Yingtong Shi, Hang Xu, Jinqiang Xu, Senlin Huang. Research progress on high-brightness electron source drive laser system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2025, 37(2): 021001
Search by keywords or author
- High Power Laser and Particle Beams
- Vol. 37, Issue 2, 021001 (2025)
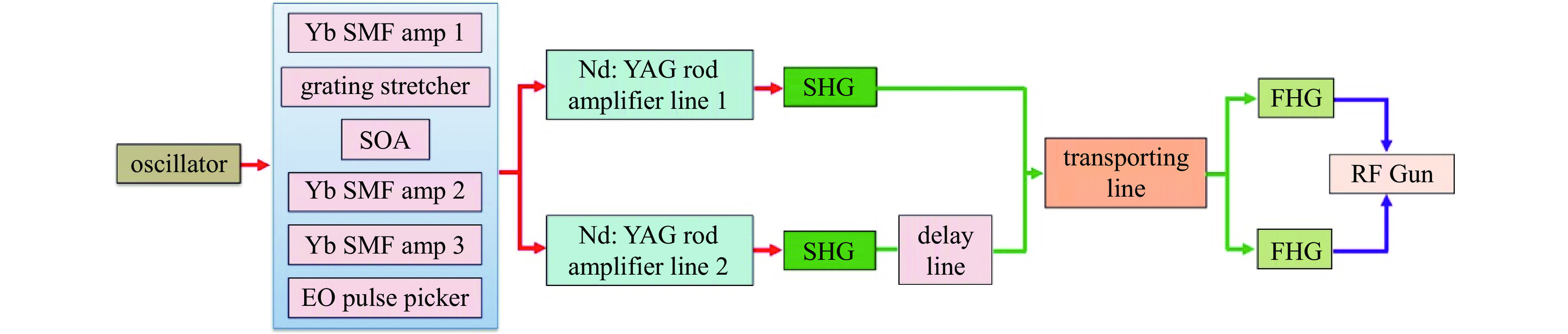
![SuperKEKB Yb/Nd drive laser system[15]](/richHtml/qjglzs/2025/37/2/021001/img_1.jpg)
Fig. 1. SuperKEKB Yb/Nd drive laser system[15]
![FLASH drive laser system[28]](/richHtml/qjglzs/2025/37/2/021001/img_2.jpg)
Fig. 2. FLASH drive laser system[28]
Fig. 3. Structure of PULSE[26]
Fig. 4. Output characteristics of PULSE amplifier[26]
Fig. 5. Schematic of the pulse picking in PULSE[26]
Fig. 6. Schematic of the rod fiber amplifier in Cornell ERL drive laser system[19]
Fig. 7. Output characteristics of the drive laser amplifier at Cornell ERL[19]
Fig. 8. Green laser output characteristics of Cornell ERL drive laser system[19]
Fig. 9. Slice emittance of optimized electron bunches for various profiles of photocathode pulses and beam current profiles[54]
Fig. 10. UV pulse shaping optical scheme at FERMI[58]
Fig. 11. Temporal intensity distribution of the incident laser and the output laser of incoherent stacking[17]
Fig. 12. Optical layout of the multiple birefringent crystal shaper used for PULSE[33]
Fig. 13. Results of both the measured and the calculated pulse profiles after the shaper[33]
Fig. 14. Beam transport and transverse beam profiles along the beam line at SwissFEL[30]
Fig. 15. UV laser beam spatial distributions without and with the application of DOE[15]
Fig. 16. Schematic diagram of 3D shaper of laser pulse intensity distribution based on zero-dispersion compressor and SLM[65]
Fig. 17. Distribution of a 0.5 nC electron beam generated by 3D-shaped lasers[54]
Fig. 18. Diffraction efficiency and reflection coefficient of the 3D CBG aperture[67]
Fig. 19. Injector building layout at EuXFEL[16]
Fig. 20. Stability of PULSE multiple birefringent crystal shaper with respect to temporal and temperature variations[33]
|
Table 1. Output parameters of class Ⅰ amplifiers in typical facilities
|
Table 2. Output parameters of class Ⅱ amplifiers in typical facilities
|
Table 3. Output parameters of class Ⅲ amplifiers in typical facilities
|
Table 4. Output parameters of harmonic generation module in typical facilities
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



