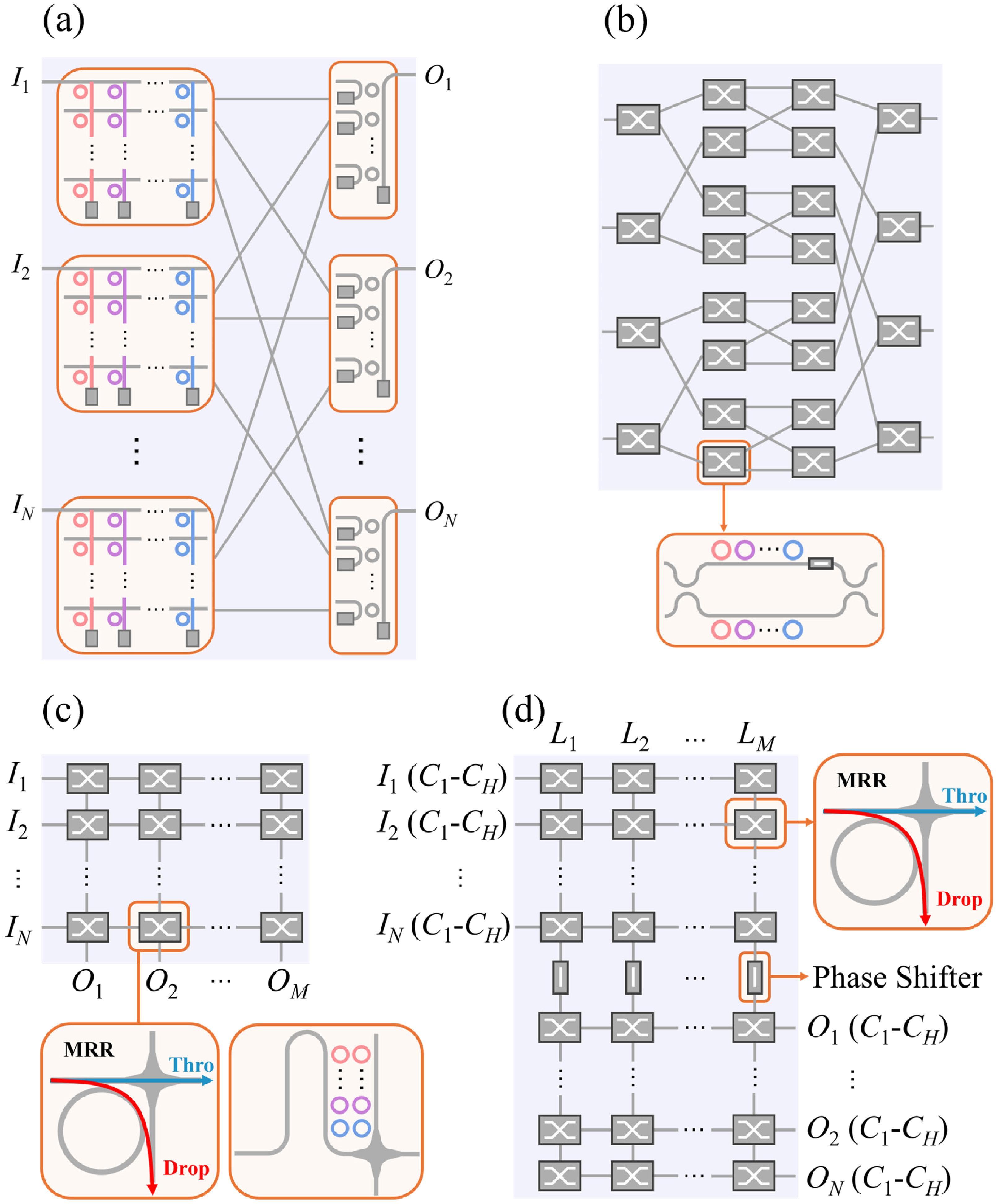
Ziyao Zhang, Minjia Chen, Rui Ma, Bohao Sun, Adrian Wonfor, Richard Penty, Qixiang Cheng, "Dilated space-and-wavelength selective crosspoint optical switch," Photonics Res. 13, 924 (2025)
Search by keywords or author
- Photonics Research
- Vol. 13, Issue 4, 924 (2025)
Abstract
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



