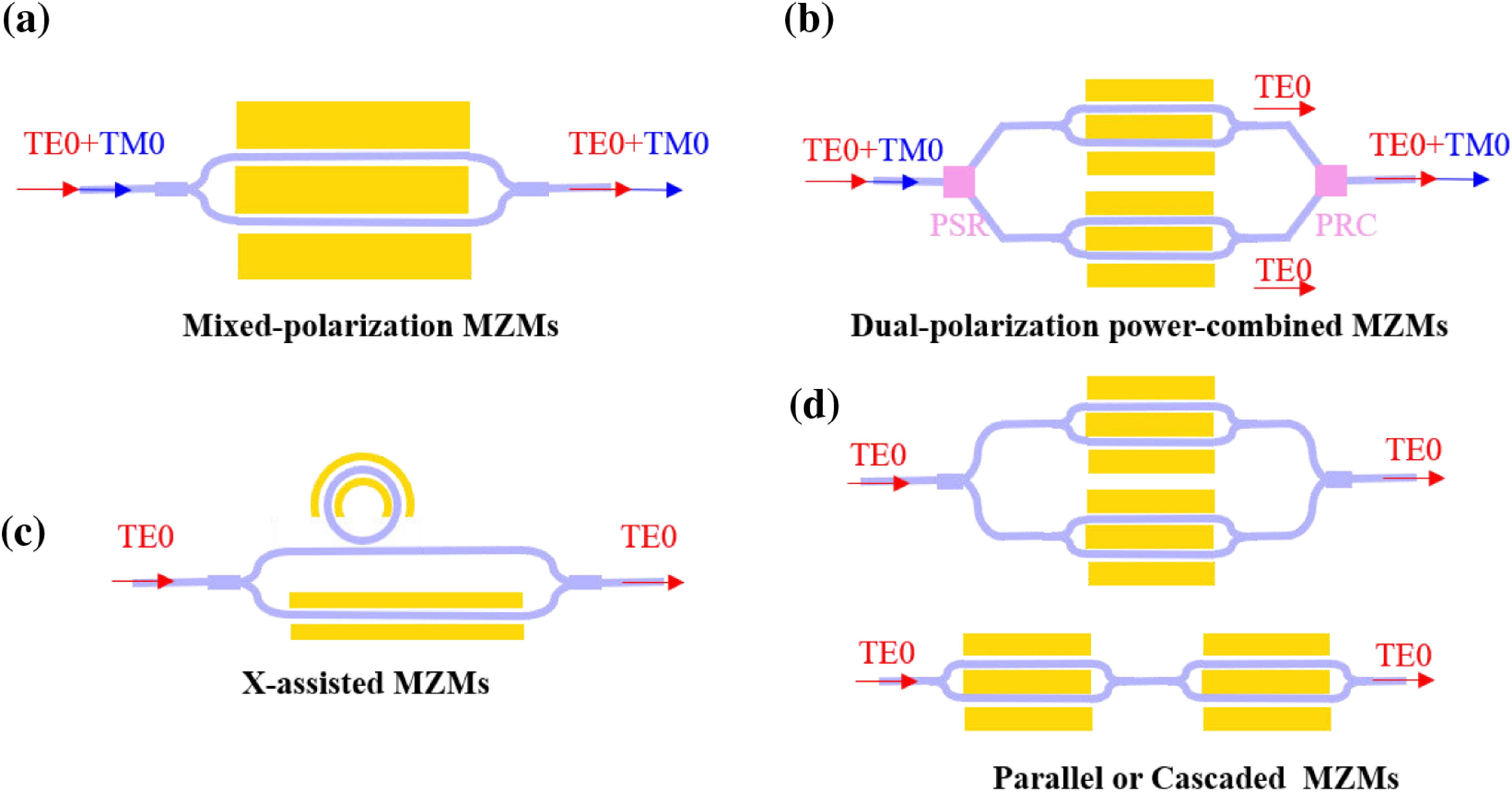
Heyun Tan, Junwei Zhang, Jingyi Wang, Songnian Fu, Siyuan Yu, Xinlun Cai, "High-linearity wide-bandwidth integrated thin-film lithium niobate modulator based on a dual-optical-mode co-modulated configuration," Photonics Res. 13, 817 (2025)
Search by keywords or author
- Photonics Research
- Vol. 13, Issue 4, 817 (2025)
Abstract
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



