Lei Sheng, Lijuan Li, Xihong Fu, Xuezhu Lin, Lili Guo. Simulation Technology for Assembly of Off-Axis Three-Mirror Optical Systems Based on KAN-Transformer[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2025, 45(5): 0522002
Search by keywords or author
- Acta Optica Sinica
- Vol. 45, Issue 5, 0522002 (2025)
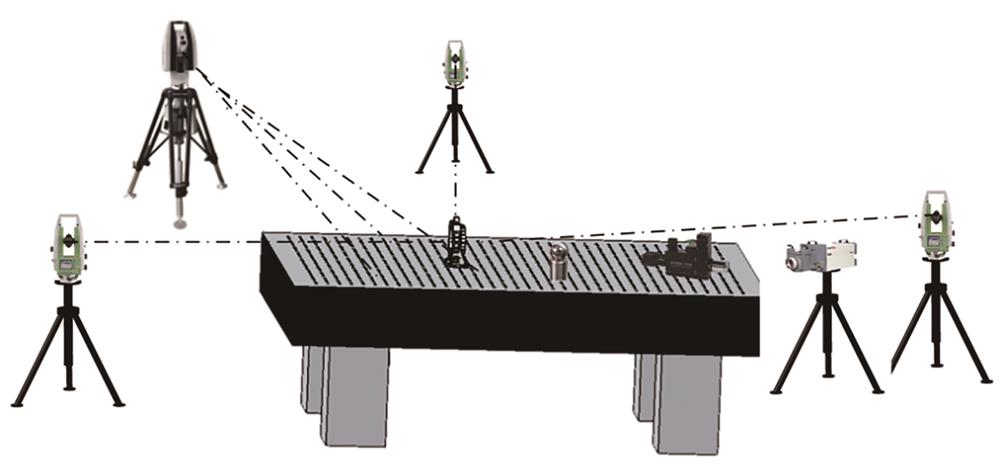
Fig. 1. Diagram of initial installation and adjustment

Fig. 2. Flowchart of model construction
Fig. 3. Structure diagram of shallow MLP and KAN. (a) Shallow structure of MLP; (b) shallow structure of KAN
Fig. 4. Structure diagram of KAN-Transformer
Fig. 5. Optical path diagram of a certain off-axis three-mirror optical system
Fig. 6. Production process of dataset
Fig. 7. MSE and MAE of different network structures under training dataset. (a) MSE; (b) MAE
Fig. 8. Linear distribution diagrams of small-scale predicted values and preset values based on Transformer. (a) X-decenter predicted values and preset values; (b) Y-decenter predicted values and preset values; (c) Z-decenter predicted values and preset values; (d) X-tilt predicted values and preset values; (e) Y-tilt predicted values and preset values; (f) Z-tilt predicted values and preset values
Fig. 9. Linear distribution diagram of small-scale predicted values and preset values based on KAN-Transformer. (a) X-decenter predicted values and preset values; (b) Y-decenter predicted values and preset values; (c) Z-decenter predicted values and preset values; (d) X-tilt predicted values and preset values; (e) Y-tilt predicted values and preset values; (f) Z-tilt predicted values and preset values
Fig. 10. Design residual wavefront aberration for F(0°, 0°), F(2°, -2°), and F(2°, 2°) fields of view. (a) F(0°, 0°); (b) F(2°, -2°); (c) F(2°, 2°)
Fig. 11. Simulating wavefront aberration in the fields of F(0°, 0°), F(2°, -2°), and F(2°, 2°) after misalignment. (a) F(0°, 0°); (b) F(2°, -2°); (c) F(2°, 2°)
Fig. 12. Wavefront aberration in the fields of F(0°, 0°), F(2°, -2°), and F(2°, 2°) after Simulated assembly. (a) F(0°, 0°); (b) F(2°, -2°); (c) F(2°, 2°)
Fig. 13. Prediction errors of different network structures
Fig. 14. Field of F(0°, 0°), F(0°, 2°), and F(2°, 2°) of PV error value and RMS error value of the system. (a) F(0°, 0°) PV error; (b) F(0°,2°) PV error; (c) F(2°, 2°) PV error; (d) F(0°, 0°) RMS error; (e) F(0°, 2°) RMS error; (f) F(2°, 2°) RMS error
Fig. 15. Training process of neural network with added noise
|
Table 1. Design parameters of three-mirror optical system
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2. Comparison between sensitivity matrix method calculation results and preset values
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Comparison between neural network calculation results and preset values
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Comparison between the second round sensitivity matrix method calculation results and preset values
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 5. Comparison between the results of the second round of neural network calculations and the preset values
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 6. Comparison between simulated noise training neural network of the first round of calculation results and preset values
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 7. Comparison between simulated noise training neural network of the second round of calculation results and preset values

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



