Ying Zhang, Hongzhi Du, Yunbo Hu, Yanbiao Sun, Jigui Zhu. Multi‑Instance Point Cloud Pose Estimation Method Based on Gaussian‐Weighted Voting Strategy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2025, 45(5): 0515001
Search by keywords or author
- Acta Optica Sinica
- Vol. 45, Issue 5, 0515001 (2025)
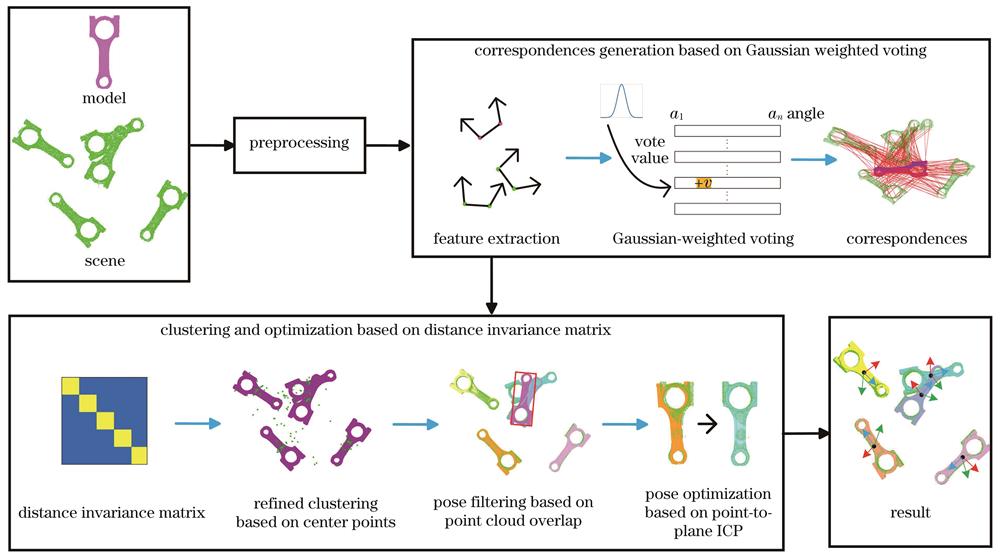
Fig. 1. Algorithmic framework

Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of point-to-point features
Fig. 3. Hash indicates intent
Fig. 4. Coordinate transformations between model and scene
Fig. 5. Correspondences generation based on Gaussian-weighted voting
Fig. 6. Schematic diagram of distance invariance matrix.
Fig. 7. Schematic diagram of refined clustering based on center point
Fig. 8. Romain dataset
Fig. 9. Partial pose estimation results of Romain dataset
Fig. 10. ROBI dataset
Fig. 11. Partial pose estimation results of ROBI dataset
Fig. 12. Experimental scenario. (a) Robotic arm sorting system; (b) before sorting; (c) after sorting
Fig. 13. Partial recognition results of connecting rod workpieces in real scenarios
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Accuracy comparison results of the best pose estimation of workpiece
|
Table 2. Pose estimation evaluation results of Romain dataset
|
Table 3. Pose estimation evaluation results of ROBI dataset
|
Table 4. Evaluation results of pose estimation of proposed algorithm under real point cloud dataset
|
Table 5. Success rate of robotic arm grasping in real scenes

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



