Mo Yang, Shangjun Lin, Jie Chen, Fangrong Hu. Detection of miRNA‑92a Concentration Using Terahertz Metasurface Sensors Based on Hybrid Chain Reaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(15): 1507402
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Journal of Lasers
- Vol. 51, Issue 15, 1507402 (2024)
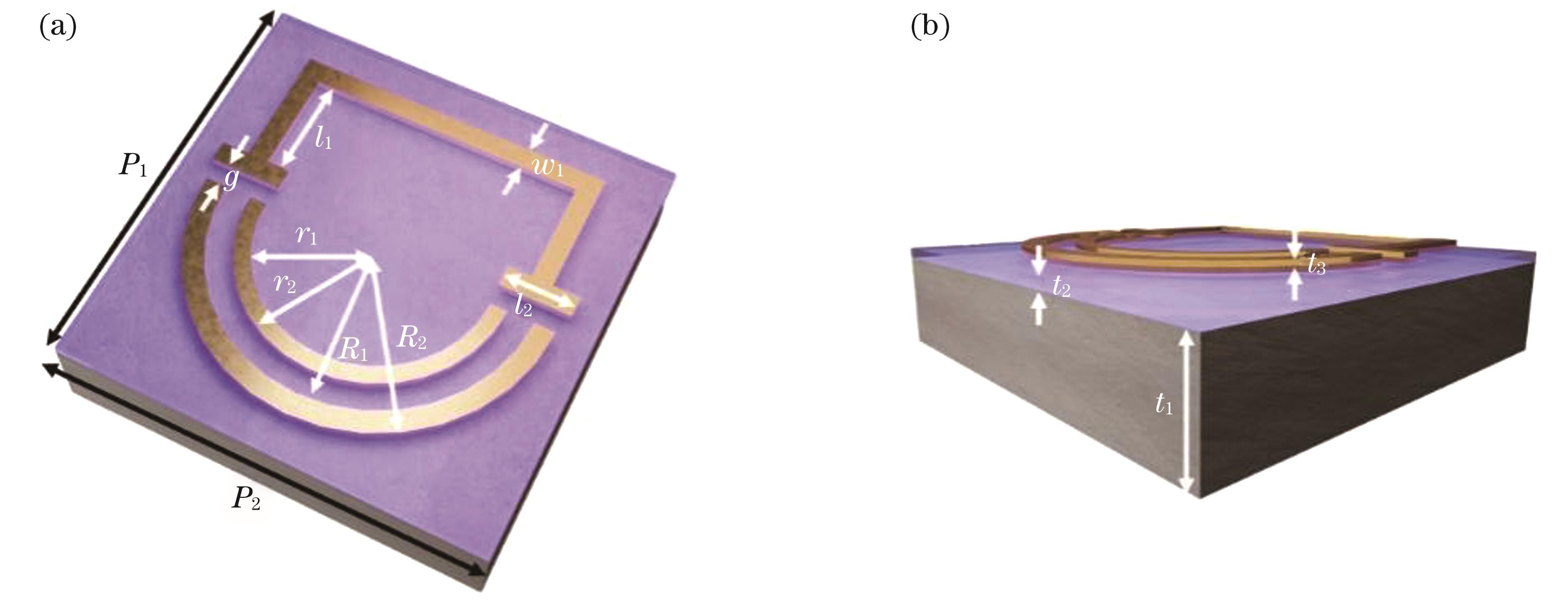
Fig. 1. Schematic of sensor structure

Fig. 2. Sensor samples and spectra. (a) Microscopic image of the sensor at 500×; (b) measured spectrum
Fig. 3. HCR amplification process at the surface of the sensor. (a) Adding AuNP+H0 to the surface of the sensor; (b) adding miRNA-92a; (c) adding hybrid chain H1; (d) adding hybrid chain H2 based on Fig.3(c)
Fig. 4. Spectral comparison between bare sensor and sensor modified with AuNP+H0
Fig. 5. Comparison of detection with and without HCR amplification.(a) Direct detection; (b) miRNA-92a detection using HCR amplification
Fig. 6. Sensor sensitivity analysis. (a) Comparison of frequency shifts caused by miRNA-92a with different concentrations;
Fig. 7. Detection of miRNA-21. (a) Direct detection; (b) detection of miRNA-21 using HCR amplification
Fig. 8. Detection of miRNA339-3p. (a) Direct detection; (b) detection of miRNA339-3p using HCR amplification
Fig. 9. Comparison of linear fitting between concentration and frequency shift. (a) Comparison of frequency shifts caused by miRNA-21 with different concentrations; (b) comparison of frequency shifts caused by miRNA339-3p with different concentrations
Fig. 10. Sensitivity comparison of sensors for detecting different miRNAs
|
Table 1. miRNA and DNA chains involved in this work

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



