3,1 | 6096 cm–1 | | δE1,1 | 1580 cm–1 | | δE2,2 | 1661 cm–1 | | δE3,0 | 1006 cm–1 | | δE5,0 | 2319 cm–1 |
|
Table 3. MPR decay rates, energy differences of two levels, and exothermic energy associated with interionic processes of Ho
3+-doped InF
3 glass [
33,
37].