Xiyuan Cao, Yifan Luo, Yangyang Zhao, Jiaxu Zhang, Nan Li. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Metals via Remote Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2025, 52(6): 0611002
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Journal of Lasers
- Vol. 52, Issue 6, 0611002 (2025)
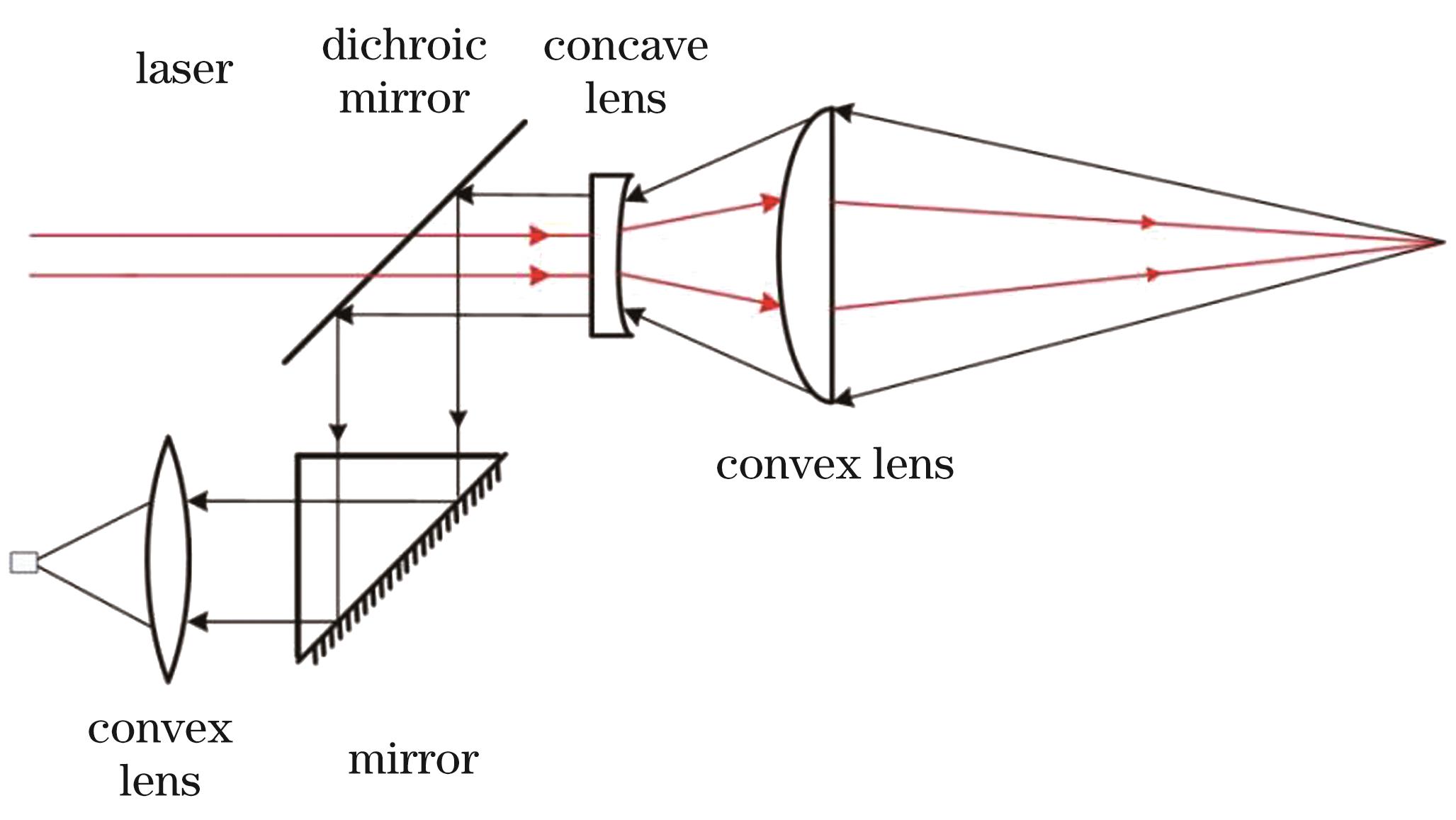
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of coaxial optical path structure design

Fig. 2. Simulation results of focusing effect of lens group. (a) Light path simulation diagram; (b) focusing spot diagram
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of LIBS remote detection system
Fig. 4. Typical LIBS lines of copper-nickel-magnesium-aluminum alloy target
Fig. 5. Spectra of various elements under different detection distances and detection delays. (a) 0 ns; (b) 500 ns; (c) 1000 ns; (d) 2000 ns
Fig. 6. Characteristic spectra of each element under different detection delays when detection distance is 5.0 m
Fig. 7. Characteristic spectral intensity of each element versus detection delay. (a) Ni I 352.45 nm; (b) Al I 396.15 nm;
Fig. 8. Characteristic spectral intensity versus laser energy under different detection distances. (a) Ni I 352.45 nm; (b) Al I 396.15 nm; (c) Mg I 518.36 nm; (d) Cu I 521.82 nm
Fig. 9. Detection results of Ni I 352.45 nm, Al I 396.15 nm, Mg I 518.36 nm, and Cu I 521.82 nm at different distances. (a) Spectral lines; (b) spectral intensity versus detection distance
Fig. 10. Calibration curves of Al under different detection distances. (a) 0.5 m; (b) 1.0 m; (c) 2.0 m; (d) 3.0 m; (e) 4.0 m; (f) 5.0 m
|
Table 1. Relationship among lens spacing, focusing distance, and focusing spot size
|
Table 2. Ni I, Al I, Mg I, and Cu I spectral line parameters for spectral analysis
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Comparison of analysis results between standard curve method and multivariate linear fitting method

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



