Dingxi XUE, Bingyao YI, Guojun LI, Shuai MA, Keqin LIU. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Stress in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Functional Gradient Anode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1189
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Inorganic Materials
- Vol. 39, Issue 11, 1189 (2024)
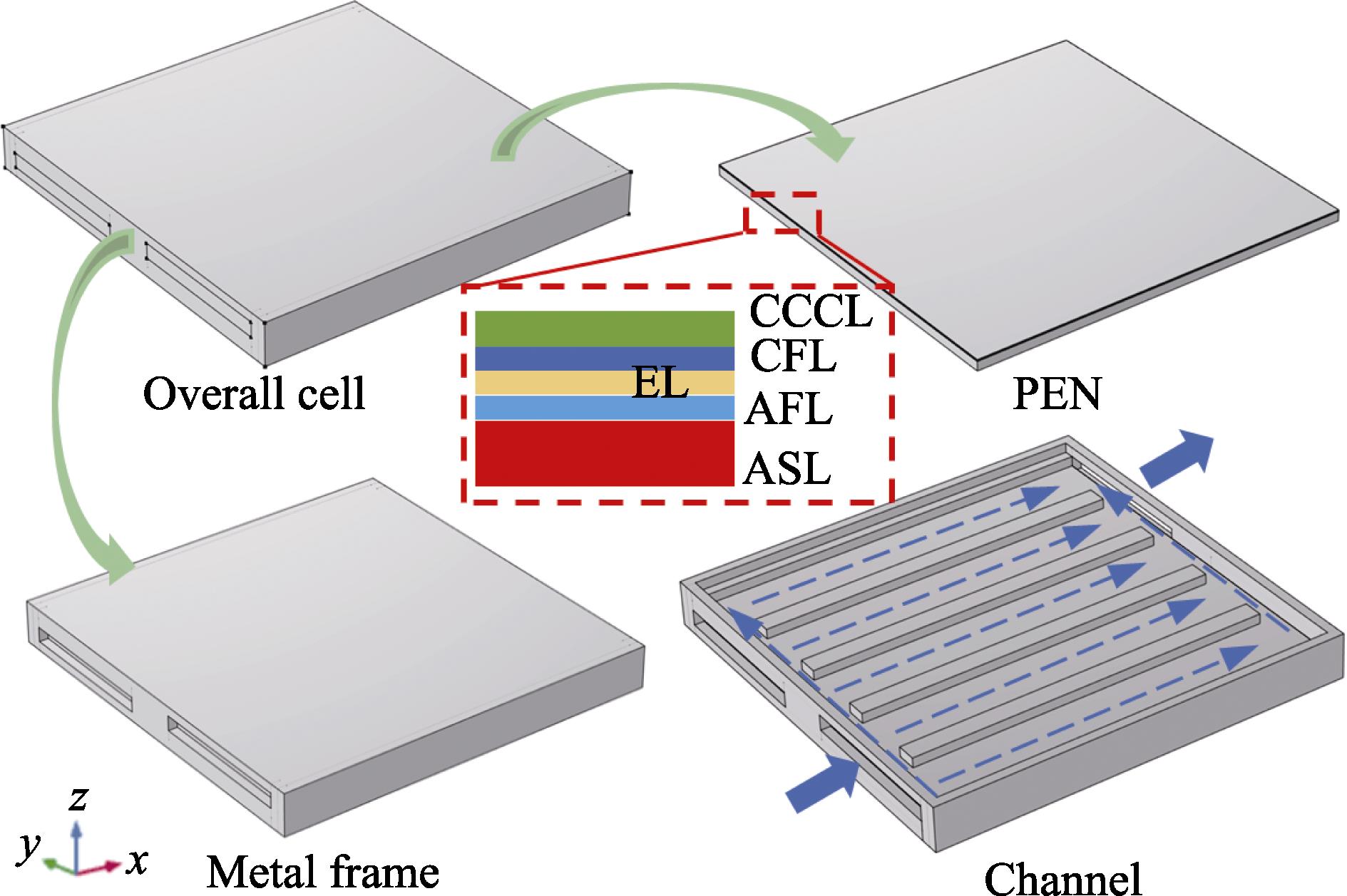
1. Geometric model of the fuel cell
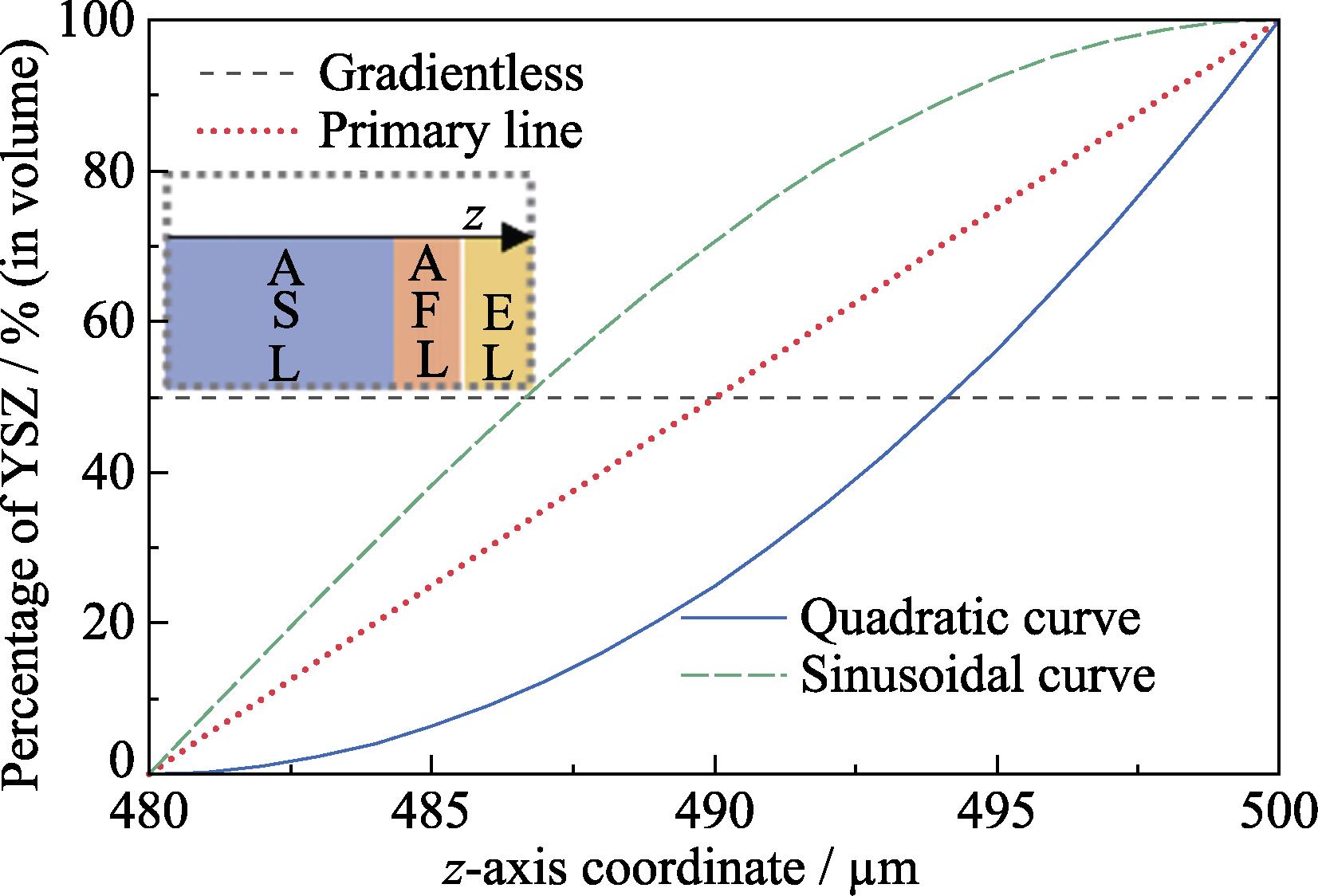
2. Distribution functions of functional gradient materials in anode
3. Effect of Ni volume fraction on TPB density
4. Distribution of residual stress in electrolyte based on model
5. Polarization curves of simulation and experiment[20]
6. Schematic of SOFC sintering process
7. First principal stresses of anode in different preparation processes
8. Maximum residual stresses in (a) anode, (b) cathode and (c) electrolyte
9. Temperature distribution of the cell during operation
10. Stress distribution in the metal frame of the cell during operation
11. First principal stress at the anode interface along y axis
12. Maximum residual stresses in SOFC under different gradient conditions
|
Table 1. Geometric parameters of the model
|
Table 2. Material parameters of the model[10, 13-17]

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



