Wanwan Cao, Junwei Zhang, Junyan Dai, Lijie Wu, Hanqing Yang, Zhen Zhang, Huidong Li, Qiang Cheng, "An efficient design method of dual-polarized reconfigurable intelligent surface," Chin. Opt. Lett. 23, 023603 (2025)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 23, Issue 2, 023603 (2025)
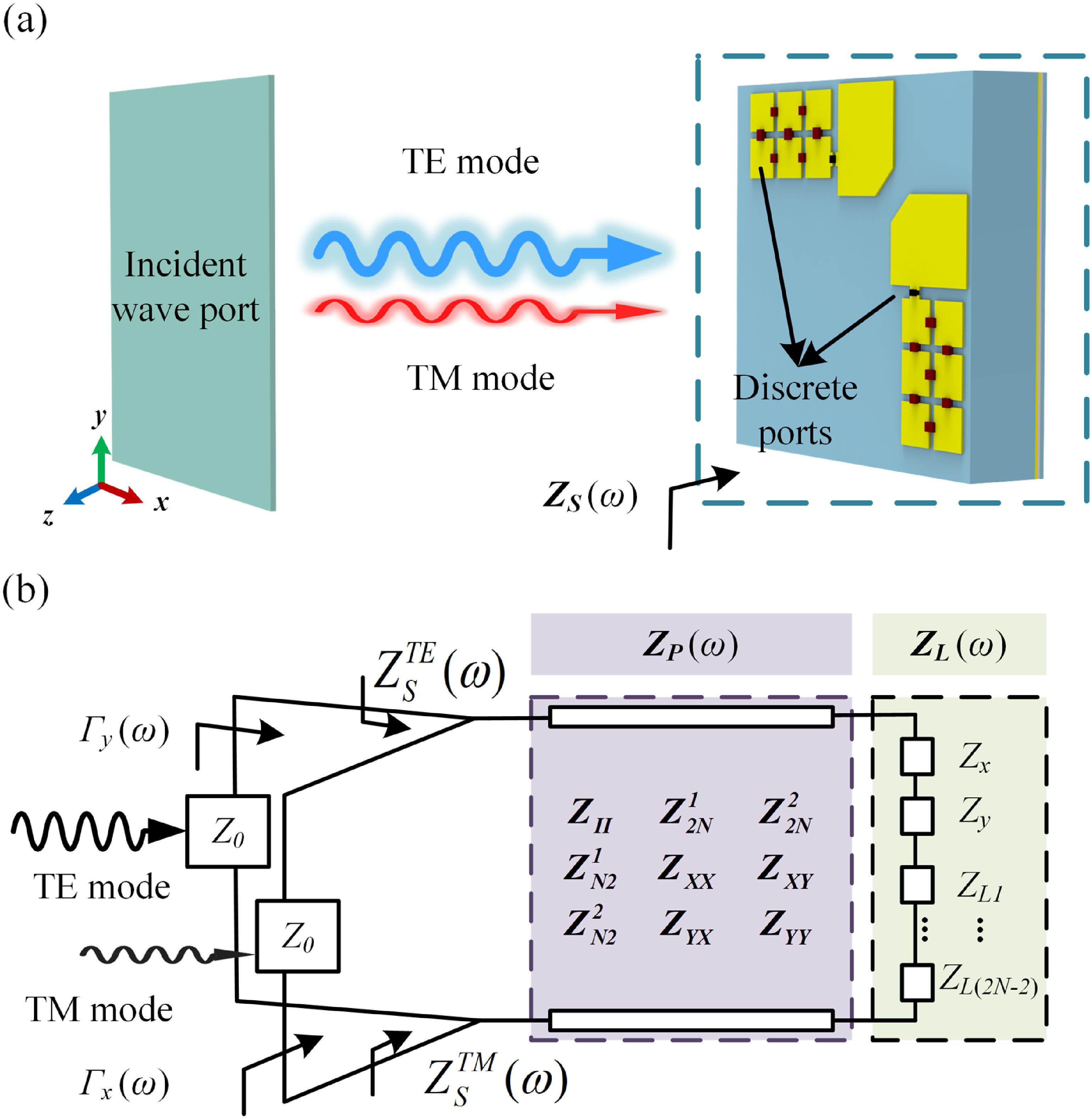
Fig. 1. Modeling of a dual-polarized RIS element with multiport. (a) Schematic of the multiport dual-polarized RIS element. (b) Equivalent network model of dual-polarized RIS element with (2N + 2) ports.

Fig. 2. Flowchart of the proposed design method of the dual-polarized RIS.
Fig. 3. Designed dual-polarized RIS. (a) 3D view of the dual-polarized 1-bit dual-polarized RIS element. (b) Top and elevation views. (c) Photograph of the fabricated dual-polarized RIS sample. (d) Equivalent RLC models for Schottky diode and simple circuits.
Fig. 4. Simulated, calculated, and experimental reflection EM responses in the x- and y-polarization directions, respectively. (a) Amplitude responses in the x-polarization directions. (b) Phase responses in the x-polarization directions. (c) Amplitude responses in the y-polarization directions. (d) Phase responses in the y-polarization directions.
Fig. 5. The far-field scattering patterns of the 1-bit dual-polarized RIS obtained by the proposed method, the EM simulation, and the measurement under vertical incidence with coding sequences “0110011001” in the x- and y-polarization, respectively.
|
Table 1. Time Cost of Designing a 1-bit Dual-Polarized RIS Element Using Two Methods

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



