Kai Huang, Junqiao Zhao, Tiantian Feng. Local Geometric Information Representation and Uncertainty Analysis in LiDAR SLAM[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2025, 52(6): 0600003
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Journal of Lasers
- Vol. 52, Issue 6, 0600003 (2025)
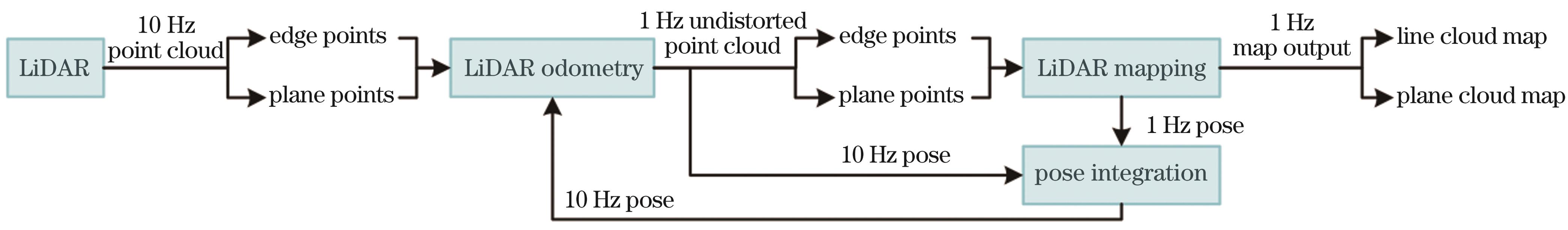
Fig. 1. Illustration of the LOAM framework

Fig. 2. Illustration of the LIO framework
Fig. 3. Recent studies based on FAST-LIO2
Fig. 4. Characterization of local geometric information of single-frame point clouds in some mainstream LiDAR SLAM systems
Fig. 5. Characterization of local geometric information of map in some mainstream LiDAR SLAM systems
Fig. 6. Structure of the map data in some mainstream LiDAR SLAM systems
Fig. 7. Illustration of the point uncertainty model
Fig. 8. Uncertainty models of point cloud in some mainstream LiDAR SLAM systems
Fig. 9. Illustration of single-frame point cloud on NTU VIRAL sequence spms_03. The points are colored according to their uncertainty
Fig. 10. Mapping comparison between LOG-LIO2 and FAST-LIO2 based on localization results in the M2DGR sequence street_07 at the same point cloud resolution
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Comparison of different LiDAR SLAM algorithms for experiments
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2. Details of the M2DGR, NTU VIRAL, and Newer College datasets
|
Table 3. Experimental results on NTU VIRAL dataset: RMSE at specified map resolutions for each algorithm
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Experimental results on M2DGR and Newer College datasets: RMSE at specified map resolutions for each algorithm
|
Table 5. Experimental results on NTU VIRAL dataset: average running time at specified map resolutions for each algorithm
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 6. Experimental results on M2DGR and Newer College datasets: RMSE at specified map resolutions for each algorithm

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



