Search by keywords or author
Journals >Chinese Optics Letters
Export citation format
Research Articles
Atmospheric, Oceanic, Space, and Environmental Optics
Single-photon laser methane detection methodology and initial validation
Shouzheng Zhu, Shijie Liu, Guoliang Tang, Xin He... and Jianyu Wang|Show fewer author(s)
Responding to the urgency of remote sensing for monitoring large concentrations of methane leakage, a high-speed modulation continuous laser methane leakage remote methodology based on a near-infrared single-photon avalanche diode detector (SPAD) and a lower power distributed feedback laser was developed. Based on the proposed laser modulation and time-correlated single-photon counting method, the method could simultaneously detect the methane concentration and background target distance. The effects of SPAD dead time and after-pulse probability on the intensity of methane spectra were investigated. The proposed ranging and methane sensing method was also demonstrated by conducting outfield observation through the verification system. The measured methane absorption spectral intensity was verified and consistent with theoretical value. The initial validation results provide a new scheme for subsequent single-photon gas detection, and reference for subsequent methane monitoring equipment development.Responding to the urgency of remote sensing for monitoring large concentrations of methane leakage, a high-speed modulation continuous laser methane leakage remote methodology based on a near-infrared single-photon avalanche diode detector (SPAD) and a lower power distributed feedback laser was developed. Based on the proposed laser modulation and time-correlated single-photon counting method, the method could simultaneously detect the methane concentration and background target distance. The effects of SPAD dead time and after-pulse probability on the intensity of methane spectra were investigated. The proposed ranging and methane sensing method was also demonstrated by conducting outfield observation through the verification system. The measured methane absorption spectral intensity was verified and consistent with theoretical value. The initial validation results provide a new scheme for subsequent single-photon gas detection, and reference for subsequent methane monitoring equipment development..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 14, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 100101 (2024)
Fiber Optics and Optical Communications
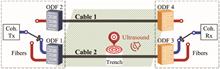
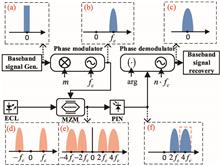
Ultrasonic phase extraction method for co-cable identification in coherent optical transmission systems
Hao Zhou, Wen Zuo, Yaojun Qiao, Yan Zhao... and Hengying Xu|Show fewer author(s)
An ultrasonic phase extraction method is proposed for co-cable identification without modifying transceivers in coherent optical transmission systems. To extract the ultrasonic phase, we apply an improved residual frequency offset compensation algorithm, an optimized unwrapping algorithm for mitigating phase noise induced by phase ambiguity between digital signal processing (DSP) blocks, and an averaging operation for improving the phase sensitivity. In a 64-GBaud dual-polarization quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) simulation system, the phase sensitivity of the proposed method reaches 0.03 rad using lasers with 100-kHz linewidth and a 60-kHz ultrasonic source, with only 400 k-points (kpts) stored data. Also verified by an experiment under the same transmission conditions, the sensitivity reaches 0.39 rad, with 3 kpts of data stored and no averaging due to the equipment limitation. The results have shown this method provides a better choice for low-cost and real-time co-cable identification in integrated sensing and communication optical networks.An ultrasonic phase extraction method is proposed for co-cable identification without modifying transceivers in coherent optical transmission systems. To extract the ultrasonic phase, we apply an improved residual frequency offset compensation algorithm, an optimized unwrapping algorithm for mitigating phase noise induced by phase ambiguity between digital signal processing (DSP) blocks, and an averaging operation for improving the phase sensitivity. In a 64-GBaud dual-polarization quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) simulation system, the phase sensitivity of the proposed method reaches 0.03 rad using lasers with 100-kHz linewidth and a 60-kHz ultrasonic source, with only 400 k-points (kpts) stored data. Also verified by an experiment under the same transmission conditions, the sensitivity reaches 0.39 rad, with 3 kpts of data stored and no averaging due to the equipment limitation. The results have shown this method provides a better choice for low-cost and real-time co-cable identification in integrated sensing and communication optical networks..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Sep. 26, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 100601 (2024)
Temperature insensitivity of an all-fiber quarter-wave plate device fabricated with a high-birefringence fiber
Beibei Xing, Jianxiang Wen, Sha Li, Yu Wen... and Tingyun Wang|Show fewer author(s)
A high-birefringence fiber, Tb:YAG crystal-derived silica fiber (TYDSF), was fabricated by CO2 laser-heating drawing technique. Its linear birefringence was 2.99 × 10-5, and it was used to fabricate an all-fiber quarter-wave plate (QWP) device. The polarization extinction ratio (PER) of the device was 0.29 dB, and its ellipticity was 44.26° at 25°C. In the temperature range of -5°C to 200°C, its PER was always less than 0.80 dB, and the fluctuation of PER and ellipticity was also small. Compared with QWPs fabricated with PANDA-type polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF) and elliptical-core PMF, the performance of TYDSF QWP was least sensitive to temperature. Furthermore, the TYDSF QWP was used in a high-power laser system, still maintaining good circular polarization state, and the nonlinear effects were suppressed in the system. The experimental results are of great significance to high-power lasers, fiber-optic current sensors, etc., in harsh environments.A high-birefringence fiber, Tb:YAG crystal-derived silica fiber (TYDSF), was fabricated by CO2 laser-heating drawing technique. Its linear birefringence was 2.99 × 10-5, and it was used to fabricate an all-fiber quarter-wave plate (QWP) device. The polarization extinction ratio (PER) of the device was 0.29 dB, and its ellipticity was 44.26° at 25°C. In the temperature range of -5°C to 200°C, its PER was always less than 0.80 dB, and the fluctuation of PER and ellipticity was also small. Compared with QWPs fabricated with PANDA-type polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF) and elliptical-core PMF, the performance of TYDSF QWP was least sensitive to temperature. Furthermore, the TYDSF QWP was used in a high-power laser system, still maintaining good circular polarization state, and the nonlinear effects were suppressed in the system. The experimental results are of great significance to high-power lasers, fiber-optic current sensors, etc., in harsh environments..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 100602 (2024)
Photonic frequency-multiplied 4096-QAM vector millimeter-wave signal generation using CE-DSM
Acai Tan, Yanyi Wang, Siyu Luo, Zhengxuan Li... and Jianjun Yu|Show fewer author(s)
We propose a photonic frequency-multiplied vector millimeter-wave (mmW) signal generation scheme based on constant-envelope delta-sigma modulation (CE-DSM). The CE characteristic of phase modulation can easily avoid intensity-dependent nonlinear distortion caused by photonic frequency multiplication. Additionally, combined with one-bit DSM, the in-band signal-to-noise ratio can be dramatically improved, enabling high-order quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) vector mmW signal generation with high spectral efficiency. Experimental results indicate that a 40 GHz four-fold frequency-multiplied 4096-QAM vector mmW signal generation system is successfully accomplished with 15-km standard single-mode fiber (SSMF) and 1-m wireless transmission, and the bit error ratio (BER) reaches the threshold of 3.8 × 10-3.We propose a photonic frequency-multiplied vector millimeter-wave (mmW) signal generation scheme based on constant-envelope delta-sigma modulation (CE-DSM). The CE characteristic of phase modulation can easily avoid intensity-dependent nonlinear distortion caused by photonic frequency multiplication. Additionally, combined with one-bit DSM, the in-band signal-to-noise ratio can be dramatically improved, enabling high-order quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) vector mmW signal generation with high spectral efficiency. Experimental results indicate that a 40 GHz four-fold frequency-multiplied 4096-QAM vector mmW signal generation system is successfully accomplished with 15-km standard single-mode fiber (SSMF) and 1-m wireless transmission, and the bit error ratio (BER) reaches the threshold of 3.8 × 10-3..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 10, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 100603 (2024)
Temperature-insensitive and high-precision frequency transfer based on fabricated in-house 1.05 km hollow-core anti-resonant fiber
Yundong Hao, Zefeng Li, Sensen Meng, Bo Liu... and Yange Liu|Show fewer author(s)
We have prepared kilometer-scale low-loss hollow-core nested anti-resonant nodeless fibers by improving their structural design, which reduces the difficulty of fabricating low-loss hollow-core fibers over long distances. The lowest loss is 2.7 dB/km at 1506 nm, and this loss is less than 5 dB/km at 1417–1620 nm. High-precision frequency transfer is achieved using the fabricated 1050 m hollow-core fiber by locking the repetition frequency of the optical frequency comb to a rubidium atomic clock. The frequency stability is 1.67 × 10-12/s and 5.66 × 10-14/1000 s when the temperature is changed, and no phase compensation device is used. It is an order of magnitude lower compared to that of the conventional single-mode fiber.We have prepared kilometer-scale low-loss hollow-core nested anti-resonant nodeless fibers by improving their structural design, which reduces the difficulty of fabricating low-loss hollow-core fibers over long distances. The lowest loss is 2.7 dB/km at 1506 nm, and this loss is less than 5 dB/km at 1417–1620 nm. High-precision frequency transfer is achieved using the fabricated 1050 m hollow-core fiber by locking the repetition frequency of the optical frequency comb to a rubidium atomic clock. The frequency stability is 1.67 × 10-12/s and 5.66 × 10-14/1000 s when the temperature is changed, and no phase compensation device is used. It is an order of magnitude lower compared to that of the conventional single-mode fiber..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 14, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 100604 (2024)
Imaging Systems and Image Processing
Single-pixel imaging of a moving object with multi-motion
Pengcheng Ji, Qingfan Wu, Shengfu Cao, Huijuan Zhang... and Yuanjin Yu|Show fewer author(s)
Motion blur restoration is essential for the imaging of moving objects, especially for single-pixel imaging (SPI), which requires multiple measurements. To reconstruct the image of a moving object with multiple motion modes, we propose a novel motion blur restoration method of SPI using geometric moment patterns. We design a novel localization method that uses normalized differential first-order moments and central moment patterns to determine the object’s translational position and rotation angle information. Then, we perform motion compensation by using shifting Hadamard patterns. Our method effectively improves the detection accuracy of multiple motion modes and enhances the quality of the reconstructed image. We perform simulations and experiments, and the results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.Motion blur restoration is essential for the imaging of moving objects, especially for single-pixel imaging (SPI), which requires multiple measurements. To reconstruct the image of a moving object with multiple motion modes, we propose a novel motion blur restoration method of SPI using geometric moment patterns. We design a novel localization method that uses normalized differential first-order moments and central moment patterns to determine the object’s translational position and rotation angle information. Then, we perform motion compensation by using shifting Hadamard patterns. Our method effectively improves the detection accuracy of multiple motion modes and enhances the quality of the reconstructed image. We perform simulations and experiments, and the results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 14, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101101 (2024)
Infrared and Terahertz Photonics
Terahertz chiral edge states enable inner-chip state transition and interchip communications over wireless terminals
Hong Chen, Hang Ren, Wenya Wang, Zhaohua Xu... and Su Xu|Show fewer author(s)
Topological valley photonics has recently gained widespread interest owing to its robustness and backscattering immunity against disorders. Previous topological valley transport based on kink states required an interface between two topologically distinct domains, while recent studies have reported that chiral edge states (CESs) can be realized at the external boundary of topological insulators by changing the on-site edge potentials. However, current research on CESs is predominantly focused on the microwave frequency range, leaving challenges for emerging terahertz communications. Here, cladding-free CESs are demonstrated at the external boundary of terahertz all-silicon topological valley photonic crystals with gapless, single-mode, and linear dispersion. We show that CESs are immune to backscattering against sharp corners and support unidirectional propagation of chiral excitations. We also achieved smooth transition between kink states and CESs supported by an all-silicon platform, which could be used as the terahertz inner-chip connection. Finally, a terahertz wireless link between two disconnected CESs is verified for the near-field information interconnection between distinct mobile phones. Our work indicates CESs can improve the compactness of terahertz circuits and inspire advanced terahertz interchip communications.Topological valley photonics has recently gained widespread interest owing to its robustness and backscattering immunity against disorders. Previous topological valley transport based on kink states required an interface between two topologically distinct domains, while recent studies have reported that chiral edge states (CESs) can be realized at the external boundary of topological insulators by changing the on-site edge potentials. However, current research on CESs is predominantly focused on the microwave frequency range, leaving challenges for emerging terahertz communications. Here, cladding-free CESs are demonstrated at the external boundary of terahertz all-silicon topological valley photonic crystals with gapless, single-mode, and linear dispersion. We show that CESs are immune to backscattering against sharp corners and support unidirectional propagation of chiral excitations. We also achieved smooth transition between kink states and CESs supported by an all-silicon platform, which could be used as the terahertz inner-chip connection. Finally, a terahertz wireless link between two disconnected CESs is verified for the near-field information interconnection between distinct mobile phones. Our work indicates CESs can improve the compactness of terahertz circuits and inspire advanced terahertz interchip communications..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 15, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 103701 (2024)
Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing
High-sensitivity closed-loop three-axis atomic magnetometer using two elliptically polarized laser beams
Yeguang Yan, Jixi Lu, Kun Wang, Fei Lu... and Binquan Zhou|Show fewer author(s)
The high-sensitivity three-axis detection of magnetic fields is widely used in various applications. Our study demonstrates an atomic magnetometer detecting vector magnetic field, of which the core components are one glass cell and two elliptically polarized laser beams. The light-intensity noise is suppressed by differential detection technology, so a higher sensitivity is obtained compared with our previous work. The three-axis average sensitivities of the atomic magnetometer simultaneously reached 14 fT/Hz1/2 along the x axis, 11 fT/Hz1/2 along the y axis, and 25 fT/Hz1/2 along the z axis. Furthermore, the atomic magnetometer’s dynamic range was further improved to 150 nT, and its bandwidth was increased to over 200 Hz using a closed-loop control system. The proposed three-axis atomic magnetometer with a large dynamic range and a wide bandwidth holds great promise for biomagnetic measurement in a more challenging environment.The high-sensitivity three-axis detection of magnetic fields is widely used in various applications. Our study demonstrates an atomic magnetometer detecting vector magnetic field, of which the core components are one glass cell and two elliptically polarized laser beams. The light-intensity noise is suppressed by differential detection technology, so a higher sensitivity is obtained compared with our previous work. The three-axis average sensitivities of the atomic magnetometer simultaneously reached 14 fT/Hz1/2 along the x axis, 11 fT/Hz1/2 along the y axis, and 25 fT/Hz1/2 along the z axis. Furthermore, the atomic magnetometer’s dynamic range was further improved to 150 nT, and its bandwidth was increased to over 200 Hz using a closed-loop control system. The proposed three-axis atomic magnetometer with a large dynamic range and a wide bandwidth holds great promise for biomagnetic measurement in a more challenging environment..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101201 (2024)
Simultaneous detection of position and temperature of micromagnet using a quantum microscope | Editors' Pick
Zhenrong Shi, Zhonghao Li, Huanfei Wen, Hao Guo... and Jun Liu|Show fewer author(s)
Micromagnets, as a promising technology for microscale manipulation and detection, have been the subject of extensive study. However, providing real-time, noninvasive feedback on the position and temperature of micromagnets in complex operational environments continues to pose a significant challenge. This paper presents a quantum imaging device utilizing diamond nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers capable of providing simultaneous feedback on both the position and temperature of a micromagnet. The device achieves a temporal resolution of 2 s and a spatial resolution of 1.3 µm. Through flux localization analysis, we have determined a positioning accuracy within 50 µm and a temperature accuracy within 0.4 K.Micromagnets, as a promising technology for microscale manipulation and detection, have been the subject of extensive study. However, providing real-time, noninvasive feedback on the position and temperature of micromagnets in complex operational environments continues to pose a significant challenge. This paper presents a quantum imaging device utilizing diamond nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers capable of providing simultaneous feedback on both the position and temperature of a micromagnet. The device achieves a temporal resolution of 2 s and a spatial resolution of 1.3 µm. Through flux localization analysis, we have determined a positioning accuracy within 50 µm and a temperature accuracy within 0.4 K..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Jul. 05, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101202 (2024)
Differential photoacoustic cell-based Fourier transform photoacoustic spectroscopy for background-free gas detection [Invited] | On the Cover
Xiaoli Liu, Jiajia Cui, Chaofan Feng, Qingyuan Tian... and Lei Dong|Show fewer author(s)
A broadband gas sensing technology is reported. The measurement principle relies on Fourier transform photoacoustic spectroscopy (FT-PAS) using a differential photoacoustic cell, in which both phase modulation and amplitude modulation are simultaneously applied to the broadband light sources. The thermal light source and supercontinuum source are employed sequentially. The performance of the FT-PAS is demonstrated by measuring the spectra of methane in the 2–10 µm range and acetylene in the 1–2 µm range. By leveraging the wavelength-independent nature of the photoacoustic effect, this system holds promise for comprehensive full-spectrum spectral detection.A broadband gas sensing technology is reported. The measurement principle relies on Fourier transform photoacoustic spectroscopy (FT-PAS) using a differential photoacoustic cell, in which both phase modulation and amplitude modulation are simultaneously applied to the broadband light sources. The thermal light source and supercontinuum source are employed sequentially. The performance of the FT-PAS is demonstrated by measuring the spectra of methane in the 2–10 µm range and acetylene in the 1–2 µm range. By leveraging the wavelength-independent nature of the photoacoustic effect, this system holds promise for comprehensive full-spectrum spectral detection..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 12, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101203 (2024)
Integrated Optics
Enhanced efficiency of high-speed Si and Si-based PbSe MSM photodiodes with integrated photon-trapping holes at 800–1550 nm wavelengths
Lixin Liu, Jun Gou, Chunyu Li, Jiayue Han... and Jun Wang|Show fewer author(s)
We theoretically and experimentally demonstrate a cylinder-shaped hole array with a small depth and an appropriate period integrated on a silicon-on-insulator substrate can enhance infrared absorption due to more bending of light and a higher back reflection. The Si metal-semiconductor-metal (MSM) photodiode with an hole array, whose depth is 250 nm, exhibits a 4-fold improved external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 81%, and an ultra-fast impulse response speed of 22 ps enabling a 3 dB bandwidth of up to 23.9 GHz. PbSe film with a thickness of 80 nm is integrated to broaden the response wavelength. A more than 500% EQE enhancement of the Si-based PbSe photodiode with 150-nm-deep photon-trapping holes is achieved at 1550 nm compared to the device without hole structures.We theoretically and experimentally demonstrate a cylinder-shaped hole array with a small depth and an appropriate period integrated on a silicon-on-insulator substrate can enhance infrared absorption due to more bending of light and a higher back reflection. The Si metal-semiconductor-metal (MSM) photodiode with an hole array, whose depth is 250 nm, exhibits a 4-fold improved external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 81%, and an ultra-fast impulse response speed of 22 ps enabling a 3 dB bandwidth of up to 23.9 GHz. PbSe film with a thickness of 80 nm is integrated to broaden the response wavelength. A more than 500% EQE enhancement of the Si-based PbSe photodiode with 150-nm-deep photon-trapping holes is achieved at 1550 nm compared to the device without hole structures..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 15, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101301 (2024)
Miniature laser frequency stabilization module for cold atom sensing
Qingzhe Gou, Ning Wei, Haixu Tao, Kang Cheng... and Jun Wang|Show fewer author(s)
In this study, a miniature laser frequency stabilization module for cold atom sensing applications was designed and realized. The module can lock the laser frequency to the saturated absorption spectrum of the D2 line of rubidium (Rb) atoms using the frequency modulation spectroscopy method. The module core is a tiny Rb cell, co-packaged with the saturation absorption optical setup, temperature control circuit, and detection circuit through a joint optical-mechanical-electrical design for a total volume of only 40 mm × 15 mm × 30 mm. The frequency fluctuation of the 780 nm laser after frequency stabilization by the module was within 1 MHz over 1000 s, which is adequate for magneto-optical trap experiments. The results verify the feasibility of the module as a frequency reference and provide a light source for portable cold atom sensing devices.In this study, a miniature laser frequency stabilization module for cold atom sensing applications was designed and realized. The module can lock the laser frequency to the saturated absorption spectrum of the D2 line of rubidium (Rb) atoms using the frequency modulation spectroscopy method. The module core is a tiny Rb cell, co-packaged with the saturation absorption optical setup, temperature control circuit, and detection circuit through a joint optical-mechanical-electrical design for a total volume of only 40 mm × 15 mm × 30 mm. The frequency fluctuation of the 780 nm laser after frequency stabilization by the module was within 1 MHz over 1000 s, which is adequate for magneto-optical trap experiments. The results verify the feasibility of the module as a frequency reference and provide a light source for portable cold atom sensing devices..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 15, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101302 (2024)
Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics
Multiphonon-assisted acousto-optical Q-switched laser at 1130 nm in Yb:YCOB crystal
Huichen Si, Fei Liang, Dazhi Lu, Haohai Yu... and Yicheng Wu|Show fewer author(s)
In this Letter, we realized the phonon-assisted Q-switched laser operation in Yb:YCOB crystal. Differing from previous laser wavelengths below 1.1 µm, we extended the wavelength to 1130 nm by amplifying multiphonon-assisted electronic transitions. At a repetition rate of 0.1 kHz, the laser output power was 82 mW with a pulse width of 466.1 ns, corresponding to a high peak power of 1.76 kW and a single pulse energy of 0.82 mJ, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the highest pulse energy among all Yb3+-doped crystal lasers at the wavelength beyond 1.1 µm. Such a large pulse energy could be explained by the laser rate-equation theory. These results indicated that the electron-phonon coupling effect not only extends the lasing wavelengths but also enables a fast temporal response to support nanosecond, picosecond, even femtosecond pulse laser operation.In this Letter, we realized the phonon-assisted Q-switched laser operation in Yb:YCOB crystal. Differing from previous laser wavelengths below 1.1 µm, we extended the wavelength to 1130 nm by amplifying multiphonon-assisted electronic transitions. At a repetition rate of 0.1 kHz, the laser output power was 82 mW with a pulse width of 466.1 ns, corresponding to a high peak power of 1.76 kW and a single pulse energy of 0.82 mJ, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the highest pulse energy among all Yb3+-doped crystal lasers at the wavelength beyond 1.1 µm. Such a large pulse energy could be explained by the laser rate-equation theory. These results indicated that the electron-phonon coupling effect not only extends the lasing wavelengths but also enables a fast temporal response to support nanosecond, picosecond, even femtosecond pulse laser operation..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101401 (2024)
Broadband continuously tunable Er:Yb:YAl3(BO3)4 1.5–1.6 μm laser
Yujin Chen, Yanfu Lin, Jianhua Huang, Xinghong Gong, and Yidong Huang
By combining the thermally-induced spectral broadening of Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped crystal and the high ratio of cavity gain to loss, a high-power broadband continuously tunable 1.5-1.6 µm laser was successfully demonstrated in an Er:Yb:YAl3(BO3)4 crystal. End-pumped by a continuous-wave 975.6 nm laser diode, three discrete tunable laser bands at 1483–1488, 1495–1503, and 1521–1612 nm were realized at an incident pump power of 7.7 W. The maximum continuously tunable bandwidth was 91 nm at 1521–1612 nm, and the maximum output power was 474 mW at 1551 nm. The output power was generally higher than 100 mW in the whole tunable range.By combining the thermally-induced spectral broadening of Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped crystal and the high ratio of cavity gain to loss, a high-power broadband continuously tunable 1.5-1.6 µm laser was successfully demonstrated in an Er:Yb:YAl3(BO3)4 crystal. End-pumped by a continuous-wave 975.6 nm laser diode, three discrete tunable laser bands at 1483–1488, 1495–1503, and 1521–1612 nm were realized at an incident pump power of 7.7 W. The maximum continuously tunable bandwidth was 91 nm at 1521–1612 nm, and the maximum output power was 474 mW at 1551 nm. The output power was generally higher than 100 mW in the whole tunable range..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101402 (2024)
Dynamics of different pulse types in a single-/dual-wavelength mode-locked fiber laser
Xueyu Yang, Chenyue Lü, Baole Lu, and Jintao Bai
We explore for the first time the real-time spectra of dissipative soliton (DS) and noise-like pulse (NLP) inter-switching by adjusting the pump power, as well as the dual-pulse collision dynamics for three modes: dual-NLP, NLP-DS, and dual-DS in a single-/dual-wavelength mode-locked fiber laser. Different types of dual-pulses differ in collision duration. During spectral reconstruction, dual-pulses exchange energy twice due to their respective accumulation dynamics. Additionally, collision-induced soliton explosions have chaotic properties, leading to each collision being random. The experimental results advance the study of the dynamics of different pulse types and also contribute to the conduction of in-depth investigations on dual-comb sources.We explore for the first time the real-time spectra of dissipative soliton (DS) and noise-like pulse (NLP) inter-switching by adjusting the pump power, as well as the dual-pulse collision dynamics for three modes: dual-NLP, NLP-DS, and dual-DS in a single-/dual-wavelength mode-locked fiber laser. Different types of dual-pulses differ in collision duration. During spectral reconstruction, dual-pulses exchange energy twice due to their respective accumulation dynamics. Additionally, collision-induced soliton explosions have chaotic properties, leading to each collision being random. The experimental results advance the study of the dynamics of different pulse types and also contribute to the conduction of in-depth investigations on dual-comb sources..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101403 (2024)
Continuous-wave and broadly tunable Cr:ZnSe laser pumped by a short wavelength Tm:YLF bulk laser
Milun Zhang, Changwen Xu, Yidan Wei, Suliao Li... and Dianyuan Fan|Show fewer author(s)
We demonstrate, for the first time and to the best of our knowledge, a continuous-wave and broadly tunable Cr:ZnSe bulk crystal laser pumped by a Tm:YLF bulk laser with 1845 nm and 1887 nm wavelengths. We compare the output characteristics and wavelength-tuning properties of the continuous-wave operation at the two pump wavelengths. In the continuous-wave operation, the maximum output power is 1.79 W with a slope efficiency of 28.8%, which is achieved at the pump wavelength of 1887 nm. In addition, a tuning range of ∼700 nm (696 nm) from 2040 nm to 2736 nm by using a reflective diffraction grating is realized. To the best of our knowledge, this is the widest tuning range realized so far for Cr:ZnSe bulk crystal tuned by gratings.We demonstrate, for the first time and to the best of our knowledge, a continuous-wave and broadly tunable Cr:ZnSe bulk crystal laser pumped by a Tm:YLF bulk laser with 1845 nm and 1887 nm wavelengths. We compare the output characteristics and wavelength-tuning properties of the continuous-wave operation at the two pump wavelengths. In the continuous-wave operation, the maximum output power is 1.79 W with a slope efficiency of 28.8%, which is achieved at the pump wavelength of 1887 nm. In addition, a tuning range of ∼700 nm (696 nm) from 2040 nm to 2736 nm by using a reflective diffraction grating is realized. To the best of our knowledge, this is the widest tuning range realized so far for Cr:ZnSe bulk crystal tuned by gratings..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 11, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 101404 (2024)
Nanophotonics, Metamaterials, and Plasmonics
Metasurface-driven dots projection based on generalized Rayleigh-Sommerfeld diffraction theory
Tianlun Jin, Chenxu Zhu, Yang Qiu, Xingyan Zhao... and Ting Hu|Show fewer author(s)
The diffractive optical element (DOE) is an important component of three-dimensional (3D) imaging systems based on structured light. In this work, we designed the metasurface-driven DOEs based on generalized Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory to project large field of view (FOV) pseudo-random dot array for 3D imaging. We measured an efficiency of 61.04% and root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 0.45 for the 60° FOV sample and an efficiency of 42.96% and RMSE of 0.75 for the 144° FOV sample. Because the pattern is designed based on the generalized Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory, the projected pattern is similar to the target pattern and has even intensity.The diffractive optical element (DOE) is an important component of three-dimensional (3D) imaging systems based on structured light. In this work, we designed the metasurface-driven DOEs based on generalized Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory to project large field of view (FOV) pseudo-random dot array for 3D imaging. We measured an efficiency of 61.04% and root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 0.45 for the 60° FOV sample and an efficiency of 42.96% and RMSE of 0.75 for the 144° FOV sample. Because the pattern is designed based on the generalized Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory, the projected pattern is similar to the target pattern and has even intensity..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 103601 (2024)
Strong light–matter coupling between excitons and chiral quasi-bound states in the continuum in van der Waals metasurfaces
Zhonghong Shi, Houjiao Zhang, and Zhang-Kai Zhou
The study of strong coupling between photonic cavities and excitons has brought about significant advances, varying from fundamental physics to applied science. However, there are several challenges hindering its further development, including obtaining photonic modes with both low room-temperature loss and high electric field (EF) enhancements, the difficulty of precisely transferring exciton materials into the photonic cavity, and the urgent need for additional manipulation approaches. In order to overcome these challenges simultaneously, we present a theoretical strong coupling system based on the chiral metasurfaces that are built by the excitonic van der Waals material of WSe2 and can support the quasi-bound states in the continuum (q-BIC) mode. The q-BIC mode can sustain EF enhancements over 80 times with loss smaller than 10 meV, and the strong coupling between q-BIC mode and WSe2 excitons can be naturally realized without material transferring. Furthermore, a large chirality beyond 0.98 can be obtained in this strong coupling system, making the circular polarization of excitation light an effective parameter to control the generation of coherent states in this metasurface system. Our results can benefit the further development of strong coupling research, shedding light onto the exploration of new quantum devices.The study of strong coupling between photonic cavities and excitons has brought about significant advances, varying from fundamental physics to applied science. However, there are several challenges hindering its further development, including obtaining photonic modes with both low room-temperature loss and high electric field (EF) enhancements, the difficulty of precisely transferring exciton materials into the photonic cavity, and the urgent need for additional manipulation approaches. In order to overcome these challenges simultaneously, we present a theoretical strong coupling system based on the chiral metasurfaces that are built by the excitonic van der Waals material of WSe2 and can support the quasi-bound states in the continuum (q-BIC) mode. The q-BIC mode can sustain EF enhancements over 80 times with loss smaller than 10 meV, and the strong coupling between q-BIC mode and WSe2 excitons can be naturally realized without material transferring. Furthermore, a large chirality beyond 0.98 can be obtained in this strong coupling system, making the circular polarization of excitation light an effective parameter to control the generation of coherent states in this metasurface system. Our results can benefit the further development of strong coupling research, shedding light onto the exploration of new quantum devices..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 103602 (2024)
Optical Design and Fabrication
Two-photon nanolithography of micrometer scale diffractive neural network with cubical diffraction neurons at the visible wavelength | Editors' Pick
Qi Wang, Haoyi Yu, Zihao Huang, Min Gu, and Qiming Zhang
Free-space diffractive neural networks (DNNs) have been an intense research topic in machine learning for image recognition and encryption due to their high speed, lower power consumption, and high neuron density. Recent advances in DNNs have highlighted the need for smaller device footprints and the shift toward visible wavelengths. However, DNNs fabricated by electron beam lithography, are not suitable for microscopic imaging applications due to their large sizes, and DNNs fabricated by two-photon nanolithography with cylindrical neurons are not optimal for visible wavelengths, as the high-order diffraction could induce low diffraction efficiency. In this paper, we demonstrate that cubical diffraction neurons are more efficient diffraction elements for DNNs compared with cylindrical neurons. Based on the theoretical analysis of the relationship between the detector area sizes and classification accuracy, we reduced the size of DNNs operating at the wavelength of 532 nm for handwritten digit classification to micrometer scale by two-photon nanolithography. The DNNs with cubical neurons demonstrated an experimental classification accuracy (89.3%) for single-layer DNN, and 83.3% for two-layer DNN with device sizes similar to that of biological cells (about 100 µm × 100 µm). Our results paved the pathway to integrate 3D micrometer-scale DNNs with microscopic imaging systems for biological imaging and cell recognition.Free-space diffractive neural networks (DNNs) have been an intense research topic in machine learning for image recognition and encryption due to their high speed, lower power consumption, and high neuron density. Recent advances in DNNs have highlighted the need for smaller device footprints and the shift toward visible wavelengths. However, DNNs fabricated by electron beam lithography, are not suitable for microscopic imaging applications due to their large sizes, and DNNs fabricated by two-photon nanolithography with cylindrical neurons are not optimal for visible wavelengths, as the high-order diffraction could induce low diffraction efficiency. In this paper, we demonstrate that cubical diffraction neurons are more efficient diffraction elements for DNNs compared with cylindrical neurons. Based on the theoretical analysis of the relationship between the detector area sizes and classification accuracy, we reduced the size of DNNs operating at the wavelength of 532 nm for handwritten digit classification to micrometer scale by two-photon nanolithography. The DNNs with cubical neurons demonstrated an experimental classification accuracy (89.3%) for single-layer DNN, and 83.3% for two-layer DNN with device sizes similar to that of biological cells (about 100 µm × 100 µm). Our results paved the pathway to integrate 3D micrometer-scale DNNs with microscopic imaging systems for biological imaging and cell recognition..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 102201 (2024)
Spectroscopy
Multiple wavelength frequency stabilization with a single transfer cavity for mercury optical lattice clock
Li Ma, Qixin Liu, Haiyang Song, Jianfang Sun, and Zhen Xu
A simple and robust multiple wavelength frequency stabilization system is demonstrated using a single transfer cavity and a 1062-nm ultra-stable laser for all the lasers used in a mercury optical lattice clock. Offset sideband locking is employed to tune the laser frequency while dichroic mirrors and differentiated modulation frequencies are utilized for the Pound–Drever–Hall locking of four-color lasers. For the most demanding lasers at 1015 nm and 725 nm, the line width of the beat note is reduced to 27 kHz and 17 kHz, respectively. The frequency fluctuation for the transfer-locked 1015-nm laser is less than 10 kHz, which is much better than the lasers locked to an atomic spectrum. Using its high stability of 5 × 10-12 over 100 s, the transfer-locked 1015-nm laser is employed for low-noise frequency modulated saturated absorption spectroscopy. This approach could also be used in various situations for the research of optical clocks, Rydberg atoms, laser cooling of molecules, and quantum computation with neutral atoms.A simple and robust multiple wavelength frequency stabilization system is demonstrated using a single transfer cavity and a 1062-nm ultra-stable laser for all the lasers used in a mercury optical lattice clock. Offset sideband locking is employed to tune the laser frequency while dichroic mirrors and differentiated modulation frequencies are utilized for the Pound–Drever–Hall locking of four-color lasers. For the most demanding lasers at 1015 nm and 725 nm, the line width of the beat note is reduced to 27 kHz and 17 kHz, respectively. The frequency fluctuation for the transfer-locked 1015-nm laser is less than 10 kHz, which is much better than the lasers locked to an atomic spectrum. Using its high stability of 5 × 10-12 over 100 s, the transfer-locked 1015-nm laser is employed for low-noise frequency modulated saturated absorption spectroscopy. This approach could also be used in various situations for the research of optical clocks, Rydberg atoms, laser cooling of molecules, and quantum computation with neutral atoms..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 14, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 103001 (2024)
X-ray Optics
Characterization of single-pulse photon energy and photon energy jitter at the Shanghai soft X-ray Free-Electron Laser
Zichen Gao, Yajun Tong, Yueran Wang, Xinyuan Wang... and Huaidong Jiang|Show fewer author(s)
The X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL), a new X-ray light source, presents numerous opportunities for scientific research. Self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) is one generation mode of XFEL in which each pulse is unique. In this paper, we propose a pinhole diffraction method to accurately determine the XFEL photon energy, pulses’ photon energy jitter, and sample-to-detector distance for soft X-ray. This method was verified at Shanghai soft X-ray Free-Electron Laser (SXFEL). The measured average photon energy was 406.5 eV, with a photon energy jitter (root-mean-square) of 1.39 eV, and the sample-to-detector distance was calculated to be 16.61 cm.The X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL), a new X-ray light source, presents numerous opportunities for scientific research. Self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) is one generation mode of XFEL in which each pulse is unique. In this paper, we propose a pinhole diffraction method to accurately determine the XFEL photon energy, pulses’ photon energy jitter, and sample-to-detector distance for soft X-ray. This method was verified at Shanghai soft X-ray Free-Electron Laser (SXFEL). The measured average photon energy was 406.5 eV, with a photon energy jitter (root-mean-square) of 1.39 eV, and the sample-to-detector distance was calculated to be 16.61 cm..
Chinese Optics Letters
- Publication Date: Oct. 09, 2024
- Vol. 22, Issue 10, 103401 (2024)