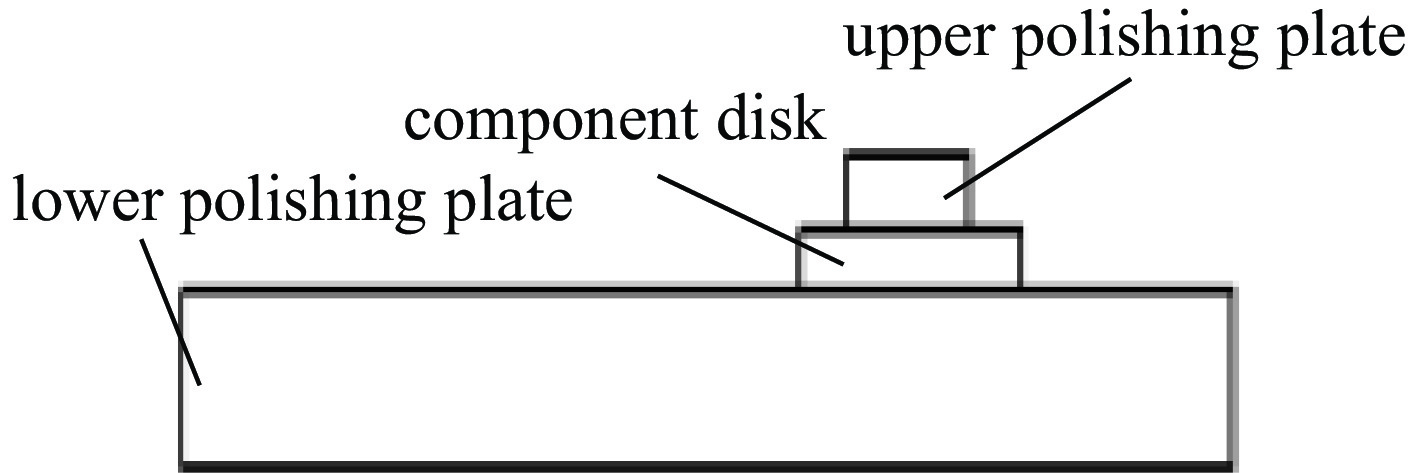
Zhikai Mi, Fengming Nie, Siling Huang, Feng Xue. Predictive modeling of the surface pattern of double-sided polishing process of optical components[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36(9): 091001
Search by keywords or author
- High Power Laser and Particle Beams
- Vol. 36, Issue 9, 091001 (2024)
Note: This section is automatically generated by AI . The website and platform operators shall not be liable for any commercial or legal consequences arising from your use of AI generated content on this website. Please be aware of this.
Abstract
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address


 AI Video Guide
AI Video Guide  AI Picture Guide
AI Picture Guide AI One Sentence
AI One Sentence


