Xin MIAO, Shiqiang YAN, Jindou WEI, Chao WU, Wenhao FAN, Shaoping CHEN. Interface Layer of Te-based Thermoelectric Device: Abnormal Growth and Interface Stability [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 903
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Inorganic Materials
- Vol. 39, Issue 8, 903 (2024)
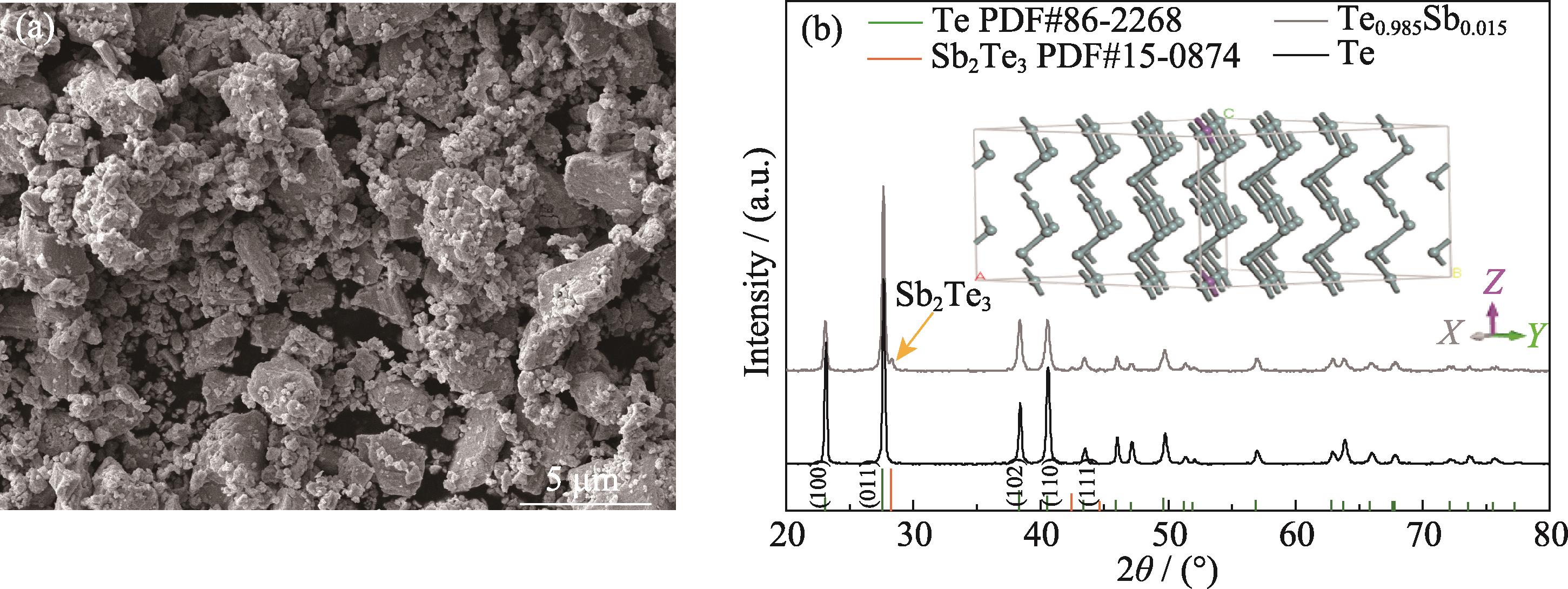
1. Microstructure and composition of Te0.985Sb0.015 precursor powder
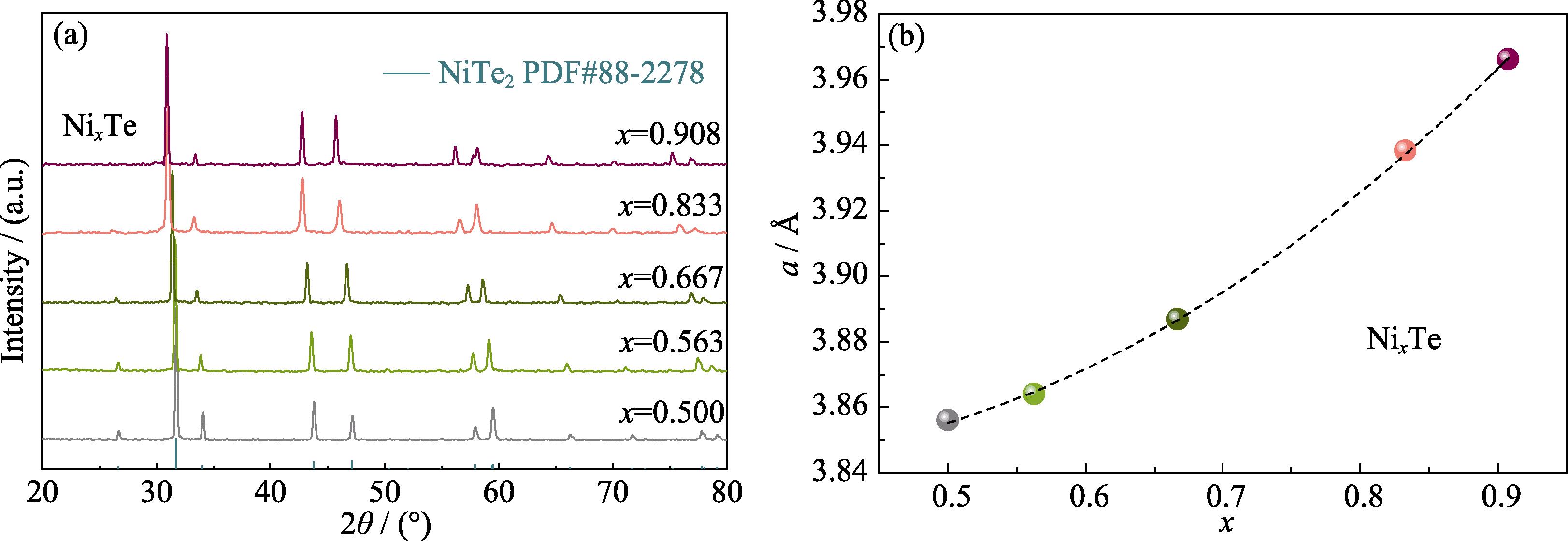
2. Composition and lattice parameters of Nix Te samples
3. (a) Thicknesses of the interface reaction layers (IRLs) at the Te0.985Sb0.015/Nix Te interfaces, and (b) formation Gibbs free energies in molar (ΔrG T) of the interface products at the Te0.985Sb0.015/Nix Te interfaces
4. Diagram of the growth of the interface reaction layer (IRL) at Te/NiTe2-m interface
5. Microstructures of Te0.985Sb0.015/Nix Te interfaces after aging at 473 K for 6 and 12 d
6. Performance of Nix Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Nix Te (x =0.500, 0.563, 0.667) single-leg devices
S1. Fracture microstructure and element distribution of sintered Te0.985Sb0.015
S2. Thermoelectric performance of Te0.985Sb0.015 in the direction parallel to the sintering pressure
S3. Electrical performance of Nix Te samples
S4. Microstructures and element distributions of sintered Te0.985Sb0.015/Nix Te interfaces
S5. Backscatter SEM image of sintered Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni interface
S6. Performance of Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te single-leg devices under a temperature difference of 180 K (Hot end: 473 K, Cold end: 293 K)
S7. Aging-time dependent performance of Ni0.5Te/Te0.985Sb0.015/Ni0.5Te single-leg devices under a temperature difference of 180 K (Hot end: 473 K, Cold end: 293 K)
|
Table 1. Total migration of atoms (CN·l) at Te0.985Sb0.015/NixTe interface
|
Table 1. Thermodynamic data. Values of entropy (ST), enthalpy (HT), and Gibbs free energy (GT) at 298.15, 600.00 and 700.00 K, respectively
|
Table 2. Molar formation Gibbs free energies (ΔrGT) of interface products at 298.15, 600.00 and 700.00 K, respectively
|
Table 3. Density (ρ), molar mass (M) and moles of the bound Te per mole substance

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



