Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) is an important component controlling the propagation of light in coastal and open sea areas, and it constitutes the largest organic carbon pool in the ocean, playing a significant role in the global carbon cycle. The laser induced fluorescence (LIF) technique is a well-known analytical method for rapid water environment monitoring. By measuring the emission spectrum of laser-induced seawater, we can quickly and in real-time obtain qualitative and quantitative information about CDOM in the ocean. Previous simulation models for marine LIF detection often ignore the influence of sea breeze and treat the sea surface as an ideal stationary interface. In reality, affected by a sea breeze, the sea surface fluctuates during LIF system operations for marine remote sensing detection. The fluctuating rough sea surface affects the laser and fluorescence, thereby influencing the fluorescence information detected by the receiving system. Therefore, based on the Monte Carlo method and a sea surface simulation model, we construct a simulation model of CDOM fluorescence characteristics under a rough sea surface and use this model to obtain the fluorescence distribution of CDOM received under an ideal stable sea surface and analyze the influence of different wind directions and wind speeds on the fluorescence signal of the rough sea surface.
We use the Monte Carlo method to simulate the transmission of photons through the sea surface in seawater. When the weight of the photon drops below the threshold, we introduce a new photon to continue the simulation. Throughout the simulation process, we record the position, weight, and direction of motion of each photon until it is finally emitted from the sea surface, and we collect and analyze the outgoing fluorescence information. The motion direction of the photon after refraction is determined based on the refraction law and relevant optical theory. We achieve the simulation of a rough sea surface by inverting the Pierson-Moscowitz wave spectrum using a linear superposition method, assuming that the rough sea surface results from the superposition of several triangular waves with varying frequencies, amplitudes, and random phases. We analyze the influence of sea surface fluctuation on CDOM detection by simulating the distribution of CDOM fluorescence under ideal smooth and rough sea surfaces. We then analyze the fluctuation of ocean CDOM fluorescence received under different wind speeds and wind directions. Finally, we validate the reasons for the fluctuations of the received fluorescence signal under the rough sea surface due to changes in the slope of the sea surface through experiments.
The simulation results show that due to the isotropy of fluorescence and the differing transmission distances of outgoing fluorescence at various zenith angles in seawater, the overall fluorescence distribution of received CDOM under an ideal and stable sea surface presents a center-symmetric hemispherical shape (Fig. 1). This indicates that the fluorescence receiving intensity is negatively correlated with the received zenith angle, and is independent of the received azimuth angle. In actual detection, due to sea breeze influences, the sea surface is not ideally stable and fluctuates (Fig. 2). The fluctuating sea surface causes variations in the fluorescence transmission distances along different azimuth angles, leading to an asymmetric fluorescence distribution (Fig. 3). Additionally, the total reflection phenomenon may diminish due to changes in the slope of the sea surface. The fluorescence intensity received at a 90° zenith angle may no longer be zero at certain azimuth angles. The overall fluctuation direction of the sea surface aligns with the wind direction (Fig. 4), with greater wind speeds resulting in larger changes in sea surface height (Fig. 7). As sea surface height and slope change significantly in the downwind and upwind directions, remote sensing detection in these directions will experience stronger fluorescence fluctuations, whereas detection along the vertical wind direction will yield more stable results (Figs. 5 and 6). The stronger the gradient change of the ocean surface with wind speed, the greater the influence on photon refraction, leading to more stable fluorescence signals detected at lower wind speeds. Experimental designs indirectly verify that changes in sea surface slope in different directions affect fluorescence reception intensity.
We establish a fluorescence simulation model of marine CDOM based on the Monte Carlo method, incorporating a rough sea surface generated by the Pierson-Moscowitz wave spectrum. The simulation results reveal how CDOM fluorescence characteristics vary with different wind directions and speeds. Finally, we validate through experiments the changes in fluorescence signals caused by sea surface tilt. The simulation results show that without considering sea breeze influences, the fluorescence signal of marine CDOM is independent of the azimuth angle and inversely proportional to the zenith angle. Therefore, during actual detection, the setting of the receiving zenith angle should not be too large. Compared with a calm sea surface, CDOM fluorescence distribution fluctuates under a rough sea surface, with received fluorescence values fluctuating more sharply downwind or upwind due to the influence of sea surface fluctuations in different wind directions. Wind speed affects the degree of fluorescence fluctuation; as wind speed increases, larger sea surface dip angles occur, leading to greater fluctuations in the received CDOM fluorescence. In remote sensing detection, the fluorescence signal measured by CDOM is relatively more stable in the direction of vertical wind. Choosing a time of lower wind speed also enhances detection stability.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601001 (2025)
Methane (CH4) is the second most important greenhouse gas in the atmosphere after carbon dioxide. Mastering precise methods for monitoring atmospheric CH4 is essential for addressing the greenhouse effect and environmental changes. This helps us better understand and predict climate change and provides policymakers with the data needed to formulate effective emission reduction measures. By accurately monitoring CH4 variations, we can identify major emission sources and assess the effectiveness of mitigation strategies, thus promoting the achievement of global climate goals.
We use ground-based high-resolution Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to collect near-infrared solar absorption spectra. These spectra are then analyzed using a nonlinear least squares fitting algorithm to retrieve the column concentrations of atmospheric CH4 in Hefei from 2018 to 2022. Our algorithm, GFIT, is the standard retrieval method of the Total Carbon Column Observing Network (TCCON), consisting of a forward model and iterative fitting process. The forward model calculates atmospheric absorption spectra through an atmospheric radiative transfer model, combining solar parameters, atmospheric parameters, and instrument line shape parameters to generate solar absorption spectra. The iterative process then compares calculated and measured spectra, adjusting retrieval parameters to achieve the best fit. Next, we process the atmospheric CH4 concentration data monitored by FTIR spectroscopy to determine the annual growth rate of atmospheric CH4 and study its seasonal variations. We then validate the ground-based FTIR CH4 data against the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) satellite data. Finally, by calculating the incremental values of CH4 and carbon monoxide (CO) relative to their background values (
Our study first uses FTIR spectroscopy to investigate the variation characteristics of atmospheric CH4 in Hefei from 2018 to 2022, as shown in Figs. 2, 3, and 4. The results show an annual increase in atmospheric
Atmospheric CH4 column concentrations in Hefei show a slow annual increase, with an approximate growth rate of 0.73%. The atmospheric CH4 column concentrations are lower in spring and winter, and higher in summer and autumn. Monthly averages peak in September and reach their lowest in March, at 1940×10-9 and 1890×10-9, respectively, with a seasonal variation amplitude of 50×10-9. Subsequently, we compare satellite data from the TROPOMI onboard the ESA Sentinel-5P satellite with ground-based FTIR data. The results demonstrate strong consistency between the two datasets, with an average absolute deviation of 5×10-9 and a correlation coefficient of 0.91. Finally, we conducted a correlation analysis between atmospheric CH4 and CO observed in Hefei, calculating the correlations of
- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601002 (2025)
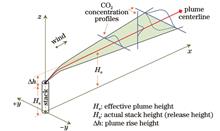
Point source emissions are a significant feature of industrial output, with thermal power plants serving as prominent examples. Globally, CO2 emissions from thermal power plants make up a substantial portion of energy-related emissions. Effective monitoring of these emissions aids in refining top-down carbon estimates worldwide. The portable EM27/SUN spectrometer, known for its mobility and ease of use, provides highly reliable and sensitive measurements and is adaptable across various environments. It has been widely adopted for satellite data validation and greenhouse gas quantification at multiple scales. However, thermal power plants, typically situated in or near urban areas, experience CO2 plume dispersion influenced by local surface features, such as buildings, which can affect EM27/SUN observation accuracy, a factor seldom addressed in previous studies. To overcome this, we focus on Hefei Wanneng Power Plant. Through multiple ground-based observations using the EM27/SUN instrument, we analyze the effect of nearby buildings on plume dispersion and assess how the spatial relationship between the measurement line and plume geometry influences site selection. This approach enables a better understanding of CO2 quantification capabilities and associated uncertainties under varying conditions, providing a foundation for optimizing measurement methods and enhancing accuracy.
To improve CO2 emission estimation accuracy from industrial point sources using the ground-based EM27/SUN, we explore optimized measurement methods. Using the Lagrangian particle dispersion model, we analyze the influence of nearby buildings on plume dispersion and assess the role of geometric positioning between the measurement line and plume in site selection. By synchronizing EM27/SUN data with TCCON observations and implementing a quality control criterion based on solar intensity, we enhance data reliability. The distance from the emission source is divided into three segments to evaluate the influence of building on measurement and examine plume positioning’s influence on CO2 column volume fraction data. Our final analysis provides insights into the limitations of current measurement methods and demonstrates how the optimized measurement method can improve emission estimation accuracy.
We begin with a data preprocessing method, using strict quality controls to minimize anomalies and ensure measurement accuracy. Corrected EM27/SUN data from 2021, benchmarked against TCCON, show significant accuracy improvement, with an R2 of 0.978 and RMSE of 0.271, compared to pre-correction values of 0.85 and 0.412. Using Hefei Wanneng Power Plant as a case study, repeated measurements from 2021?2023 indicate that downwind
Our analysis reveals that nearby buildings and the observation path significantly influence EM27/SUN measurement accuracy. Close to the emission source, CO2 diffusion is limited, making deviations from the plume axis critical. In contrast, far-section measurements face challenges from complex wind patterns shaped by surrounding buildings, resulting in increased variability in
- Publication Date: Mar. 26, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601003 (2025)
High-spectral-resolution LiDAR (HSRL) is essential for precise detection and retrieval of aerosol optical properties, making it a valuable tool in atmospheric aerosol studies. While the HSRL technique has seen rapid advancements in ultraviolet and visible wavelengths 355 nm/532 nm, development in the near-infrared HSRL domain is constrained by the limitations of spectral discriminators. In 2017, the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) has proposed a 780 nm near-infrared micro-pulse HSRL technique using rubidium (Rb) atom absorption lines and 780 nm semiconductor lasers. This approach provides a promising solution to the challenges facing near-infrared HSRL and has become a research focal point worldwide. However, the effect of various Rb absorption cell parameters on detection errors in the 780-nm HSRL system remains unexplored. In this paper, we address this gap by analyzing the influence of Rb cell parameters, system signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and laser frequency stability on detection results, based on the absorption spectrum of rubidium isotope (87Rb). This study offers theoretical guidance for designing 780-nm near-infrared HSRL systems, particularly in optimizing the temperature settings of the Rb cell spectral discriminator.
We employ the Monte Carlo method in this analysis. First, the HSRL error formula is derived, and the absorption spectrum is obtained based on the hyperfine structure of rubidium atoms. An error analysis model for the 780-nm HSRL system is then established. Subsequently, a simulated atmospheric model is developed (Fig. 6), incorporating the U.S. Standard Atmosphere Model for background aerosols, urban aerosols, and dust. Using this model, we evaluate the effects of system detection SNR, Rb cell temperature fluctuations, laser frequency stability, and the omission of Mie scattering signal transmittance Ta (Ta=0) on detection errors. The Monte Carlo method is applied to establish LiDAR equations under the conditions described, enabling backscattering coefficient retrieval based on theoretical derivation. Retrieval errors are then computed to demonstrate the integrated effect. Specifically, the retrieval error of the backscattering coefficient is calculated under the conditions where the Rb cell operates at 70 ℃ with a ±1 ℃ temperature fluctuation and laser output frequency fluctuation within 100 MHz.
HSRL system measurement accuracy is highly sensitive to the SNR, especially at elevated Rb cell temperatures, which can degrade the molecule channel signal. When the Rb cell temperature exceeds 65 ℃, SNR becomes the primary factor affecting measurement results, with retrieval errors reaching up to 20%. In addition, the retrieval error of the backscattering coefficient increases with higher Rb cell temperature due to decreased Rayleigh echo transmittance (Fig. 9). If the Rb cell temperature fluctuation is within ±1 ℃ when the temperature exceeds 65 ℃, the influence on backscattering coefficient retrieval error is relatively minor (Fig. 12). Higher Rb cell temperatures can also help reduce the measurement error from temperature fluctuations. With an Rb cell temperature above 65 ℃ and Mie scattering transmittance Ta set to zero, the backscattering coefficient retrieval error remains below 1%. Moreover, higher Rb cells correlate with reduced retrieval error at higher aerosol concentrations. Finally, fluctuations in laser source frequency significantly influence retrieval results. When frequency fluctuations reach 1 GHz, retrieval errors exceed 10%, even in the absence of other error factors. By contrast, at a 70 ℃ operating temperature with a 100 MHz frequency fluctuation range, the relative retrieval error reduces to 0.1% (Fig. 14).
The operational temperature of the 87Rb absorption cell critically influences HSRL system retrieval accuracy. With an absorption cell length of 63 mm, the recommended temperature range is 65 ℃ to 75 ℃. Within this range, system SNR, laser frequency stability, and Rb cell temperature stability are vital factors influencing detection accuracy. The simulation results demonstrate that when the 87Rb absorption cell is 63 mm in length, operating at 70 ℃ with laser frequency stability within 100 MHz, the comprehensive retrieval deviation of the backscattering coefficient remains below 10% (Fig. 15).
.- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601004 (2025)
Water color is a fundamental parameter for describing the optical properties of water bodies and encapsulates vital information about the aquatic environment. As the most visually direct indicator in marine surveys, water color reflects not only change in the aesthetic quality of water bodies but also plays a key role in environmental impact assessments, especially in sensitive areas. Water color is influenced by light scattering and changes in environmental conditions, closely related to factors such as chlorophyll, suspended particulate matter (SPM), and the absorption and scattering of colored dissolved organic matter. Previous research has mainly relied on the Forel-Ule index (FUI) for measuring water color. However, due to the complexity and variability of China’s coastal waters, the FUI may not capture detailed water color information or accurately represent the environmental conditions of the water body. In contrast, the hue angle (α) in the Commission internationale de l’éclairage (CIE) color system, as a continuous variable, provides a more accurate representation of water color characteristics and helps extract detailed water quality information. Monitoring water color not only provides vital information on global and regional water quality assessments but also plays a crucial role in marine environmental protection and the maintenance of ecological balance.
Based on data collected during research cruises, including Secchi depth (Zsd), mass concentration of suspended particulate matter (SPM), and phytoplankton absorption coefficient (aph), we develop inversion models for Zsd, SPM, aph (443), and aph (670) using the hue angle as the key variable. These models are validated using the leave-one-out cross validation method. Utilizing hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) data collected during the cruise, we perform stepwise regression analysis with SPSS software. The hue angle serves as the dependent variable, while Rrs values at the MODIS’s central spectral bands act as the independent variables. The data are divided so that 2/3 of data are used to calculate the chroma parameter K. Finally, long-term hue angle information for China’s coastal waters is obtained using satellite Rrs data. This study also compares the effectiveness of the hue angle and the FUI in characterizing changes in water color parameters based on cruise-measured data. The results reveal that the hue angle provides a more detailed and continuous representation of variations in water color parameters.
This study uses Rrs data of MODIS and SeaWiFS to obtain long-term hue angle information for China’s coastal waters, utilizing a method that extracts hue angles from multispectral Rrs (Fig. 6). The highest hue angles are recorded near the coast (around 200°), with values decreasing offshore. The Bohai Sea has the highest average hue angle (180°), followed by the Yellow Sea, which also shows the most significant seasonal variation, with offshore values ranging from 70° to 140°. The East China Sea has the lowest average hue angle (60°) and the least seasonal fluctuation. Seasonal patterns are observed, with hue angles decreasing from spring to summer, reaching their lowest in summer, then increasing in autumn and peaking in winter. In certain characteristic sea areas, the hue angle shows strong covariation with water quality parameters like mass concentrations of Chl-a and SPM. In areas with high hue angles, a significant correlation is observed between hue angles and mass concentration of SPM, while in areas with lower hue angles, strong covariation is observed among hue angles, mass concentration of SPM, and mass concentration of Chl-a (Fig. 7). Using in-situ data from the East China Sea, we develop models for several water quality parameters based on hue angles and validate their accuracy using the leave-one-out cross validation method. This approach can be applied to portable high-definition imaging devices, such as smartphones and digital cameras, to capture ocean water color images, extract hue angle information, and obtain water quality data. A comparison of the hue angle (α) and FUI reveals that the discrete nature of FUI leads to the loss of water color information (Fig. 8). In contrast, the continuous nature of the hue angle captures more detailed color data (Figs. 9 and 10).
We applied the CIE-XYZ color system and a hue angle retrieval method based on satellite multispectral remote sensing reflectance. By combining data from the MODIS and SeaWiFS satellites, a long-term dataset of hue angle for China’s coastal waters was obtained. The study reveals that the hue angle exhibits distinct spatiotemporal distribution characteristics. The Bohai Sea has the highest monthly average (180°), followed by the Yellow Sea (100°), both showing significant seasonal variability. In contrast, the East China Sea has a lower monthly average (60°) with minimal seasonal variability. In addition, there is a strong covariation between hue angles and water quality parameters. Based on cruise-measured data, we developed retrieval models for water quality parameters using hue angle. The results demonstrate that the models for transparency (R²=0.79), suspended particulate matter concentration (R²=0.90), phytoplankton absorption coefficient at 443 nm (R²=0.79), and phytoplankton absorption coefficient at 670 nm (R²=0.80) exhibit high goodness of fit and accuracy. Furthermore, we analyzed and discussed the advantages of using hue angle over traditional water color indices for representing water color information in the complex coastal waters of China. The findings suggest that the hue angle provides a more accurate and effective measure of water color, offering superior capability in conveying aquatic environmental information. This highlights the potential application value of the hue angle as a parameter for accurately expressing oceanic water environmental information.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601005 (2025)
The vertical number density of ozone from the ozone mapping and profiler suite (OMPS) limb measurements is firstly retrieved using wavelength pairing and multiplicative algebraic reconstruction technique. Our retrieved algorithm uses radiance in the visible (VIS) band to obtain ozone concentrations at altitudes of 12.5‒39.5 km, with a vertical resolution of 1 km. The results are compared with the OMPS/LP v2.6 ozone profile products provided by the national aeronautics and space administration (NASA), showing high consistency (<6%) between 16‒38 km. The correlation coefficient for the total ozone column in the stratosphere is 0.953. Using these retrievals, we investigate changes in stratospheric ozone concentration following the Tonga volcanic eruption and analyze the key physical and chemical processes affecting ozone concentration. The Tonga eruption releases a large amount of sulfate aerosols into the middle and lower stratosphere at 20°‒60°S. In mid-to-low latitudes of southern hemisphere, the enhanced sulfate aerosols increase ozone concentration in the middle stratosphere while reducing it in the lower stratosphere. Additionally, sulfate aerosols are transported through the Brewer‒Dobson (BD) circulation to Antarctica, where the enhanced Antarctic upwelling and polar stratospheric clouds (PSC) contribute to the enlargement of the polar ozone hole. Ozone plays a crucial role in the evolution of life on Earth. As an important trace gas in the atmosphere, ozone regulates the Earth’s climate, particularly in terms of temperature and energy distribution. Therefore, its concentration, distribution, and temporal evolution of ozone are closely related to research on ozone layer recovery, stratospheric circulation, and temperature response to increasing greenhouse gases. Therefore, obtaining daily global ozone profiles is crucial. In this study, we report the stratospheric ozone concentrations monitored by OMPS, validated against NASA’s OMPS/LP v2.6 products. Additionally, based on the retrievals, we analyze annual changes in stratospheric ozone before and after the Tonga submarine volcano eruption, as well as the chemical and kinetic mechanisms underlying these changes. This research is crucial for understanding how stratospheric ozone protects life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. We hope our research can provide a technical foundation for future data products from China’s space-based atmospheric remote sensing limb observations.
First, the limb radiances of the selected wavelengths are normalized to a reference tangent height that is insensitive to ozone. Using wavelength pairing, we retrieve ozone concentrations at different heights based on the variation in ozone’s absorption of solar radiance in the VIS band. Second, the SCIATRAN radiative transfer model is used to establish limb-simulated radiance. The observed and simulated radiances are transformed into retrieval vectors through radiance normalization and wavelength pairing, respectively. Finally, the multiplicative algebraic reconstruction technique (MART) algorithm is applied iteratively to correct and converge the ozone profile.
To verify our retrievals, we compare them with OMPS/LP v2.6 profiles provided by NASA. The retrieved ozone profiles are in good agreement with OMPS/LP v2.6, with high consistency in structure, peak height, and size [Fig. 5(a)], and a deviation of less than 2% between 18‒31 km [Fig. 5(b)]. The tropical profiles also show good consistency [Fig. 6(a)], with deviations of less than 10% across six latitude bands between 15‒38 km, except for the southern latitude band [Fig. 6(b)]. In addition, the total ozone column in the stratosphere shows a correlation coefficient of 0.953 with OMPS/LP v2.6 (Fig. 7). The retrievals from September 1, 2021, September 1, 2022, and September 1, 2023, are highly consistent with the global map of OMPS/LP v2.6 ozone concentrations (Fig. 8). Based on our data, we compare ozone concentrations on September 1, October 1, and November 16 from 2021 to 2023 (Fig. 9). We find that in mid-to-low latitudes, the abundance of active nitrogen in the stratosphere decreases due to sulfate aerosols formed after the Tonga volcanic eruption, leading to an increase in ozone concentration in the middle stratosphere. Sulfate aerosols also weaken solar radiation, resulting in negative ozone anomalies in the lower stratosphere. These aerosols are transported southward by the BD circulation, causing significant ozone loss in the lower polar stratosphere (60°S). After over a year of sedimentation, total ozone columns in mid-to-high latitudes of the southern hemisphere recover in 2023 (Fig. 11).
In this study, we use wavelength pairing and the MART algorithm to retrieve the stratospheric ozone profiles from OMPS limb measurements. Our retrievals are validated against OMPS/LP v2.6 products provided by NASA, showing good consistency. Additionally, we analyze the influence and mechanisms of the Tonga submarine volcanic eruption on stratospheric ozone before and after the event. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of wavelength pairing and MART in retrieving OMPS/LP ozone profiles, providing a solid technical foundation for future applications. However, studying stratospheric ozone recovery requires long-term, consistent datasets, and using the same retrieval scheme is critical in minimizing discrepancies between different satellite data.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601006 (2025)
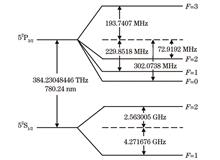
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O) play crucial roles in global climate change through the carbon?water cycle. Semi-heavy water, as a stable isotope of water vapor, helps deepen our understanding of the water cycle process. A large number of active and passive remote sensing technologies based on absorption spectroscopy have been applied to the detection of atmospheric CO2 and H216O. However, passive remote sensing, which relies on sunlight, cannot provide continuous day-and-night monitoring, while active remote sensing based on differential absorption LiDAR (DIAL) can effectively compensate for this limitation. Research has shown that H216O is the primary interfering gas in CO2 detection that causes measurement errors. Since dual-wavelength DIAL can only measure one type of gas, the interference effect of H216O on CO2 is minimized by selecting an appropriate absorption line, where the absorptions of H216O at the on-line and off-line wavelengths are almost equal. However, HD16O, a stable isotope of H216O, also affects the detection accuracy of CO2, though this is rarely addressed. In addition, in terms of vertical height, especially within the troposphere, H2O and atmospheric parameters can vary significantly. To date, no DIAL system can simultaneously provide vertical profile measurements for CO2 and HD16O, and there has been limited theoretical analysis and feasibility verification of this. In the present study, we report the sensitivity analysis of simultaneous remote sensing of atmospheric CO2 and HD16O profiles using LiDAR. This analysis is based on the MODTRAN atmospheric model. This sensitivity analysis aids in improving the inversion algorithm for the concentration profiles of CO2 and HD16O, which is significant for enhancing the detection capability and inversion accuracy of both ground-based and airborne DIAL systems. It also provides a theoretical framework for accurate remote sensing of greenhouse gases and a deeper understanding of climate change in the context of carbon neutrality.
The sensitivity analysis of simultaneous remote sensing of atmospheric CO2 and HD16O profiles using LiDAR, based on the MODTRAN atmospheric model, is conducted. First, the mixed spectral lines of CO2 and HD16O under different atmospheric models are calculated using HITRAN spectroscopy parameters, and the feasibility of simultaneous measurement of these two gases by LiDAR is verified by selecting appropriate absorption lines. Next, considering the variation of atmospheric parameters with vertical height, the column and range-resolved concentration inversion errors of CO2 and HD16O are evaluated based on the optimization of weight functions and spectral line shapes. Further investigation is conducted on atmospheric factors, the frequency stability of LiDAR laser emissions, the overlapping effects of CO2 and HD16O, and the influence of altitude changes on concentration inversion errors.
In response to potential sources of error in the inversion of column and range-resolved concentrations of CO2 and HD16O, we comprehensively consider atmospheric factors, laser frequency stability, the overlap effect of the two gases, and altitude-induced changes in concentration inversion. When the temperature variation is ±1 K, the column concentrations of CO2 and HD16O reach their maximum temperature sensitivity of 0.18% and 0.09% at altitudes of 12.6 km and 23.4 km, respectively. The range-resolved concentrations of the two gases show maximum sensitivity of 0.21% and 0.38% near the tropopause. At a pressure variation of ±0.5 hPa, the sensitivity of both column and range-resolved concentrations of CO2 and HD16O gradually increases with altitude. The column concentration errors for CO2 and HD16O reach 0.33% and 0.03% at the top of the stratosphere, while the range-resolved concentration errors reach 0.54% and 0.83% at 20 km. The frequency sensitivity for CO2 column and range-resolved concentrations is generally higher than that of HD16O, and the frequency sensitivity at the center of both gas absorption lines is close to zero at any altitude. When the H2O mixing ratio variation is 5%, errors in CO2 column and range-resolved concentrations due to overlapping effects decrease with increasing altitude, reaching 0.15% and 0.01% at sea level in tropical and sub-arctic winter models, respectively. For altitudes greater than 5 km, the range-resolved concentration error of CO2 at the line centers for all atmospheric models is less than 0.001%, and the error caused by the overlapping effect can be ignored. When the tropic model and the 1976 U.S. standard atmospheric model are used, without considering the absorption of HD16O, the errors for the range-resolved CO2 concentrations at sea level are 1.87% and 0.60%, respectively. Even under the sub-arctic winter model, the column concentration error at the center line reaches 0.17%, which confirms the non-negligible role of HD16O in CO2 inversion. In addition, with an 80 dB signal-to-noise ratio at the LiDAR origin in mid-latitude regions, the altitude sensitivity of CO2 and HD16O column concentrations at the top of the troposphere is 0.10% and 0.18%, respectively, while the sensitivity of range-resolved concentrations is 1.1% and 6.3%, respectively.
To meet precise greenhouse gas monitoring requirements, we conduct a theoretical analysis on the simultaneous remote sensing of atmospheric CO2 and HD16O using LiDAR. Based on the MODTRAN atmospheric model, independent and mixed optical depth spectra of CO2, H216O, and HD16O are derived under different models. The absorption lines suitable for detecting CO2 and HD16O are identified by analyzing the relative absorption intensities and spectral parameters of each gas. The spectral broadening of CO2 and HD16O caused by collision and Doppler effects is calculated based on temperature and pressure profiles from the 1976 U.S. standard atmospheric model. The two spectra exhibit Voigt line shapes in the altitude ranges of 9.4?34.5 km and 8.3?33.8 km, and their absorption lines are optimized for different altitudes. The systematic errors in range-resolved and column concentrations of CO2 and HD16O, considering factors like atmospheric conditions, laser frequency stability, and the overlapping effect of the two gases, are analyzed. Our findings confirm that HD16O plays a critical role in CO2 inversion at the R16 line. Considering the errors introduced by these factors, inversion accuracy for CO2 and HD16O column concentrations of better than 1% and 2%, respectively, and range-resolved concentrations of 2% and 8%, respectively, can be achieved in the troposphere of mid-latitudes.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 27, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601007 (2025)
When laser propagates through the atmosphere, it encounters atmospheric turbulence that distorts the laser wavefront, resulting in turbulence effects such as beam drift, spot expansion, scintillation, and fluctuations in the angle of arrival. In studies about these turbulence effects, Fried’s atmospheric coherence length (r0) expresses changes in both the amplitude and phase of light waves and serves as a representation of the overall intensity of atmospheric turbulence, making it a standard metric for quantitative description. We propose the use of the differential image motion monitor (DIMM) to measure this parameter. During the measurement, relevant parameters, including the device’s exposure time, must be specified. Since the turbulence freezing time varies across different regions, the selected exposure time for measuring atmospheric coherence length also varies. The different exposure times of the equipment affect the measurement results. Therefore, we propose a dual-camera synchronous measurement scheme based on a beam-splitting prism, which is built upon the traditional DIMM, to construct a system for measuring the optimal exposure time. This system employs a beam-splitting prism with a 50∶50 splitting ratio to achieve comparative measurements of different exposure time under “atmospheric freezing” conditions. Through comparative experiments and evaluation methods based on the ratio of system uncertainty and centroid variance, the optimal exposure time is selected.
We first summarize the theory of atmospheric coherence length, the relationship between coherence length and exposure time, and the theoretical basis for selecting exposure time. Based on this, we improve the existing atmospheric coherence length measurement instrument (aperture of 280 mm, focal length of 2800 mm, sub-aperture center distance of 205 mm, sub-aperture diameter of 61 mm) by using a beam-splitting prism to achieve dual-camera synchronous measurement. Experiments are conducted using this system to collect image data generated during the process. Since the star images exhibit Gaussian spot characteristics, we propose an image processing method based on centroid extraction. This method first locates and separates the star spots using adaptive threshold segmentation and morphological operations, and then calculates the centroid position through a grayscale-weighted subpixel subdivision algorithm, achieving subpixel accuracy in star centroid extraction. Based on the centroid coordinates and theoretical formulas, we derive the atmospheric coherence length parameter. Next, we analyze the effect of different exposure time on the system’s measurement results. By comparing the centroid variance ratio and system uncertainty ratio between the experimental and control groups, we evaluate the measurement accuracy under different exposure time and determine the optimal exposure time under local measurement conditions. Finally, we compare the selected optimal exposure time measurement results with long-term measurement results under conventional exposure time, confirming that the optimal exposure time significantly improves measurement accuracy and system performance. This study provides theoretical support and experimental evidence for the accurate measurement of atmospheric coherence length and offers a reference for optimizing exposure time selection in various measurement scenarios.
In the synchronous measurement system (as shown in Fig. 1), we implement an adaptive exposure time measurement function. Through this system, we dynamically adjust the exposure time to adapt to changes in atmospheric turbulence. Statistical analysis of the star image centroid extraction (Fig. 3) demonstrates that our proposed method can accurately extract the centroid of the spots, further validating the precision and stability of centroid extraction. Regarding the selection of the optimal exposure time, we evaluate measurement performance at different exposure time through statistical analysis of system errors and centroid variance (Fig. 6). The analysis results show that when the exposure time is 5 ms, the system error is minimized, and the centroid variance fully reflects changes in atmospheric turbulence. Therefore, for measuring atmospheric coherence length in the Changchun region, we recommend using 5 ms as the standard exposure time. Subsequent long-term measurement data comparisons further validate the effectiveness of this choice. The 5 ms exposure time captures richer atmospheric turbulence signals and accurately reflects the dynamic turbulence changes at the time. This provides a reliable experimental basis for efficient measurement of the system in practical applications.
We propose a dual-camera synchronous measurement scheme based on a beam-splitting prism, constructing a system to determine the optimal exposure time for measuring atmospheric coherence length in this region. The scheme uses a beam-splitting prism to replace the original single detector with two detectors, ensuring that each detector receives the same amount of energy. By simultaneously detecting atmospheric turbulence with both detectors, we conduct comparative experiments under atmospheric freezing conditions, avoiding the impact of continuously changing turbulence on the experiment. We process the images collected by the detectors for centroid extraction and calculate the atmospheric coherence length at different exposure time. By analyzing the system’s measurement accuracy and the variance of the spot centroids, we determine the optimal exposure time. Our research results indicate that a 5 ms exposure time should be chosen for measuring local atmospheric coherence length. Under strong wind conditions, we suggest an exposure time of 4 ms to better capture high-frequency signals, while in windless conditions, we consider 6 ms. Comparative measurements of local atmospheric coherence length at these exposure time verify that the exposure time derived from our experimental conclusions can better reflect changes in atmospheric turbulence. This study is of great significance for improving the accuracy of atmospheric coherence length measurements.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601008 (2025)
Accurate measurement of seawater absorption coefficients is important for ocean radiative transfer simulations, biogeochemical parameter inversion, and calibration and validation of ocean color satellites. Reflective-tube absorption meters are the most commonly employed instruments for seawater absorption coefficient measurement, but the measured absorption coefficient must be corrected for scattering due to instrumental design limitations. There have been a few studies evaluating the ac-9/ac-s scattering correction methods. However, there is a lack of application evaluation of these correction methods applied to the coastal waters of China. We evaluate the ac-9/ac-s scattering correction methods based on field measurements from the coastal waters of China’s sea. Based on the evaluation, guidance is provided for the selection of scattering correction methods when reflective-tube absorption meters are employed in different water bodies.
We introduce five scattering correction methods to evaluate their performance on the field measured data from the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea. The data includes the absorption coefficient measured by the reflective-tube absorption meters of ac-9, ac-s, and the point source integrating cavity absorption meter (OSCAR), the backscattering coefficients measured by the backscattering instrument HS6, the volume scattering function measured by LISST-VSF and the temperature, salinity, and depth data measured by CTD. The absorption coefficients are measured by adopting ac-9 and ac-s for two cruises to independently evaluate the performance of different scattering correction methods applied to ac-9 and ac-s. In the South China Sea, the absorption coefficient measured by OSCAR is taken as the true value to evaluate the application of scattering correction methods to the ac-s/ac-9 measurements. In the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea, there is no synchronous OSCAR measurement. Meanwhile, the absorption coefficient corrected by the volume scattering correction method is utilized as a reference for evaluating other scattering correction methods. Since the volume scattering function is measured independently, the error obtained by integrating it in the limited angle is the scattering error measured by the reflection-tube absorption coefficient measurement instrument, thereby making this method a more accurate scattering correction method. Prior to each cruise, all instruments have undergone rigorous calibration, including pressurized flow ultra-pure water calibration for ac-s and ac-9 in the laboratory, integrator cavity reflectivity calibration for OSCAR, and calibration for HS6 to ensure the accuracy of field measurements.
The results show that for the clean water in the South China Sea, little difference is found among different scattering correction methods. The baseline method and volume scattering correction method have better correction effects, and the relative errors after data correction are 25.05% and 23.24% respectively. The relative error of the semi-empirical correction method is 36.01%. The performance of the proportional method and iteration correction method is poor. In the Bohai Sea, the proportional method and semi-empirical correction method perform better, with relative errors of 29.22% and 25.02% respectively. After the correction of the baseline method and iterative method, the correction results of each band have a large deviation from the reference value. In the Yellow Sea, the proportional method is relatively sound, with 23.17% of the relative error. The baseline method and the semi-empirical correction method are similar, and the relative error after data correction is 30.94% and 31.68% respectively. In the East China Sea, the semi-empirical correction method has the best correction effect, and the relative error after data correction is 14.71%, followed by the proportional method. Additionally, the relative error after data correction is 24.02%, and the baseline method performs slightly worse.
We evaluate five representative scattering correction methods for reflective-tube absorption coefficient measurement based on field data from several regions of China’s sea. These methods include the baseline method, proportional method, semi-empirical correction method, iterative correction method, and volume scattering function correction method. Generally, all these scattering correction methods can reduce the scattering error from reflective tubes, and make the absorption coefficient approximate to the true value. However, the performance of each method varies between different types of water. Based on the analysis results of all the data, our suggestions for selecting scattering correction methods for the reflective-tube absorption meters are as follows. The baseline method is more suitable for clean water bodies (the South China Sea), the semi-empirical correction method is suited for turbidity water (the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea, and coastal water), and the volume scattering method is preferred if the measured volume scattering function of water is available.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 26, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601009 (2025)
Lidar is a powerful tool for detecting atmospheric temperature, humidity, and aerosols. The lidar echo signal forms the basis for retrieving these parameters. Currently, data acquisition cards with fixed sampling rates are widely used to sample lidar echo signals. However, the bandwidth of the lidar echo signal is much larger than the sampling rate of the acquisition card, which inevitably leads to distortion of the signal. In addition, high-speed data sampling consumes substantial resources for data acquisition, storage, and processing, which is particularly problematic in space-borne lidar systems. With the development of digital signal processing technologies, compressed sensing has found widespread application in data compression, noise reduction, and other fields. We aim to reconstruct the lidar echo signal precisely with fewer sampling points using compressed sensing.
In this paper, compressed sensing theory is used to reconstruct the lidar echo signal with fewer sampling points. First, the sparsity of the lidar echo signal is analyzed using the db4 wavelet base. Then, based on the wavelet basis and the orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm, the downsampling and compressed reconstruction of the lidar echo signal are investigated under different noise conditions. The error between the reconstructed and original lidar echo signals is analyzed in detail. Finally, the extinction coefficient of aerosols below 10 km is retrieved using the reconstructed lidar echo signal through the Fernald method, and the error between the retrieved extinction coefficient and the standard atmosphere model is analyzed. The validity of the reconstructed lidar echo signal for data retrieval is confirmed.
In the wavelet decomposition, three decomposition layers are used, with 0.01% of the maximum value of the wavelet coefficient set as the threshold. The research results show that most of the wavelet decomposition coefficients are close to zero, which indicates the sparsity of the lidar echo signal in the wavelet basis (Fig. 3). When the lidar detection height is 10 km, the total number of decomposition coefficients is 10020, with 1238 non-zero coefficients after thresholding. Using these non-zero coefficients, the lidar echo signal is reconstructed through inverse wavelet transform. The similarity of the reconstructed lidar echo signal is as high as 0.999, and the root-mean-square error is 8.666×10-17, further confirming the high sparsity of the lidar echo signal in the wavelet basis (Fig. 4). Based on the high sparsity of the lidar echo signal, downsampling and compressed reconstruction are performed under different noise conditions. The results show that the lidar echo signal can be reconstructed using fewer sampling points through compressed sensing. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the similarity of the reconstructed signal improve as the SNR of the input signal increases. When the data compression ratio is 5∶1 and the input signal’s SNR exceeds 25 dB, the similarity between the reconstructed and original signals is greater than 0.997 (Table 3). The SNR of the reconstructed signal is higher than that of the input signal, indicating that the OMP algorithm has a certain denoising effect (Fig. 8). Finally, the extinction coefficient of aerosols below 10 km is retrieved using the reconstructed lidar echo signal through the Fernald method. The lidar echo signal is reconstructed from the input signal, with an SNR of 30 dB. The profile of the extinction coefficient is consistent with the standard atmosphere model. The relative error of the retrieved extinction coefficient at different heights is below 15.81%, confirming the validity of the reconstructed lidar echo signal for retrieving aerosol extinction coefficients (Fig. 11).
First, the high sparsity of the ground-based lidar echo signal is confirmed. The results show that when the detection distance is 10 km, the sparsity of the lidar echo signal in the wavelet basis is only 1238. Second, the lidar echo signal can be accurately reconstructed using the orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. The SNR of the input signal significantly affects the reconstruction quality. When the data compression ratio is 5∶1 and the SNR of the input signal exceeds 25 dB, the similarity between the reconstructed and original signals exceeds 0.997, and the root-mean-square error is less than 1.769×10-13. Finally, the extinction coefficient of aerosols below 10 km is retrieved using the reconstructed lidar echo signal through the Fernald method. When the input signal’s SNR is 30 dB, the absolute error in the retrieved aerosol extinction coefficient is less than 2.440×10-7 m-1, and the relative error is less than 15.81%, which verifies the effectiveness of the reconstructed signal for retrieving aerosol extinction coefficients.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0601010 (2025)
The in-situ measurement of cloud microphysics parameters such as cloud droplet spectrum and particle number concentration, is of great significance to research in cloud and precipitation physics, weather modification, and optoelectronic engineering for national defense. Currently, various methods for observing cloud microscopic characteristics have been developed, combining space-based in-situ observation, ground-based remote sensing, and space-based remote sensing. Due to differences in data and the theoretical basis among different inversion methods, significant variations exist among different cloud inversion products. Scholars typically aim to validate the accuracy of various remote sensing inversion products using in-situ measurements of cloud parameters. The measurement of cloud particles using research aircraft is a relatively representative in-situ method. However, the high-speed motion of the aircraft can cause particle breakup, and the rapid changes in the flow field can lead to errors in particle spectrum measurement. Additionally, due to safety concerns, research aircraft cannot operate in harsh environments such as thunderstorm centers and supercells. Lightweight cloud particle detectors, mounted on balloons and UAVs, have garnered increasing attention as an important supplementary method for in-situ measurements. Therefore, we design a lightweight cloud particle imager (LCPI) based on forward scattered light imaging. The LCPI can meet the needs of both ground-based and balloon-borne observations.
LCPI primarily utilizes the Tyndall effect to capture particle images in dark-field conditions. LCPI is mainly composed of three parts: a ring-shaped light source, a magnifying lens, and an imaging unit (CMOS). Designed for field experiments, LCPI features a lightweight and miniaturized design, weighing less than 2 kg and measuring 110 mm (base diameter) ×310 mm (height). The CMOS has a resolution of 640 pixel×480 pixel with a pixel size of 3.75 μm. A magnifying lens with a magnification of 2.5 is used in front of the CMOS, which results in a theoretical resolution of 1.5 μm and an effective sampling field reduced to 960 μm×720 μm. The ring-shaped light source consists of 8 high-brightness white LEDs with uniform specifications, mounted on a circular base to minimize beam divergence. When there are no cloud particles in the sampling volume, the 8 illumination beams intersect at the front of the magnifying lens and illuminate the sampling volume. Since light cannot directly enter the CMOS, the image appears visually pure black in this scenario. As cloud particles enter the sampling volume with airflow, these 8 illumination beams are scattered by the cloud particles. Forward scattered light from particles forms bright images on the CMOS through the magnifying lens. To avoid repeated sampling of the same particles, sampled air flows out through small holes beneath the fan, which are located underneath the fan.
To verify the accuracy of microphysical characteristic parameters such as particle size, shape, and spectrum distribution of cloud particles detected by LCPI, we first design a high-precision calibration device for it and calibrate the instrument in the laboratory (Fig. 3). The magnification of the imaging system can be directly obtained through magnification calibration, and the actual magnification of LCPI is 2.5 (Fig. 4). Measurement accuracy calibration shows that LCPI can accurately measure particle sizes under sunny, cloudy, and night conditions (Fig. 5). The measurement error of LCPI is within ±10% (Fig. 6). Sampling volume calibration demonstrates that the sampling volume increases linearly with particle diameter (Fig. 7). To further evaluate LCPI’s performance in measuring actual cloud and fog conditions, we conduct a comparative experiment in Lushan Mountain using LCPI and FM-120. The experimental results show good agreement between the two instruments (Fig. 9). The consistency in particle number density, volumetric water content, and mean diameter obtained by the two instruments reach 0.9316, 0.8221, and 0.8645, respectively, which indicates that LCPI can accurately measure microscopic cloud characteristics (Fig. 11).
In this paper, we present the calibration and preliminary experimental results of a novel LCPI. Based on the dark-field imaging principle, the instrument uses a ring-shaped light source composed of 8 high-brightness white LEDs to improve the imaging effect of small particles, which effectively solves the problem where small particles are easily submerged by background light and cannot be imaged. To ensure measurement accuracy, we design and complete magnification, measuring accuracy, and sampling volume calibration using a high-precision calibration platform developed for this purpose. The calibration results show that the actual magnification of the detector is 2.5, the measurement error is within ±10%, and there is a linear relationship between sampling volume and particle diameter. The particle size can be accurately measured under different lighting conditions. Comparative observational experiments with LCPI and FM-120 are conducted at Lushan Mountain. The comparison reveals high consistency in cloud particle number density (0.9316), volumetric water content (0.8221), and average diameter (0.8645), which proves the LCPI’s accurate measurement of cloud particle microphysical characteristics. Compared to the FM-120, this instrument can also capture images of particles, which can subsequently be used to study cloud microphysical processes involving particles of various shapes, such as ice clouds and mixed-phase clouds.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 26, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0604001 (2025)
Wireless UV scattering communication is a technology that leverages the scattering of atmospheric particles to enable wireless communication. Its strong scattering characteristics make it suitable for specialized applications, such as non-line-of-sight (NLOS) communication. However, these same characteristics limit it to short-range transmissions and cause significant path loss. Moreover, atmospheric temperature and pressure variations can lead to fluctuations in the air’s refractive index, causing turbulence and random signal fluctuations at the receiver. To mitigate high path loss and signal scintillation from turbulence, relay-assisted UV optical communication has emerged as an effective solution. Most existing UV relay systems are designed for terrestrial applications, while ground-to-air communications remain underexplored. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offer a promising option for mobile air relays due to their high maneuverability, compact design, and low cost. As UAV technology continues to advance, UAV-based communication systems are expected to play a vital role in next-generation wireless networks. UAV-assisted UV communication dynamically optimizes relay positions and establishes flexible NLOS links, which traditional ground relays lack.
In this paper, we propose a novel framework for analyzing and optimizing a decode-and-forward (DF) relay in UAV-assisted NLOS UV communication systems. The analysis accounts for attenuation losses and atmospheric turbulence. Specifically, the effects of log-normally distributed turbulence on both the source-to-UAV and UAV-to-destination links are evaluated. The probability density function (PDF) of the ground-to-air link is derived to establish closed-form expressions for the end-to-end outage probability and the average bit error rate (ABER) under the DF relay protocol. In addition, we explore the optimal system and channel parameters to enhance the UAV-assisted UV relay system’s performance. We evaluate the performance of UAV-assisted NLOS UVC systems, analyze the influence of various system and channel parameters, and provide valuable engineering insights for optimizing UAV-assisted NLOS UVC systems.
The system’s performance is analyzed based on two key metrics: outage probability and ABER. At a power margin of 6 dB, an increase in turbulence intensity from
Using UAVs as relay nodes in UV optical communication systems not only extends communication coverage but also mitigates atmospheric impairments affecting UV signal quality. In this paper, we propose and evaluate a UAV-assisted UV optical communication system using a DF relay under low-altitude turbulence. A log-normal fading model, accounting for both path loss and turbulence-induced fading, is developed. Closed-form expressions for the source-to-destination outage probability and ABER are derived from the PDF of the channel power fading factor. Using these analytical expressions, we investigate the effects of various atmospheric turbulence intensities, system parameters, and channel parameters on the performance of the airborne UV relay system. Simulation results show that the proposed system achieves a performance improvement of about 10 dB with an outage probability of
- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0606002 (2025)
Efficient identification of orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes in vortex beams is critical for enhancing capacity and spectral efficiency in wireless optical communication systems. However, turbulent atmospheric channels pose significant challenges due to phase distortion in vortex beams and the complexity of traditional optical approaches. In this paper, we propose a novel methodology that integrates an enhanced convolutional neural network (CNN-transformer) hybrid model with double-slit interference. The proposed approach enables simultaneous and precise identification of both the magnitude and sign of high-order OAM modes under turbulent atmospheric conditions, offering significant improvements in recognition accuracy and system performance.
To address the challenges of identifying OAM mode magnitude and sign in turbulent atmospheric environments, we propose a novel method combining an improved CNN-transformer hybrid model with double-slit interference. When Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) beams propagate through turbulent atmospheres, phase distortions result in skewed and twisted interference fringes when passing through a double slit. These patterns are captured and processed using the proposed CNN-transformer hybrid model, named CACSIV3-Net. The model employs Inception_V3 as its backbone and incorporates a coordinate attention module (CAM) to dynamically weight channel relationships and spatial features. In addition, the cross-shaped window transformer (CSWT) is introduced to extract multi-scale features and long-range dependencies, achieving high-precision OAM mode recognition.
In this paper, we propose an improved CNN-transformer hybrid model, CACSIV3-Net, designed to enhance the recognition accuracy of OAM modes in turbulent atmospheric environments. To evaluate its performance, we compare CACSIV3-Net with mainstream classification networks (AlexNet, VGGNet, ResNet, and Inception_V3) using identical system configurations and hyperparameter settings. Training is conducted on an LG beam double-slit interference dataset across varying atmospheric turbulence conditions. The performance results, illustrated in Fig. 4 show that CACSIV3-Net achieves the highest Top-1 accuracy for OAM modes, reaching 96.45%. This represents improvements of 24.00, 14.25, 11.12, and 5.34 percentage points over AlexNet, ResNet, VGGNet, and Inception_V3, respectively. In addition, CACSIV3-Net demonstrates the fastest reduction in average loss within the first 50 epochs and maintains convergence after approaching 0.1. Comprehensive analysis indicates that CACSIV3-Net offers superior adaptability and higher recognition accuracy for LG beam datasets under unknown intensity turbulence compared to other networks. To further analyze its components, ablation experiments are conducted by progressively integrating CAM and CSWT to evaluate their influence on OAM mode recognition, with results provided in Fig. 5. As shown in Fig. 5(a), the ROC curve of CACSIV3-Net is closest to the upper-left corner, achieving a micro-averaged area under the curve of 0.79, outperforming models such as Inception_V3, Inception_V3+CAM, and Inception_V3+CSWT. This indicates superior decision-making ability and stability. CACSIV3-Net processes 24, 15, and 7 more images per second compared to the baseline models, including Inception_V3, Inception_V3+CAM, and Inception_V3+CSWT, respectively, reducing the total recognition time by 2.8, 0.9 and 0.4 s, as shown in Fig. 5(b). This demonstrates the higher recognition efficiency of the CACSIV3-Net model. The classification performance metrics indicate that incorporating both CAM and CSWT into the Inception_V3 model results in optimal performance, with an accuracy of 91.55%, precision of 91.29%, recall of 91.33%, and F1-score of 91.29%, as shown in Fig. 5(c). The confusion matrix shown in (Fig.6) illustrates the prediction performance of CACSIV3-Net across 20 OAM modes, with sparse and low-proportion off-diagonal elements, signifying excellent classification capabilities. Moreover, robustness tests conducted on three newly added test sets under conditions of noise intensity σ=0.1, transmission distance z=2000 m, and beam wavelength λ=850 nm achieve OAM mode recognition accuracies of 80.1%, 85.4%, and 87.95%, respectively, as shown in Table 1 and Fig. 7.
In this paper, we propose an improved CNN-transformer hybrid model integrated with double-slit interference for high-precision OAM mode recognition, By embedding CAM into the Inception_V3 backbone and utilizing CSWT, the model captures long-range dependencies and enhances recognition accuracy in turbulent atmospheric environments. The trained model achieves 96.45% accuracy for OAM modes ranging from -10 to +10 at a transmission distance of z=1000 m, an improvement of 4.9 percentage points over the baseline network. In addition, robustness tests are conducted on three newly added test sets under conditions of noise intensity σ=0.1, transmission distance z=2000 m, and beam wavelength λ=850 nm, yielding OAM mode recognition accuracies of 80.1%, 85.4%, and 87.95%, respectively. This method provides a novel and effective solution for high-order OAM mode recognition in turbulent environments, with significant potential for OAM multiplexing communications.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 24, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0606003 (2025)
Free-space optical communication (FSOC) offers significant advantages in high bandwidth, low latency, electromagnetic interference resistance, and high confidentiality due to its excellent beam characteristics, making it well-suited for long-distance, large-capacity data transmission. However, optical signal propagation inevitably passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, which significantly influences the signal. In particular, the scintillation caused by atmospheric turbulence results in received power jitter and inter-symbol interference, leading to a degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and an increase in the bit error rate (BER), which limits the transmission efficiency, stability, and reliability of high-speed optical communication systems. Existing compensation methods often require additional communication feedback links, and for atmospheric turbulent channels with rapidly changing fading characteristics, compensation within the turbulence coherence time is challenging. Utilizing the channel reciprocity property to obtain real-time channel state information can substantially reduce delay, but the actual accuracy of turbulence fading compensation is still limited by device noise and nonlinear effects. In this paper, we propose a real-time scintillation suppression system for atmospheric optical transmission based on fuzzy adaptive control, establishing a correlation model between reciprocal channel state information and optical intensity scintillation. A turbulence scintillation adaptive suppression algorithm is proposed and deployed on an field programmable gate array (FPGA) platform to improve the pre-compensation of light intensity scintillation at the transmitter. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we build an experimental system for atmospheric optical transmission scintillation suppression and show that it suppresses amplitude jitter in received optical signals across various atmospheric turbulence environments. This represents a breakthrough in stable optical signal transmission technology.
A real-time optical intensity scintillation suppression model is established based on the bidirectional reciprocal channel by leveraging the relationship between channel state information and optical intensity scintillation. By adaptively controlling the transmitted optical power, pre-compensation for optical intensity scintillation at the transmitter is achieved. In this scenario, the optical terminals at both ends of the communication, Alice and Bob, interact with each other. The detector at Alice receives a beacon optical signal from Bob, which is affected by atmospheric turbulence. The system extracts transient turbulence decay characteristics from the received signal. Based on this, Alice generates an optical power compensation signal to adaptively adjust the transmit power, compensating for the turbulence fading the signal will experience in the turbulent channel. The accuracy and real-time performance of the compensation signal generation are crucial for effectively compensating turbulence fading. To address the challenges posed by photoelectric conversion device noise, as well as the nonlinear effects of optical power regulation devices such as optical attenuators and erbium-doped optical fiber amplifiers, we propose a transmit power adaptive control algorithm to ensure stable control of the devices during the duration of reciprocity. The algorithm is implemented on an FPGA, which enables powerful parallel data processing. During each operation cycle, the light intensity jitter signal is filtered and extracted. The optical power compensation value required for steady amplitude transmission control is calculated based on the turbulence decay signal and the feedback control signal. The fuzzy PID control algorithm then adjusts the control parameters according to the system state, calculating the optimal compensation signal for the next moment, thus achieving adaptive transmit power control.
To verify the suppression effect of turbulence perturbations, an amplitude jitter suppression experiment based on channel reciprocity is conducted (Fig. 5). The test is set up with bidirectional reciprocity between Alice and Bob, with acquisition cards at both ends sampling at 1 kHz to synchronously capture turbulence fading signals (Fig. 6). By calculating the correlation coefficient, the reciprocity of the communication link is maintained above 0.9. To assess the stability of signal amplitude transmission, the received light intensity before and after transmit power adaptive compensation is compared under conditions of maximum and minimum light intensity scintillation (Fig. 7). The results show that after compensation, the received light intensity stabilizes in a straight line, with only minimal jitter due to measurement equipment noise. The experiment, measuring optical signal amplitude jitter suppression over several hours with varying turbulence intensity from afternoon to night, compares the received signal scintillation index before and after compensation (Fig. 9). The results show that before compensation, the received signal power fluctuates between -22 dBm and -31 dBm. At maximum turbulence intensity during midday, the scintillation index reaches 0.6602, while at lower turbulence intensity during the night, the scintillation index drops to 0.0287. The depth of scintillation index compensation remains consistently above -16 dB, regardless of changes in turbulence intensity.
In this paper, we investigate a real-time method for suppressing free-space optical signal amplitude jitter caused by atmospheric turbulence. Based on bidirectional reciprocity, a real-time optical intensity scintillation suppression model is developed, utilizing the relationship between channel state information and optical intensity jitter. To meet the real-time requirement for turbulence fading compensation, we design a transmit power adaptive control algorithm, which is deployed on the FPGA platform to ensure that signal processing converges faster than the channel coherence time. The proposed transmit power adaptive system is verified through an outfield wireless laser transmission test under varying turbulence intensity. The experimental results demonstrate that the transmit power adaptive compensation significantly reduces the scintillation index of the received optical signal. Specifically, the scintillation index decreases from 0.6602 to 0.0127 under maximum turbulence intensity and from 0.0287 to 0.0002 under minimum turbulence intensity. In addition, the depth of scintillation index compensation remains consistently above -16 dB, effectively mitigating the amplitude jitter caused by turbulence and enabling stable transmission under varying turbulence conditions.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 24, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0606004 (2025)
Tower solar thermal power is a flexible and green power source that is clean, environmentally friendly, stable, and efficient, especially for energy storage and peak shifting. It plays a significant role in the carbon peaking and carbon neutral strategy. The reflective mirrors of heliostats are the core optical components for concentrating solar energy, typically shaped into spherical mirrors or other optically curved surfaces. However, in tower solar thermal power stations, the large scale of heliostats and their varying distances from the central heat absorber require reflective mirrors with different optical focal lengths, usually ranging from 100 m to several kilometers. Manufacturing reflective mirrors with varying focal lengths using traditional thermoforming methods requires numerous molds, resulting in limited flexibility and significantly higher manufacturing costs. This approach is unsuitable for the construction needs of large-scale tower solar power plants. Therefore, it is crucial to explore high-precision, low-cost methods for molding and manufacturing optically curved mirrors for heliostats. This has been an ongoing pursuit within the industry.
In this paper, we focus on the regular pentagon heliostat widely used in engineering. We propose a novel manufacturing approach to form an optical spherical surface by directly jacking up several support bolts on the back of a flat mirror. The optical-mechanical integration analysis method is employed to investigate the influence of key geometric parameters, including the number of support bolt rings N, desired bolt spacing d, target spherical focal length f of the formed surface, and the reflective area of the heliostat, on the optical precision of the formed surface. The influence of gravity load and static wind load on the service optical accuracy of the mirror surface is also examined under the assumption of truss rigidity.
The total slope error St of the jacked mold reflective mirrors gradually decreases as the number of bolt rings N increases, but this improvement diminishes with further increases in N. Reducing the bolt spacing d also decreases St, with St being more sensitive to d when N is larger
As the target spherical focal length f increases, the optical accuracy of the jacked mirror improves, with the influence of N and d on the total slope error St decreasing. This characteristic is particularly favorable for tower solar thermal power stations, where the focal length of the heliostat mirror can extend to several kilometers. For mirror areas ranging from 50.0 m2 to 175.5 m2, the total slope error St of the mirror with f=50 m and N=10 can be controlled within the range of 0.912‒1.380 mrad. In typical long focal length applications with f=750 m, even with N=5, St can be controlled within 0.110‒0.185 mrad. In terms of jacking molding accuracy, the bolt jacking method is applicable across the full span of heliostat sizes, from short to long focal lengths and from small to larger areas. The total slope error of the mirror in service increases linearly with the wind loads, and increasing N or reducing d can improve optical accuracy in service. However, a well-designed arrangement of the support bolts and a robust heliostat support structure are essential prerequisites for maintaining optical accuracy in service.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0608001 (2025)
LiDAR imaging in foggy conditions is essential for applications such as autonomous driving, aviation navigation, and surveillance. However, traditional LiDAR systems face significant limitations in such environments due to the scattering and absorption of laser beams by fog, resulting in reduced detection range and degraded image quality. Single photon avalanche diode (SPAD) technology, with its exceptional sensitivity and high resolution, has emerged as a promising solution. SPAD systems can operate under extremely low light conditions. When combined with time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC), they can effectively detect and process individual photon signals. This capability enables reliable detection and imaging even in low-visibility environments like fog and haze. Therefore, investigating the performance of SPAD-based LiDAR systems in foggy conditions is crucial for advancing these applications.
In this paper, we utilize high-sensitivity SPAD combined with the TCSPC method to extract the depth and intensity information of targets in foggy environments. Monte Carlo simulations are conducted to analyze the transmission characteristics of laser beams in fog, providing a robust scientific foundation for this study. A Gamma distribution is used to model the scattering peaks caused by fog, while a Gaussian distribution is applied to represent peaks generated by target reflections. To enhance image quality, the Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) algorithm is combined with total variation (TV) regularization, significantly improving target reconstruction accuracy and clarity in fog conditions.
The photon echo data collected in foggy environments are analyzed using a Gamma-Gaussian mixture model to reconstruct depth and intensity images. Three-dimensional image reconstruction (Fig. 7) is performed using the peak value method, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) algorithm, and the proposed LM-TV algorithm. Comparative analysis demonstrates that the LM-TV algorithm outperforms traditional methods, reducing the root mean square error (RMSE) of the depth image by 1.0231 and increasing the structural similarity index (SSIM) of the intensity image by 0.5485 (Table 1). These results highlight the effectiveness of the LM-TV method in fog penetration imaging, delivering more accurate and robust target reconstruction.
In this paper, TCSPC technology is utilized to obtain photon echo data in the time domain under foggy conditions. A Gamma-Gaussian mixture model is employed to separate fog echo signals from target reflections, enabling precise depth and intensity to be extracted using the LM algorithm. Compared to the peak value method, the LM algorithm reduces the RMSE of the reconstructed depth image by 0.9475 and improves the SSIM of the reconstructed intensity image by 0.4720. The integration of TV regularization with the LM algorithm further reduces the RMSE of the depth image by an additional 0.0756 and enhances the SSIM by 0.0765. When compared to the MLE algorithm, the combined LM-TV method achieves a reduction in RMSE of 0.4788 and an improvement in SSIM by 0.4563. These findings demonstrate that the hybrid LM-TV algorithm significantly outperforms traditional methods, offering a more accurate and robust solution for target reconstruction in foggy environments.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0611001 (2025)
Solar thermal power generation is a clean and renewable energy technology that utilizes focusing mirrors to concentrate solar radiation, converting it into high-temperature thermal energy, which is then used to generate electricity. Focusing mirrors play a crucial role in solar thermal power systems and surface shape errors can lead to significant optical efficiency losses. Therefore, accurate measurement of the mirror surface shape is essential. Currently, there are three primary methods for measuring the surface shape of solar focusing mirrors: laser scanning, photogrammetry, and fringe reflection methods. Among these, laser scanning and fringe reflection can obtain the normal data of the mirror surface, while photogrammetry directly captures the three-dimensional (3D) shape data of the mirror. In practical applications, it is often necessary to measure both the normal data to assess optical performance and the 3D shape data for feedback on support point adjustments. To enable fast, batch, and online measurement of mirrors, the fringe reflection method is particularly suitable. Therefore, we explore the theoretical foundations of fringe reflection-based surface shape measurement and propose a 3D surface reconstruction method based on the L-BFGS-B optimization algorithm. The four-step phase-shifting algorithm, normal calculation method, and L-BFGS-B optimization algorithm are described in detail. A fringe reflection measurement system (FRMS) is designed and implemented, enabling the normal measurement and 3D surface reconstruction of heliostat mirrors.
In this study, we use the fringe reflection method to acquire the normal data of the mirror surface, followed by 3D surface reconstruction using the L-BFGS-B algorithm. Initially, sinusoidal patterns with varying brightness are projected onto a screen via a projector. The patterns, after reflecting off the measured mirror, form an image on the camera, and images with different periods and phases are captured. Subsequently, the four-step phase-shifting algorithm is used to process the images and determine the coordinates of point T on the screen corresponding to point P on the captured image. Through coordinate transformations, the coordinates of point M on the mirror surface, point P on the image, and point T on the screen are unified in the same coordinate system. The direction vectors of the incident light MT and the reflected light PM are calculated. According to the law of reflection, the normal vector at point M on the mirror surface is determined. From the normal data, the 3D surface profile of the mirror is reconstructed using the L-BFGS-B algorithm. Lastly, the surface height of the focusing mirror is measured using a FARO Vantage laser tracker, and the results are compared with experimental outcomes to verify the accuracy of the reconstruction.
A FRMS is designed and developed (Fig. 5) for experiments on a focusing mirror with dimensions of 2060 mm×1605 mm. By processing the captured stripe images (Fig. 6), the normal distributions of the mirror surface along the X and Y axes are obtained (Fig. 7). Using the normal data acquired through the system, a 3D reconstruction of the mirror surface is performed, producing a height distribution map [Fig. 8(a)]. To validate the accuracy of this height distribution, the surface is pre-measured with the FARO Vantage laser tracker. The point cloud data obtained from the laser tracker [Fig. 8(b)] are then interpolated to yield the height distribution [Fig. 8(c)]. A comparison between the results from the fringe reflection method and the laser tracker [Fig. 8(d)] reveal a root mean square (RMS) deviation of 0.22 mm in the height measurements between the two methods.
Solar concentrator mirrors are essential components in solar thermal power generation systems, and their surface shape accuracy significantly affects the optical efficiency of the system. In this study, we propose a method for surface shape measurement of solar concentrator mirrors based on fringe reflection, addressing the need for fast, batch, and online detection. The four-step phase-shift algorithm and the method for calculating surface normals are detailed. We also propose a surface reconstruction technique using the L-BFGS-B optimization algorithm, leading to an accurate height distribution of the mirror surface. A FRMS is designed and validated through the measurement and reconstruction of a 2060 mm×1605 mm mirror. The system’s accuracy is verified through comparison with measurements obtained from a FARO Vantage laser tracker, showing an RMS deviation of 0.22 mm between the two methods.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0612001 (2025)
The influence of greenhouse gases, industrial pollutant gases, and volatile organic compounds on the living environment and ecology is becoming increasingly severe. It is necessary to regularly monitor their concentrations in the atmosphere. Satellite remote sensing with high spectral resolution and high sensitivity can realize high accuracy determination of gas concentration, which has been an important technology for air pollution monitoring and global change research. Two main types of passive remote sensing payloads for atmospheric composition detection are Fourier transform spectrometer (FTS) and grating spectrometer. The former has wide spectral coverage and big throughput. However, the spatial continuous detection of gas concentration distribution is limited, and the system performance of FTS is better in the infrared band. The advantages of grating spectrometers are a big field of view (FOV), spatial continuous imaging, and high spectral resolution. The spatial and spectra information can be obtained at the same time by an area array detector. The development of atmospheric composition monitoring payload technology needs to realize the rapid change monitoring of gas composition with rapid chemical reaction and short life in the atmosphere, so as to meet the needs of atmospheric chemistry research and pollutant gas emission supervision and law enforcement. The quantitative detection of a variety of atmospheric components at the same time can provide a more effective means for analyzing and evaluating the situation and law of atmospheric compound pollution. This requires the payload to achieve wide spectral coverage, ultra-high spectral resolution, and high sensitivity while having larger swath and higher spatial resolution. The improvement of the performance will directly lead to an increase in the volume and weight of the spectrometer, increasing the cost of payload and satellite development and launch. The focus of our study is how to achieve a compact design of the spectrometer while meeting high-performance requirements.
Considering the application requirements and system performance, the spectrometer is designed to have four bands: ultraviolet (B1), ultraviolet-visible (B2), near-infrared (B3), and short-wave infrared (B4). Applying fully freeform optics, the telescope system with only two off-axis reflective mirrors realizes aberration correction along a large FOV. The design of large F-number and different focal lengths in meridian and sagittal directions is used to simplify the structure and effectively reduce the alignment tolerance. Through the processing of free-form aluminum mirrors and the assembly and adjustment test of the telescope system, the verification of the free-form telescope system with a large FOV is realized. A reflective slit of ultraviolet (UV) band to divide the FOV and the entrance slit of the other three bands are integrated into one assembly. For the ultraviolet band, especially before 320 nm, the spectral radiance after atmospheric absorption in orbit is very weak, so the dichroic is replaced by the FOV splitting method. The optical design is optimized to reduce the number of optical elements, so as to ensure the high transmittance of the ultraviolet band. According to the spectral line dispersion requirements and the grating equation, the focal length and grating parameters of the imaging system are determined. The nonlinear dispersion of the grating is corrected by selecting the appropriate prism parameters. Correction of aberrations using aspheric surfaces in the collimator and imager simplifies system architecture while achieving high image quality. Using silicon immersed grating, the short-wave infrared region (SWIR) spectrometer has high dispersive capability. Meanwhile, the aperture of grating diffraction surface and the volume are reduced considerably.
Both the primary mirror and the secondary mirror use the freeform surface to achieve 108.8° full-field aberration correction (Fig. 3). The volume of the telescope system is only about 1/5 of the volume of the off-axis three-mirror system with the same specifications. Our optical path design is more compact, and the transmittance of the UV band without a dichroic is higher due to the integrated slit assembly (Fig. 7). The volume of the SWIR spectral imaging system with silicon immersion grating is only about 1/40 of that of the ordinary reflection grating spectrometer (Fig. 10). The addition of immersion medium to the grating, which reduces the angle of incidence and diffraction, can further reduce the aberration in the focal plane. The spectral resolution of each band is better than 0.53 nm (B1), 0.54 nm (B2), 0.44 nm (B3), and 0.25 nm (B4) (Fig. 12 and Table 3). The signal-to-noise ratios of B1, B2, B3, and B4 bands are better than 120, 200‒1000 (Fig.13), 640, and 130, respectively.
To meet the urgent needs of atmospheric composition monitoring in orbit with high temporal resolution, we develop a spectrometer prototype with a spectral resolution of 0.25‒0.55 nm covering the range of 270‒2385 nm. With a large coverage of better than 2600 km, the instrument can monitor the daily emission variation of polluting gases and greenhouse gases. The hyper-spectral optical system, which includes multiple complex optics and four different channels is aligned, integrated, and tested. The spectral and radiometric performance of the instrument is validated, laying the foundation for engineering development. Our technical results can be directly applied to the development of a spaceborne spectrometer for large-swath, multi-channel spectrometer in low Earth orbit, and can also be used for monitoring atmospheric composition in geostationary Earth orbit.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0622001 (2025)
Solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) is a valuable metric for assessing photosynthesis and vegetation stress. However, as SIF radiance constitutes less than 3% of the reflected canopy radiance, the spectral resolution of a spaceborne SIF detector should be below 0.3 nm. To ensure adequate signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), current spaceborne SIF imagers typically achieve spatial resolutions above 1 km. European Space Agency’ FLEX (Fluorescence explorer) mission recommends spatial resolution below 300 m, particularly for monitoring field and forest areas in Europe. The complex terrain and vegetation types in China, however, demand even higher spatial resolutions. In this paper, we propose a mid-resolution ultraspectral imager (MIRUS), designed for satellite-based SIF detection at a spatial resolution of 100 m. To evaluate the SIF retrieval performance of MIRUS, we develop a model that leverages SIF imaging spectrometer (SIFIS) data to calculate SIF retrieval accuracy.
Given the weak SIF radiance relative to canopy reflectance, the design specifications for MIRUS are shown in Table 1. MIRUS employs a low F# optic and a Littrow-Offner spectrometer to improve irradiance on the focal plane array (FPA) and reduce chromatic aberration, as shown in Fig. 2. The modulation transfer function (MTF) is optimized to be greater than 0.9, as shown in Fig. 3, while smile and keystone distortions are controlled to below 1.0% pixels and 3.3% pixels, respectively, as shown in Table 3. The spectral resolution is set at 0.3 nm, with a convex grating designed using rigorous coupled-wave analysis (RWCA) (Fig. 5), achieving an average diffraction efficiency of 0.7 (Fig. 7). The mechanism is designed as shown in Fig. 8. A prototype of MIRUS is produced, combining a telescope, a spectrometer, and an FPA. The prototype’s performance, including instrument line shape (ILS), spectral resolution, smile, keystone, and SNR, is tested, with results shown in Figs. 9?13.
To assess MIRUS’s SIF detection performance, we build a model relating SIF retrieval accuracy to the SNR of the spectral imager. The spectral range and resolution of the SIFIS on the Goumang satellite are comparable to the designed performance of MIRUS, with SIFIS achieving a maximum spatial resolution of 0.375 km×0.800 km in non-binning mode. In addition, we analyze 48 SIFIS image orbits from January to October in 2023, covering diverse environments such as tropical rainforests, savannas, deserts, and polar regions. Using singular value decomposition (SVD) in the 743?758 nm range, we measure retrieval errors across different radiance levels (Fig. 17) and develop an SNR model for SIFIS data (Fig. 16). The radiance of MIRUS within the same wavelength range is simulated using the MODTRAN 6.0 model, based on MIRUS’s orbital parameters and typical atmospheric, aerosol, and ground albedo parameters, as shown in Table 4. Subsequently, the SNR for MIRUS is calculated from this radiance, as shown in Fig. 16. Finally, the SIF retrieval accuracy for MIRUS is evaluated using a polynomial function of SNR, with results shown in Fig. 18. The relative errors for SIF retrieval are 1.22%?1.38% for 100 m GSD mode and 0.69%?0.86% for the 200 m GSD mode.
SIF serves as a “probe” for photosynthetic activity. “The remote sensing of chlorophyll fluorescence is a rapidly advancing front in terrestrial vegetation science, with emerging capability in space-based methodologies and prospects for diverse applications,” as noted by G. H. Mohammed. Due to the weak SIF radiance, it must be captured with an ultraspectral imager. Considering the imaging SNR, the spatial resolution of SIF radiance retrieved by spaceborne instruments typically exceeds 1 km. In this paper, we propose a mid-resolution spaceborne SIF detector featuring a small F# TMA and a Littrow-Offner spectrometer. The high-groove-density convex grating is designed using rigorous coupled-wave analysis (RCWA), resulting in significantly greater irradiance on the FPA compared to SIFIS. A prototype is produced and tested, achieving a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of 0.3 nm, a spectral sampling interval (SSI) of 0.1 nm, a smile distortion of less than 0.0035 nm, a keystone of under 0.06 pixel, and an SNR exceeding 206 at 10 mW·m-2·sr-1·nm-1. To evaluate the SIF retrieval accuracy of MIRUS, we develop a method to estimate accuracy based on the instrument’s SNR. The designed spectral performance of SIFIS matches that of MIRUS, and the spatial resolution of SIFIS is comparable to MIRUS. A polynomial relationship between SNR and SIF retrieval accuracy is established using radiance data from SIFIS. After calculating the typical radiance received by MIRUS, we use the SNR model to determine its typical SNR. Finally, the SIF retrieval accuracy is calculated using the polynomial, yielding relative errors of 1.22%?1.38% for the 100 m GSD mode and 0.69%?0.86% for the 200 m GSD mode, comparable to SIFIS performance.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0622002 (2025)
Adhesive bonding has become one of the most popular methods and a unique method sometimes for connecting optical components to their support structure in optical systems. For high-precision optical systems, the shrinkage stress caused by adhesive curing has a non-negligible influence on the mirror figure accuracy. At present, there is a lack of methods for monitoring the figure precision during the bonding, which makes the bonding process hard to control in time. The bonding process is planned to be optimized, and the dynamic monitoring problem of the bonded mirror figure should be solved to reduce the relative figure change rate before and after mirror bonding. We investigate thin glass mirror specimens with a diameter of Ф100 mm and a thickness of 10 mm to optimize the stress-relieving structure. Finally, a foundation can be laid for promoting stable opto-mechanical integration quality and widening the engineering application of light-thin mirrors.
Firstly, the principle of curing shrinkage stress of adhesive layers is analyzed. Secondly, based on the constitutive theory of adhesive materials, the viscoelastic mechanical model of the adhesive layer is introduced, and the relationship between the shrinkage stress of the adhesive layer and the curing time is analyzed. Then, the equivalent temperature loading method is adopted to simulate the influence of the adhesive shrinkage stress on the mirror figure, based on which the optimal design of the curing stress unloading structure is carried out by topology optimization. Finally, by employing the proposed adhesive bonding technique, a dynamic monitoring test platform for the curing figure of the adhesive layer is built, with the bonding process and optical tests carried out.
Based on the viscoelastic theory, the mechanical model of the adhesive layer is built, and the performance parameters of the adhesive layer are determined according to the theoretical calculation and finite element simulation, with the 0.2 mm thickness of the adhesive layer and minimum adhesive area of 300 mm2. The equivalent temperature loading method is adopted to simulate the effect of the adhesive curing shrinkage on the mirror figure, and it is verified that the results of the curing shrinkage stress of the adhesive layer before optimization are consistent with those of theoretical analysis. The results show that the shrinkage stress of the adhesive layer is 0.016 MPa and the mirror figure accuracy RMS is 0.018λ after the optimized bonding structure, which indicates that the designed adhesive structure meets the application requirements. According to the whole history curves of the PV and RMS values of the mirror figure during the curing process, it is found that the curing time is recommended as 15000 s, and the final figure accuracy RMS is 0.021λ/0.018λ for the non-optimized/optimized structure respectively. The test results show that the structure of the optimized adhesive joint is better than that before optimization, and the simulation results are verified by experiments.
In studying the influence of optomechanical hetero-bonding processes on the mirror figure, the mechanical model of the adhesive layer is built by analyzing the principle of curing shrinkage stress of the adhesive layer combined with the viscoelastic theory, with the curing stability time of the adhesive layer recommended as 15000 s. By adopting the combination of viscoelastic finite element modeling method and the equivalent temperature loading method, the influence of adhesive curing shrinkage stress on the figure is simulated, and then a reasonable stress-relieving bonding structure is optimized. By conducting the optimal design of structural topology, the adhesive layer bonding area is optimized from 490 to 300 mm2, a reduction of 39%, and the corresponding RMS of the optimized mirror surface is stabilized around 0.018λ. The mirror bonding equipment for monitoring the mirror figure dynamically is designed to ensure the bonding quality. The dynamic monitoring bonding process of the adhesive layer curing figure is established at room temperature. The curing time and surface deformation are tested during the curing process focusing on the mirror figure stability. As a result, we verify the effectiveness of the structural optimization, the bonding process, and the finite element model.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0622003 (2025)
Hyperspectral remote sensing technology has become increasingly crucial in agricultural and environmental monitoring. Targeting the high-dimensional spatial characteristics of hyperspectral remote sensing data, we propose an advanced machine learning method to extract and validate the characteristic bands associated with soil nutrient contents. By applying this method, characteristic bands of various soil nutrients can be identified, and their contents efficiently assessed. This research provides a solid theoretical foundation for large-scale, rapid soil nutrient monitoring using drone-based hyperspectral remote sensing. It presents a reliable solution for the development and application of hyperspectral remote sensing technology, offering significant value for agricultural production and environmental protection.
Spectral experiments are conducted using drones equipped with hyperspectral sensors, collecting soil reflectance data across 176 spectral bands within the range of 398?1003 nm. The extraction of soil nutrient characteristic bands involves two main steps. The importance of the 176 spectral bands is ranked using a combination of random forest (RF) and differential evolution (DE) algorithms. The random forest method evaluates the importance of each spectral band, while the differential evolution algorithm refines the selection of spectral features, ensuring that the most informative bands are retained. This process results in a subset of spectral features indicative of soil nutrient content. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is employed to determine the relative importance of the spectral features in the subset. By ranking and applying weight thresholds, characteristic bands of different soil nutrients are successfully identified from the hyperspectral data. Finally, a quantitative inversion model for soil nutrient content is developed using a back-propagation neural network (BPNN).
Using available potassium as an example, the extracted characteristic bands are identified as 469.0, 501.6, 581.2, 697.2, 791.8, 795.4, 802.5, and 954.8 nm. Among these, the three most significant bands, 469.0, 501.6, and 954.8 nm, show the highest correlation with soil potassium content, making them critical for accurate nutrient assessment. The back-propagation neural network model trained with these characteristic bands achieves remarkable results. In the Training set, the coefficient of determination (R2) is 0.954 (Fig. 8), the ratio of performance to deviation (RPD) is 4.78, and the root mean square error (RMSE) is 14.32 mg/kg (Fig. 11). In the validation set, the model achieves R2 of 0.848, RPD of 2.21, and RMSE of 16.71 mg/kg (Fig. 11). These results significantly outperform those obtained using the traditional first-order derivative mathematical transformation method, which yields R2 values of 0.729 and 0.521, RPDs of 1.81 and 1.13, and RMSEs of 36.02 mg/kg and 191.05 mg/kg in the modeling and validation sets, respectively (Table 2).
The findings of this paper demonstrate the effectiveness and feasibility of machine learning methods for extracting hyperspectral soil nutrient characteristic bands. By integrating advanced algorithms such as random forest, differential evolution, and analytic hierarchy process, we offer a robust solution for the application of hyperspectral remote sensing technology. It enables more accurate and efficient soil nutrient assessments, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with traditional soil sampling and analysis. The successful extraction of characteristic bands and the development of a reliable predictive model underscore the potential of drone-based hyperspectral remote sensing technology for large-scale, rapid soil nutrient monitoring. This approach not only improves the precision of soil nutrient assessments, but also supports informed decision-making in agricultural production and environmental management. The outcomes contribute to enhanced crop yields, better resource allocation, and more sustainable agricultural practices.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628001 (2025)
Place recognition is designed to help a robot or a navigation system determine if it is in a previously visited location. Specifically, it involves querying the image or LiDAR point clouds of the local scene of a given robot or a navigation system to find the best match within the acquired sequence data. Position recognition is a key step to eliminating the accumulated errors of robot motion over time and restoring high-precision maps. It is often used in dynamic real-time positioning and mapping, virtual reality technology, automatic driving, and other fields. Place recognition can be divided into two categories: visual and laser. LiDAR 3D point cloud data effectively mitigates the influence of lighting and seasonal changes, which makes it suitable for large-scale, complex scenes. However, it faces challenges such as occlusion and large viewing angles. Although methods like PointNetVLAD have made progress in point cloud processing by extracting the global descriptor of a single-frame point cloud, they ignore the correlation between different clouds in the feature pooling stage. These methods mainly rely on the powerful NetVLAD clustering network for point cloud classification. However, NetVLAD has a large number of parameters and is computationally complex, which seriously affects operational efficiency. Therefore, this paper proposes a deep learning-based place recognition method that uses feature fusion. In this method, two frames of point clouds are regarded as a new point cloud, and by aggregating the features of the point clouds, the method determines whether the two frames represent the same place. The key innovation of this method lies in the design of the feature enhancement module, which effectively extracts the relevant information between the two frames of point clouds. Additionally, to improve operational efficiency, this paper employs a lightweight feature aggregation network to achieve faster processing while maintaining high precision.
We propose a LiDAR point cloud place recognition network based on feature fusion. The network is mainly divided into four steps. Firstly, two point clouds are preprocessed, which includes downsampling and ground filtering. Next, feature extraction is carried out to obtain the local features of each point cloud. The local features are then regarded as the local features of a new point cloud (z), and the new local features are weighted by the feature enhancement module. Afterward, the feature aggregation network is used to aggregate the local features of the new point cloud (z) into global features. Finally, the global descriptor is normalized through a full join to obtain the similarity score.
As shown in Table 1, the Our-MV method and Our-NV method show superior performance compared to all other methods. In contrast, the two traditional methods, SC and M2DP, which are capable of describing the global characteristics of the point cloud, do not perform as well as deep learning methods in terms of generalization. For example, in the 02 sequence, due to severe occlusion in most point clouds, the performance of the SC method is suboptimal, with an accuracy of only 0.858. In the 08 sequence, due to the existence of a large-scale reverse closed-loop, the SC method also performs poorly, achieving an accuracy of only 0.811. This is mainly because the SC method mainly focuses on the top view of the point cloud, neglecting details from other angles, which results in the loss of many key features during projection. When comparing the Our-MV and Our-NV methods, it can be found that Our-MV outperforms Our-NV in each sequence and overall accuracy. This is mainly because MixVPR accounts for long-term feature relationships during feature aggregation, while NetVLAD focuses more on local features. Therefore, Our-MV can capture the characteristic information of point clouds more comprehensively. Figure 6 shows the accuracy-recall curves for the comparison methods. The method proposed in this paper maintains stable accuracy across different thresholds, which fully demonstrates its high performance in distinguishing between positive and negative samples. According to the visualization results in Figs. 7 and 8, it can be seen that the performance of the Our-MV method is superior to that of Our-NV in different scenes, which confirms the effectiveness of our changes. The ablation experiment in Table 2 fully reflects the effectiveness of the feature enhancement module. In addition, as shown in Table 3, the number of parameters in the Our-MV method is reduced by up to 73.88%, and the processing time is slightly decreased (by about 7%). Table 4 shows the effects of the proposed method under different thresholds, which illustrates that the proposed method is robust to changes in the distance threshold.
In this paper, we propose a feature fusion-based deep learning place recognition method. In this method, two frame point clouds are regarded as a single point cloud, and by aggregating features from the point clouds, the method determines whether the two frame point clouds represent the same place. The key innovation of this method lies in the design of the feature enhancement module, which effectively extracts the relevant information between the two frame point clouds. Moreover, to improve operational efficiency, we also adopt a lightweight feature aggregation network to achieve faster processing while maintaining high precision. However, the loss function adopted in this paper is mainly a global optimization function, which imposes relatively weak constraints on the features of local key points. During global optimization, the model may ignore the influence of local features in the learning process, potentially affecting the accuracy of place recognition. To further improve the model's performance, we plan to explore increasing the model's complexity in future research and consider incorporating a local feature similarity loss function to enhance the accuracy of local feature extraction.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628002 (2025)
To address the issue of stripe noise in the overlap regions of multispectral images captured by focal plane modules (FPMs) with charge-coupled devices (CCDs), we propose a method to reconstruct the radiometric model in these areas by synchronizing the correction of overlapping pixels with the normalization of radiometric data. After correcting the same pixels within the overlap region, the radiometric model is rebuilt by summing the detected energy and applying a moment-matching technique to ensure smooth transitions along the region’s edges. The method proposed in this paper reduces image saturation in the overlap regions post-correction and effectively addresses stripe noise. In addition, it optimizes the stripe coefficient to be more responsive in affected regions without influencing non-affected regions, enabling a quantifiable analysis of stripe energy. The experimental results show significant reductions in stripe noise or even its complete elimination, a decline in stripe coefficients, and a notable improvement in image radiometric consistency.
When capturing the same object, incident light is split, resulting in the overlap area detector receiving less incident energy and a lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) than the non-overlap area detector. This leads to inconsistent responses and greater susceptibility to stripe noise in the overlap area. In this paper, we propose a relative radiometric correction method that reconstructs energy in these regions by combining the radiometric values from adjacent CCDs. By superimposing the digital number (DN) of pixels with the same name from adjacent CCDs, this approach restores the average DN of the overlap area detector to align with that of non-overlap areas, thus enhancing SNR and response consistency while reducing stripe noise. The basic principle is illustrated in Fig. 1.
In the gobi in Dunhuang and Qinghai Lake regions, generalized noise in overlap area images after correction is reduced to 4.5‰ and 4.1‰, respectively, well below the 3% threshold, demonstrating the efficacy of this energy reconstruction method in removing strip noise while maintaining radiometric accuracy. The radiometric uniformity in the overlap areas across the regions is compared, demonstrating that the proposed method effectively eliminates stripe noise, resulting in a significant improvement in image quality (Fig. 11). A comparison between Figs. 12 and 13 reveals that the stripes in images processed by the proposed method have disappeared, significantly enhancing image quality. Detailed comparisons of the two methods, based on the average DN of pixels at fringe positions, are provided in Fig. 14. As shown, the histogram statistics method results in pronounced spikes in the average DN when detecting streaks. In contrast, the proposed method yields a relatively smooth average DN in fringe areas, eliminating visible fringes in the image. Using the traditional histogram-based matching method, the peak values of fringe coefficients in overlap areas for city, desert, and snow mountain images are approximately 50, 15, and 70, respectively. However, the proposed method reduces these peaks to around 10, 3, and 15, respectively. Fig. 15 further illustrates that the peak position of the fringe coefficient corresponds to the location of the fringe. As shown, the fringe coefficient in overlap areas is notably lower with the proposed method, eliminating visible fringes and resulting in superior image quality.
In this paper, we reconstruct the radiometric model in overlap areas by employing same-pixel matching and summation of detection energies, followed by a relative radiometric correction. Transitional color leveling is then applied to overlap edges using the moment-matching method, which achieves effective relative radiometric correction. The method addresses stripe noise in multispectral image overlap regions, reduces saturation, and ensures uniformity post-correction. Compared to traditional histogram-based matching methods, this method significantly minimizes or eliminates stripe noise in overlap areas. In tests with city, desert, and snow mountain images, peak strip coefficients drop from 50, 15, and 70 to 10, 3, and 15, respectively, enhancing radiometric consistency and image quality. This method shows great potential for broad applications in optical image processing.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628003 (2025)
The atmospheric boundary layer height (ABLH) is a critical factor in determining air pollution levels. Continuous observation of ABLH throughout the day and night is crucial for evaluating air quality. Light detection and ranging (LiDAR), one of the most traditional methods for measuring ABLH, offers high measurement accuracy and can provide detailed vertical atmospheric profiles with high temporal and spatial resolutions. However, there are several limitations. Current methods have low time resolution, with most sites operating only at specified times. Some sites provide data up to four times a day, which does not allow for continuous monitoring of the ABLH. LiDAR is an effective remote sensing method for detecting boundary layer height because it offers continuous measurements and provides high-resolution vertical atmospheric profile data. However, current LiDAR algorithms are prone to interference from complex atmospheric structures, such as cloud layers and suspended aerosols, which can affect the accuracy of boundary layer height detection under various conditions. Therefore, addressing these interferences is crucial. We propose an improved deep forest algorithm that integrates different remote sensing data to address the challenges associated with detecting boundary layer height using LiDAR.
We propose an improved deep forest algorithm that fuses multiple sources of remote sensing data. The optical data from micro-pulse LiDAR and the Doppler LiDAR, along with temperature, humidity, wind speed, and air pressure data from ground meteorological stations, are used to construct the dataset. We improve the deep forest algorithm in two main ways: 1) by employing feature selection methods to replace multi-dimensional scans, effectively removing redundant variables, and enhancing the dataset’s ability to capture relevant features; 2) a level-linked forest approach is used, where the input of each level in the linked forest is a combination of the output vectors from all previous levels and the original input feature vectors. The influence of the final result of the linked forest is evaluated, and the final output of the linked forest is used to replace that of the averaging method with a weighted approach. This adjustment aims to reduce the influence of weaker learning models on the outcome. Ultimately, by enhancing deep forest algorithms and applying them to train and predict the fused dataset, we obtain the final boundary height with improved accuracy.
The correlation coefficient between the boundary layer height obtained from the proposed method and the radiosonde measurements at the SGP site in 2020 is as high as 0.935 (Fig. 4). This is significantly higher than those of traditional methods like the gradient method and the threshold method, and it compares favorably with other machine learning algorithms. Case studies on clear days (Fig. 7) and cloudy days (Fig. 8) demonstrate that the results of the proposed method aligns closely with radiosonde measurements on clear days and remains unaffected by clouds and aerosols on cloudy days. To further validate the method’s performance, 103 cases of clear weather data (Fig. 7) and 50 cases of cloudy or aerosol weather data (Fig. 8) are analyzed. The results show that the proposed method improves the accuracy of ABLH retrieval on clear days and is robust against cloud and aerosol interference on cloudy days. In addition, an analysis of 377 daytime cases (Fig. 14) and 50 nighttime cases (Fig. 15) indicates that the method effectively improves the accuracy of ABLH retrieval during both day and night.
The improved deep forest algorithm, based on fused remote sensing data, significantly enhances the accuracy of LiDAR-based ABLH retrieval, achieving a correlation coefficient as high as 0.935 with radiosonde data. The method is effective in tracking the diurnal variation of the boundary layer height. Case analyses under different weather conditions demonstrate that the proposed method is robust and unaffected by complex atmospheric structures or nighttime conditions, providing reliable ABLH measurements.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 21, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628004 (2025)
In recent years, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) based on light detection and ranging has been playing an increasingly important role in computer vision, robotics, and other fields. Existing SLAM frameworks are generally based on the assumption of a static world; however, dynamic objects in the environment, such as walking people and moving vehicles, inherently exist. These objects leave ghosts on the 3D map constructed using SLAM. These ghosts are treated as obstacles in the map, hindering the motion planning of mobile robots, causing errors in LiDAR odometry, which affects the effectiveness of SLAM. Therefore, detection and removal of dynamic points from the point-cloud map are particularly important before performing the corresponding tasks. To address the challenge of mapping in dynamic environments, numerous researchers have proposed methods for building static maps that leverage the geometric discrepancies between individual scans and a map cloud. Despite these advancements, two primary limitations remain in many current systems. First, when the pose estimations derived from scan registration become imprecise, the geometric relationship between the current scan and map cloud is compromised, leading to the erroneous exclusion of numerous static points. Second, most existing approaches overlook instance-level information, which causes points belonging to moving objects to persist within a map cloud. To address these limitations, this study proposes a LiDAR static mapping method based on spatiotemporal constraints.
To enhance the effectiveness of dynamic point removal, this study proposes a new method for building static maps using LiDAR, considering spatiotemporal constraints. First, a ground segmentation algorithm based on candidate height values is introduced to improve ground segmentation. Second, a dynamic point detection algorithm based on grouped optimization and a pseudo-occupied grid is proposed to group scan frames, thereby introducing a new feature descriptor to perform the initial detection of dynamic points within the groups. Third, by leveraging temporal information before and after grouping, a dynamic point region-growing algorithm based on interframe matching distance constraints and a clustering verification strategy based on edge detection are combined to address the issues related to false positives and false negatives in dynamic point detection. Finally, all dynamic points are removed to obtain the ultimate static map.
In this study, sequences 00 (frames 4390?4530), 01 (frames 150?250), 02 (frames 860?950), 05 (frames 2350?2670), and 07 (frames 630?820) were selected as static map construction benchmarks, with the numbers in parentheses indicating the start and end frames. The selected frames encompassed diverse scenes such as rural areas, highways, and intersections, with a substantial presence of dynamic objects for simulation validation. To quantitatively assess the efficacy of our algorithm, we relied on three key metrics: static point-cloud preservation rate (PR), dynamic point-cloud removal rate (RR), and their harmonic mean
To address the issue of decreased quality in static maps generated by LiDAR due to the presence of dynamic objects in real-world environments, this paper proposes a spatiotemporally constrained method for constructing static maps using LiDAR. This method leverages the temporal inconsistency of dynamic point clouds and introduces a novel feature-descriptor constraint to obtain preliminary detection results for dynamic points. Subsequently, by utilizing the temporal information before and after multistep checks, growth operations were conducted on the dynamic points. The experimental results consistently demonstrated that compared with existing methods, the proposed approach exhibits superior performance in both the removal of dynamic points and preservation of static points. Future work will involve incorporating point-cloud distribution characteristics, utilizing statistical hypothesis test to eliminate falsely detected points with low confidence, and adapting thresholds based on the motion speed of dynamic objects to further enhance the quality of the static maps generated by LiDAR.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628005 (2025)
The laboratory module II of the China Space Station (CSS), known as the Mengtian lab experiment module, has been part of the CSS since its launch in October 2022. It carries a Sr optical clock, an H-maser, and a laser-cooled microwave clock, along with a microwave link and a pulsed laser link. The CSS mission’s pulsed laser time-frequency transfer (CLT) system is led by the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO). In this paper, we aim to present the development and performance evaluation of the CLT system.
The CLT payload unit measures 230 mm×190 mm×169 mm, with a mass of 6 kg and power consumption of approximately 25 W, subject to fluctuations depending on the operating mode. The onboard hardware includes a laser retro-reflector, a single-photon detection package, and an event timer. The CLT detector utilizes an avalanche photodiode operating in Geiger mode, featuring the K14 SPAD chip with a 100
The temperature-induced delay drift of the CLT detector is mitigated through optimization of the comparator configuration and bias voltage, including the adjustment of the feedback coefficient. Experimental results demonstrate that, with a turning point at 21 ℃, the CLT detector achieves temperature drift compensation of 0.14 ps/℃ when operating above 21 ℃. The detection optics maintain a 25% relative photon change across varying incident optical angles. Ground-based laboratory tests have confirmed that the CLT payload achieves a timing precision of 23 ps, with an instability of less than 0.5 ps over the course of one day and 0.09 ps over 300 s. Ranging experiments using the CLT laser retro-reflector array (LRA) are conducted by ground-based satellite laser ranging (SLR) systems located in Shanghai, Xi’an, and Beijing. Moreover, dedicated CLT ground stations in Xi’an and Beijing conduct satellite-based CLT measurements. The results indicate that the ranging precision of the Xi’an and Beijing ground stations is approximately 4 mm, with a clock bias measurement precision of 22 ps.
Our research marks a breakthrough in the engineering development of the pulsed laser time-frequency transfer system. As ground stations connect to high-performance atomic clock signals and sufficient measurement data is collected, the system offers profound insights into the fields of time-frequency metrology, space geodesy, and fundamental physics research. It enables the calibration and validation of microwave systems, a better understanding of clock behavior, comparison of clocks across remote observatories, and testing of Einstein’s gravitational redshift effect.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628006 (2025)
The terrestrial ecosystem carbon monitoring satellite (CM-1) is China’s first forestry-focused remote sensing satellite designed to measure the vertical structure of terrestrial ecosystem forests. Equipped with a 5-beam LiDAR, the satellite collects high-precision ground elevation data. However, laser altimetry data is affected by atmospheric conditions and complex terrain during transmission, making it unsuitable for direct use as elevation control points in its raw form. To address this challenge, we develop an automatic classification extraction method for laser elevation control points tailored to CM-1. This method leverages the characteristics of satellite data and employs multi-criteria constraints to ensure high elevation accuracy, providing critical support for generating regional digital surface model (DSM) using stereo images.
To ensure the extracted laser elevation control points meet accuracy requirements, we propose a multi-criteria constraint-based automatic classification method. First, the elevation difference between the laser point and an open digital elevation model (DEM) is calculated, and laser points with differences exceeding 30 m are flagged as gross errors. Coarse screening is then conducted to assess data validity. The maximum amplitude of the echo waveform is analyzed to identify and eliminate saturated data, while low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) data is also eliminated. Subsequently, only laser data with a single waveform peak is retained to mitigate the influence of complex ground surfaces on elevation accuracy. Using the laser radar equation, the relationship between surface slope, received waveform pulse width, and elevation accuracy is analyzed. The pulse width is employed to estimate the elevation accuracy of laser points, which are then classified based on different accuracy levels.
High-precision airborne laser point cloud data from Shenyang and Pennsylvania are used to validate the accuracy of extracted laser elevation control points. In Shenyang, 1353 laser points are initially identified, of which 778 are retained after screening. The overall elevation accuracy improves from 2.410 m to 0.440 m (Table 3). In Pennsylvania, 23713 laser points are identified with 5226 retained, resulting in an accuracy improvement from 4.130 m to 0.747 m (Table 4). The influence of different screening parameters, including DEM elevation difference, saturation, SNR, and waveform peak count, is statistically analyzed in the two test areas (Table 5). A regional DSM test is conducted by integrating laser elevation control points with stereo images. The results demonstrate a significant improvement in DSM accuracy, with elevation errors reduced from 11.45 m to 2.27 m.
In this paper, we first analyze the quality of multi-beam laser data from the CM-1. Based on the characteristics of the laser data, a multi-criteria constraint method for extracting laser elevation control points is developed, enabling classification by elevation accuracy. Validation in Shenyang and Pennsylvania demonstrates significant improvements in elevation accuracy. The errors of the extracted laser elevation control points are reduced from (0.099±2.410) m and (0.945±4.130) m to (-0.007±0.440) m and (-0.086±0.607) m, respectively. The extracted points meet elevation control requirements for 1∶50000 or larger scale stereo mapping. Moreover, integrating laser elevation control points with multi-angle block adjustment reduces the root mean square error (RMSE) of 10 m grid DSM, generated from ±19° images, from 11.45 m to 2.27 m, meeting the elevation accuracy requirements for 1∶50000 scale topographic mapping.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628007 (2025)
As a key element in geographic information systems, building change detection plays a crucial role in evaluating land use, urban development, and disaster damage assessment. Over the past decade, many methods have been proposed for change detection, evolving from pixel-based to object-based approaches that incorporate contextual information. However, traditional methods often struggle with the complexities of high-resolution remote sensing imagery, particularly in handling challenging scenes, leading to limitations in accuracy. With the advent of deep learning, especially deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), change detection in remote sensing has seen significant improvements. Despite these advancements, deep learning-based methods still face challenges such as such as insufficient utilization of multi-scale information, weak feature representation, and inadequate suppression of pseudo-changes. To address these limitations, we propose a novel method for building change detection in high-resolution remote sensing images, leveraging a dense hybrid attention network (DHANet).
The proposed DHANet utilizes an encoder-decoder architecture. During the encoding phase, a Siamese ResNet network with shared weights extracts multi-level, multi-scale features from bi-temporal images. In addition, dilated convolution (DC) is incorporated to enhance the receptive field of the ResNet, allowing for better feature extraction. A multi-scale feature aggregation module (MSA) is then utilized to effectively integrate the extracted multi-level and multi-scale features between the encoder and decoder, facilitating the detection of changed buildings of various shapes and sizes, while preserving spatial details. Furthermore, to fully exploit contextual information, reduce redundant feature interference, and generate more discriminative features for change detection, multi-level features are refined using a hybrid attention module (HAM), which combines the interlaced sparse self-attention module (ISSA) with the convolutional block attention module (CBAM). Finally, a deep supervision strategy is applied to optimize model performance. Multiple change prediction maps are generated at various stages during the feature fusion process, and the total loss value is obtained through weighted calculation.
LEVIR-CD and WHU-CD. On the LEVIR-CD dataset, DHANet significantly outperforms models such as FC-EF, FC-Siam-Conc, FC-Siam-Diff, STANet, IFN, and BIT in both F1 score and Intersection over Union (IoU), with F1 scores improving by 7.64, 7.35, 4.73, 3.78, 1.49, and 0.89 percentage point, respectively. On the WHU-CD dataset, DHANet also surpasses the aforementioned models in F1 and IoU, with F1 scores increases of 11.25, 8.51, 8.13, 7.19, 2.28, and 2.08 percentage points, respectively. Moreover, qualitative visual results demonstrate that DHANet achieves superior change detection outcomes, particularly in identifying buildings of varying shapes and sizes. The resulting change maps exhibit clearer building boundaries and maintain high internal compactness, closely aligning with actual labels. To validate the effectiveness of the key modules (DC, MSA, and HAM), we conduct a series of ablation experiments on the LEVIR-CD dataset. The significant improvements shown in the quantitative results (Table 3) not only confirm the individual effectiveness of the DC, MSA, and HAM modules but also highlight their synergy in enhancing change detection performance.
In this paper, we propose a novel DHANet for building change detection in high-resolution remote sensing images. DHANet effectively integrates multi-scale feature extraction through a Siamese ResNet network with shared weights, attention mechanisms, and DC. The MSA enhances feature fusion, while the HAM refines features for improved discriminative power. A deep supervision strategy ensures the progressive refinement of change maps throughout the feature fusion process. Experimental results indicate that DHANet achieves superior performance compared to other mainstream methods and strikes a good balance between accuracy and computational complexity. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of the proposed modules, demonstrating the potential of DHANet for detecting building changes in complex scenes using high-resolution remote sensing data.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628008 (2025)
Supercontinuum lidar (SC lidar) is a type of lidar with both broad spectrum and laser characteristics. SC lidar combines the advantages of passive spectrometers and monochromatic lidars, offering significant potential for atmospheric multi-element monitoring. However, the broader application of SC lidar depends on increasing its laser’s average output power. In this article, we use numerical simulation to establish the SC lidar function and models for background radiation during both daytime and nighttime. We also analyze the contributions of various noise sources and perform sensitivity analysis on parameters influencing atmospheric radiation transmission. Finally, we discuss the power requirements for spaceborne greenhouse gas detection applications using SC lidar (Fig. 1).
We present an SC lidar equation in section 2.1, based on the traditional lidar equation. The supercontinuum laser source used in this paper is from NKT Photonics, with its spectral power density shown in Fig. 2. Additional parameters of SC lidar are shown in Table 1. Solar radiation is considered the primary background noise during the day, while lunar radiation and nighttime light (NTL) radiation are the main nighttime background noises (Sections 2.2 and 2.3). Lunar irradiance is calculated by multiplying solar irradiance by lunar albedo (Fig. 3), empirically fitted based on the robotic lunar observatory (ROLO) model. National aeronautics and space administration (NASA)’s Black Marble product, specifically the monthly moonlight and atmosphere-corrected NTL composite (VNP46A3), is used to calculate nighttime light intensity. By combining the distribution ratios of nighttime light sources with VNP46A3 products, we obtain characteristic nighttime light radiance spectra for cities like Las Vegas and Guangzhou (Fig. 4). The SCIATRAN radiative transfer model is then used to simulate the SC lidar backscatter signal power, as well as the solar and lunar radiation intensities. The baseline results are shown in Fig. 5.
We use the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to evaluate error contributions and conduct sensitivity analyses. Besides background radiation, SC lidar performance is influenced by internal detector noise, such as dark current noise and shot noise [Eq. (7)]. The total SNR is defined in Eq. (8). To estimate the contribution of each noise term to the total noise, we calculate the derivative of various noise sources relative to the total noise at an altitude of 120 km (Table 3). Solar radiation dominates daytime noise, while dark current noise is the main factor at night. Surprisingly, lunar and NTL radiation contribute minimally to the total nighttime noise compared to the lidar signal power. Sensitivity analysis of variables such as atmosphere models, solar zenith angle (SZA), aerosol models, dark current density, and surface reflectance (Figs. 6 and 7) show that water vapor absorption bands are highly sensitive to changes in all selected parameters, particularly the atmospheric model [Fig. 6(a)]. Other spectral bands show minimal sensitivity to atmospheric model changes. SZA affects solar intensity; thus, as SZA increases, solar intensity decreases, leading to higher SNR [Fig. 6(b)]. We examine six aerosol scenarios with varying types and visibilities [Figs. 6(c) and (d)], finding that SNR decreases sequentially across maritime (23 km), maritime (50 km), rural (50 km), rural (23 km), urban (50 km), and urban (23 km) scenarios. Notably, aerosol influences at nighttime are greater than during the day. Reducing dark current density improves SNR [Figs. 7(a) and (b)], as dark current noise significantly influences nighttime SNR. High surface reflectivity also enhances SNR [Figs. 7(c) and (d)]. To estimate the total peak power needed for spaceborne SC lidar applications, we conduct experiments under the following conditions: 1) daytime with SZA is 30°, 70°, 89° and
Through simulation experiments and error analysis, the following conclusions are drawn: 1) Solar background radiation and dark current noise are the primary sources of errors, while lunar and NTL radiation have limited influence. 2) Sensitivity analysis shows that during the day, changes in most parameters are not significant except for SZA due to the influence of solar radiation. At night, various parameters have a more noticeable effect on SNR. 3) The total peak power of SC lidar is the main obstacle to its application. The minimum required total peak power is 1×108 W. Further research is essential for future SC lidar applications.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628009 (2025)
Image data has been widely used in various applications due to advancements in data acquisition platforms such as satellites, drones, and mobile measurement vehicles, as well as sensors like multispectral and hyperspectral cameras, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), and lidar scanners. These advancements enable high-resolution data collection across different wavelengths and perspectives, enhancing applications in remote sensing, real-time localization, and medical diagnostics. However, integrating multimodal image data from various sensors presents challenges due to nonlinear radiation distortion (NRD) and geometric variations like rotation and scale differences. Traditional multimodal image matching methods often struggle with these complexities. Conventional approaches either convert images to a common modality or enhance feature robustness against modality differences. While recent advances in deep learning have improved matching performance, practical applications still face challenges due to the lack of comprehensive datasets, difficulties with complex data, and high computational demands. To address these issues, we propose a nonlinear radiation and geometric invariant matching (NRGM) method. NRGM effectively handles NRD, scale variation, and rotation by using multi-directional and multi-scale filtering to build direction index maps with stable local structures. A robust principal direction estimation method achieves rotation invariance, and a novel matching framework combining geometric invariant and template matching improves accuracy. This approach significantly enhances multimodal image matching by overcoming both geometric and radiometric distortion.
NRGM adopts a two-stage framework involving feature matching and template matching. In the feature matching stage, images are transformed into the frequency domain using Log-Gabor filters, and key features are detected via phase congruency and weighted moment maps to improve robustness against illumination variation. The primary direction estimation technique involves extracting a directional index map from Log-Gabor filter responses, summing the index values within a local region, and analyzing the histogram to determine the feature’s primary orientation. Feature correspondences are established using nearest-neighbor distance, with outlier removal refined by the fast sample consensus algorithm. In the template matching stage, high-dimensional template features are constructed from Log-Gabor responses, and a three-dimensional phase correlation strategy is employed for precise matching, effectively aligning features despite variations in scale and rotation. NRGM integrates robust feature detection, accurate direction estimation, and precise template matching, delivering high-quality results even in the presence of severe NRD and geometric distortions.
A comprehensive evaluation of NRGM is presented, including parameter settings, qualitative and quantitative comparisons with advanced algorithms such as SIFT, RIFT, ASS, GIFT, HOWP, MatchFormer, and SemLA, as well as robustness testing. A diverse set of multimodal images—such as visible light, infrared, and depth images—is used to assess NRGM’s performance. Sensitivity analysis identifies optimal parameters for NRGM: scale s=4, orientations o=12, and window size l=84, resulting in the highest number of correct matches (NCM) and the lowest root mean square error (RMSE) (Table 2). Figs. 8?10 demonstrate that SIFT performs well for RGB-NIR pairs but struggles with modality differences, while RIFT, despite its robustness to NRD, fails to handle scale variations effectively. HOWP, MatchFormer, and SemLA show instability with multimodal images. While ASS and GIFT perform reliably, they exhibit limitations with Optical-SAR and Optical-IR pairs. In contrast, NRGM excels by correctly matching all 9 image pairs. Its advanced feature detection, descriptor, and matching enhancement strategies ensure high precision and robustness, making it highly effective across diverse modalities and conditions. Tables 3?5 provide detailed quantitative results for different algorithms across visual, medical, and remote sensing datasets. SIFT performs well with RGB-NIR pairs but struggles with larger modality differences. HOWP, MatchFormer, and SemLA show some robustness but deliver inconsistent results across modalities. RIFT, ASS, and GIFT demonstrate higher reliability, with GIFT particularly excelling with Optical-SAR and Optical-IR pairs. NRGM, however, outperforms all algorithms, successfully matching all image pairs and achieving superior metrics in NCM, Precision, Recall, and RMSE. NRGM's advanced feature detection, feature description, and enhancement strategies make it highly effective and precise in addressing diverse multimodal challenges. In addition, NRGM demonstrates stable performance with periodic accuracy fluctuations during image rotations. Table 6 shows average run times for SIFT, RIFT, HOWP, ASS, MatchFormer, SemLA, GIFT, and NRGM on various datasets. While SIFT, implemented in C++, remains the fastest, SemLA, MatchFormer, and HOWP perform efficiently but struggle on challenging multimodal datasets. RIFT has the lowest efficiency due to its iterative optimization. ASS, GIFT, and NRGM share similar efficiency levels, outperforming RIFT, with NRGM showing advantages in both accuracy and efficiency.
A novel method, NRGM, is introduced for multimodal image matching, designed to effectively handle various image modalities, scales, rotations, and other geometric transformations. NRGM leverages multi-scale and multi-directional Log-Gabor filter responses, providing the algorithm with inherent robustness against noise. The method begins by detecting prominent and highly repetitive feature points on the phase congruency maps. It then utilizes directional index information to describe local image structures and estimate the principal orientation, ensuring that NRGM remains invariant to image rotations. Finally, NRGM enhances matching performance by constructing template features from multi-scale and multi-directional filter results. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments across diverse image modalities validate NRGM's effectiveness. Future research will focus on using convolutional neural networks to create more precise orientation index maps, improving the estimation of principal orientation and feature descriptor construction. To mitigate the high computational cost associated with Log-Gabor filters, alternative lightweight filters or methods will be explored to extract multi-scale and multi-directional image information, aiming to improve the algorithm's computational efficiency.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628010 (2025)
Ozone is a crucial trace gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, known for its highly active chemical properties and its involvement in numerous photochemical processes. The temporal evolution and spatial distribution of ozone mixing ratio have significant implications for ecological and climate change, and understanding their vertical distribution is essential for studying mesospheric states and processes. Satellite remote sensing technology plays a key role in ozone monitoring due to its advantages, including low environmental influences, good spatial and temporal continuity, and high resolution for global coverage. However, direct detection via satellite remote sensing, using occultation or ultraviolet absorption and infrared radiation principles, faces several engineering challenges that can lead to inaccuracies in ozone mixing ratio measurements. The O2(a1?g) airglow produced by ozone ultraviolet photolysis, however, offers several advantageous properties, such as strong bulk emissivity, wide spatial coverage, and minimal self-absorption effects. Indirect retrieval of ozone profile information using the O2(a1?g) airglow is both accurate and stable. In this paper, we explore the intrinsic connection between the modeling of airglow photochemical reactions in the O2(a1?g) band and ozone mixing ratio. Using the limb-viewing observation mode, airglow radiance spectral signals in the O2 infrared atmospheric bands are processed with kinetic photochemical modeling to accurately retrieve ozone profiles in the mesosphere (50?90 km).
Satellite remote sensing of ozone profiles using the O2(a1?g) band as a target source aims to enhance the accuracy of mesospheric ozone mixing ratio retrieval. First, we develop an airglow radiation model that combines the photochemical reaction process with the kinetic processes of resonance absorption in the O2 infrared atmospheric band. A steady-state equation between the O2(a1?g) state mixing ratio and O3 mixing ratio is derived based on this model, providing the physical foundation for retrieving ozone profiles from O2(a1?g) band airglow spectra. Next, the airglow emission spectra from SCIAMACHY’s limb-viewing observation mode are processed to extract the O2(a1?g) band airglow in the target layer, using the “onion peeling” algorithm. The molecular number density profile of the O2(a1?g) state airglow is then obtained via spectral integration, which, combined with kinetic model retrieval, yields mesospheric ozone profiles (50?90 km). Finally, the accuracy and technical advantages of O2(a1?g) band airglow retrieval are verified by comparing the results with ozone data from remote sensing satellites such as sounding of the atmosphere using broadband emission radiometry (SABER) and michelson interferometer for passive atmospheric sounding (MIPAS).
The results show that the indirect retrieval method of ozone profiles, using satellite remote sensing technology and the O2 infrared atmospheric band airglow radiation spectra as the detection source, coupled with kinetic photochemical modeling, allows for accurate global detection of mesospheric ozone profiles. The retrieval results exhibit high accuracy, with a relative error of less than 10% compared to ozone data products from satellites such as SABER (Fig. 7) and MIPAS (Fig. 8). Although MIPAS and SCIAMACHY on the Envisat satellite platform provide a large amount of simultaneous observation spectral data, MIPAS obtains ozone profile information using the thermally excited radiation of ozone at 9.6 μm. However, it experiences data gaps in certain latitudinal regions and at altitudes above 70 km (Figs. 8 and 10). The retrieval of mesospheric ozone profiles using O2 infrared atmospheric band airglow can fill these gaps in vertical and horizontal coverage, with improvements of 21.4% and 23.1%, respectively. This demonstrates that the O2 molecular airglow radiation method, using 1.27 μm wavelength band in the mesopause region, offers significant advantages in both horizontal and vertical coverage.
Using O2 infrared atmospheric band airglow radiation enables accurate global detection of mesospheric ozone profiles, with retrieval results in good agreement with ozone profile data from remote sensing satellites such as SABER and MIPAS. In addition, the retrieval of ozone profiles using SCIAMACHY’s oxygen airglow radiation spectral data can complement the ozone retrieval results from MIPAS on the same satellite platform, confirming that the O2 molecular airglow radiation method at 1.27 μm has substantial advantages in both horizontal and vertical coverage.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 17, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628011 (2025)
Low-light remote sensing is a remote sensing imaging technology for remote sensing observation in low-light conditions. Compared with traditional remote sensing technology, low-light remote sensing can be observed in low-light environments such as night, dawn, or dusk, and has extensive applications in urban lighting monitoring, night navigation, disaster monitoring, and other fields. However, in the case of weak lighting conditions at night, remote sensing cameras need a longer exposure gaze to ensure the desired signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). During long-time gaze exposure, the relative motion of low-orbit satellites and ground objects brings serious geometric distortion and motion blur to the image, which results in an imaging resolution decrease. To this end, we combine video snapshot compressive imaging (SCI) technology with remote sensing imaging technology and propose a low-light remote sensing imaging technology based on video SCI. This technology slices and reconstructs the exposure process of remote sensing sensors in low-light conditions, and shortens the exposure time of a single time frame. Additionally, the imaging SNR is ensured, and the geometric distortion and motion blur of the image are reduced.
According to the characteristics of low-light remote sensing imaging, we transform the low-light imaging problem into a low SNR imaging problem. Meanwhile, we add different levels of noise to the ideal image to simulate the low-light image in different lighting conditions. Based on the image motion theory and single-exposure compressive imaging principle, we propose a remote sensing imaging model for video SCI and an evaluation index for remote sensing images. 32 consecutive frames of remote sensing video in the VISO dataset are selected as the simulation original image, and Poisson noise corresponding to the given imaging conditions is obtained according to the low-light remote sensing imaging model. The simulated low-light images are then encoded and compressed according to the video single-exposure compressive imaging model. After the compression observation, the deep learning algorithm EfficientSCI with the best reconstruction effect currently is adopted for reconstruction, and the proposed remote sensing image evaluation index is employed to evaluate the imaging SNR.
According to the simulation reconstruction results and the fitting model, the conclusions are drawn as follows. In the illumination condition of equivalent entry pupil radiance of 1×10-3 W/(sr·m2), the image quality after coding modulation and reconstruction increases with the rising camera integration time, and the relationship is basically a logarithmic function (Fig. 5). As the compression ratio rises, the overall reconstruction effect increases first and then decreases, and the increase in single frame integration time increases the amount of information in a single frame, with the peak reconstruction quality appearing at a lower compression ratio. Under the single frame integration time of 3.9, 9.8, and 19.6 ms, the peak SNR will appear at the compression ratio of 16, 12, and 10 respectively (Fig. 7). The acceleration of the target motion speed will cause a more serious degree of motion blur in remote sensing images. The signal in the image will be dispersed due to motion blur, which will reduce the signal intensity, thereby resulting in a higher level of noise relative to the signal, and a lower SNR in imaging (Fig. 8). The experimental results of the real prototype show that the integration time increase of the image sensor under the low-light environment is conducive to the target information accumulation, and the overall image brightening is accompanied by the improvement of image detail (Fig. 10). Additionally, the image quality increases first and then decreases with the rising compression ratio (Fig. 11), which is consistent with the simulated experimental results.
Based on the principle of video SCI and the theory of low-light remote sensing imaging, we propose a novel remote sensing imaging technology for video single-exposure compression, which can decompose a long exposure process into multiple short time frames, thus alleviating the image motion problem caused by long exposure imaging. Meanwhile, a remote sensing imaging model based on video compressive imaging is built, and the effects of the camera integration time, compression ratio, and target motion speed on imaging quality are explored via simulation experiments. The results show that the SNR of 8.45 dB, 8.31 dB, and 8.29 dB can be improved at 31.38, 78.46, and 313.86 ms respectively in the illumination condition of 1×10-3 W/(sr·m2) equivalent entry pupil radiance of the remote sensing camera. Additionally, the resolution of remote sensing images increases with the rising camera integration time. When the integration time increases from 31.38 to 313.86 ms, the SNR rises by 5.88 dB. Under the single frame integration time of 3.9 ms, the increase in the compression ratio from 4 to 16 is conducive to the improvement of the reconstructed SNR, and under the compression ratio higher than 16, the reconstruction quality gradually decreases with the increasing compression ratio. Based on the simulation experiments, we verify the correctness of the imaging model and simulation results by conducting the principal prototype imaging experiment. These results can provide not only a solution to the image motion in low-light remote sensing but also theoretical guidance and engineering references for the design of new optical remote sensing.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 26, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628012 (2025)
Aerosol particles are a crucial component of Earth’s atmosphere, significantly affecting the solar radiation balance and driving both climate and environmental changes, making aerosol research a priority in atmospheric science. In addition, greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), primarily emitted by human activities, are the main drivers of global warming. Controlling these anthropogenic carbon emissions is essential to mitigating global temperature rise. Through the Paris Climate Conference, countries have implemented a series of policies to address the influences of climate change, providing critical support to mitigate the negative effects of the greenhouse effect. Satellite remote sensing, with its advantages of objectivity, continuity, stability, broad coverage, and repeatability, has become an indispensable tool for monitoring global atmospheric greenhouse gas volume fraction. It is also emerging as the next-generation, internationally recognized approach for global carbon verification. The United States, European Union, Japan, Canada, and China have successively launched satellites equipped for atmospheric greenhouse gas monitoring, with increasingly advanced technology and enhanced detection precision. To meet the high-precision demands of carbon accounting, developing high-accuracy algorithms and data products is also essential. Thus, research into high-precision retrieval methods for greenhouse gases using fully physical algorithms in satellite remote sensing is of great significance. Satellite remote sensing has become an essential tool for monitoring aerosols and greenhouse gases (CO2 and CH4). The combination of polarization and hyperspectral techniques can reduce aerosol-induced XCO2 retrieval errors by more than twofold. To improve the retrieval accuracy of CO2 and CH4 in the shortwave infrared (SWIR) band, it is crucial to effectively correct aerosol influences to meet the high-precision requirements for satellite-based greenhouse gas retrievals.
In this paper, we utilize a two-pronged technical approach: forward model construction and joint retrieval of aerosols and greenhouse gases. Observational data, integrating spectral, polarization, and spatial information, are acquired using polarized hyperspectral imaging. A vector radiative transfer model is used for forward simulations, incorporating both spectral radiance measurement covariance and state vector covariance to quantify uncertainties. Retrieval is performed using an optimal estimation method, iteratively adjusting the state vector by comparing actual observations with simulated data to ensure convergence. Once the retrieval process is complete, an error analysis is conducted to assess the reliability of the results, ultimately yielding retrieved parameters for aerosols and greenhouse gases.
In this paper, we integrate observations from multi-band polarimetric sensors and hyperspectral instruments to investigate the influence of different spectral band combinations on the retrieval of aerosol parameters and greenhouse gas column volume fraction, using a radiative transfer model and full-physics inversion method. The results indicate that adding shortwave infrared bands (1610 nm and 2250 nm) to the polarimetric sensor significantly improves the retrieval accuracy of aerosol optical depth (AOD). Specifically, the bias for AOD decreases from 0.078 to 0.024, and the root mean square error (RMSE) is reduced from 0.212 to 0.161 (Fig. 6). The improvement is more pronounced for coarse-mode aerosols, with an RMSE difference of 0.109 and a bias difference of 0.056 compared to fine-mode aerosols (Table 5). In addition, the combined retrieval results from polarimetric and hyperspectral data show high accuracy, with the AOD bias at 1600 nm reaching 0.015 and an RMSE of 0.040 (Fig. 7). The column volume fraction of methane (XCH4) reaches 4.644×10-9, and XCO2 reaches 0.990×10-6 (Fig. 9). For fine-mode aerosols, the percentage change in error for XCO2 and XCH4 is mostly around 0.01, whereas the error percentage distribution for coarse-mode aerosols is more uniform (Fig. 11). Moreover, simulated band tests based on the BK-1 satellite further validate the importance of the 1610 nm band in the polarimetric sensor for greenhouse gas retrievals (Fig. 12).
In response to the strategic demands of global carbon accounting and China’s dual-carbon goals, there is an urgent need to develop high-precision retrieval algorithms for aerosols and greenhouse gases (GHGs). Addressing the significant influence of aerosols on GHG retrieval processes, we conduct a collaborative simulation of aerosol and GHG satellite remote sensing based on a full-physics algorithm. Utilizing observation modes of multispectral polarization sensors and hyperspectral instruments, the LINTRAN vector radiative transfer model is employed to simulate multispectral single-angle polarization and radiance measurements under various scenarios, followed by aerosol-synchronized correction for GHG retrieval. Based on these simulations, we analyze trends in aerosol parameters and major GHG parameters across different payloads and spectral band combinations, leading to the following conclusions. When retrieving aerosol parameters using polarized payloads, the addition of SWIR vector information at 1610 nm and 2250 nm significantly enhances the retrieval of AOD, with notable improvements for coarse-mode aerosol variations. In the joint retrieval of aerosol and greenhouse gas parameters based on polarization and hyperspectral data, aerosol parameter retrievals exhibit high stability. The incorporation of hyperspectral bands effectively reduces the variability of coarse-mode aerosols, while the addition of SWIR bands improves retrieval accuracy for XCH4 and XCO2. Comparing retrieval results across three aerosol modes reveals that mode 1 (fine-mode aerosols) achieves better retrieval accuracy, while mode 2 (dust-type aerosols) proves more challenging, resulting in lower precision. The analysis of the influence of XCH4 and XCO2 variability across different aerosol modes indicates that fine-mode aerosols tend to cluster at lower values, while the density distribution of coarse-mode aerosols is relatively uniform. As the scattering angle increases, errors in XCH4 and XCO2 remain within the range of -0.2% to 0. Validation using band retrievals from the BK-1 satellite further confirms the importance of the 1610 nm band for improving GHG retrieval accuracy. In summary, future research should incorporate multi-angle, multi-band polarized observations to enhance GHG retrieval capabilities, thus providing more precise scientific support for achieving China’s carbon peak and carbon neutrality objectives.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 24, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0628013 (2025)
Bioaerosols, as a critical component in atmospheric aerosols, significantly affect regional climate, environmental systems, and human health. These microscopic airborne particles encompass a wide range of biological entities, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and pollen. Their interactions with atmospheric processes can alter the chemical and physical properties of the atmosphere, influencing ecosystems and public health through multiple mechanisms. For instance, the dispersion of specific pathogens via bioaerosols can trigger infectious disease outbreaks, posing serious public health challenges. Pollen, a common allergen, affects millions of people worldwide by causing allergic reactions. In addition, bioaerosols play a pivotal role in the climate system. They can serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and ice nuclei (IN), thus influencing cloud formation, water cycles, and precipitation patterns. Furthermore, bioaerosols can modify the Earth’s radiation budget by absorbing and scattering solar radiation, which in turn affects temperature and precipitation. This dual influence on both climate and public health highlights the importance of understanding and monitoring bioaerosol dynamics. In recent years, advancements in optical detection technologies have revolutionized real-time bioaerosol monitoring, enabling researchers and public health agencies to better understand and manage bioaerosols. These technologies offer several advantages, such as high sensitivity, rapid response, and non-invasive detection, which are crucial for accurately tracking bioaerosol concentrations and compositions in the atmosphere. The integration of these advanced optical technologies is essential in bioaerosol research, enhancing our understanding of bioaerosol dynamics and their influence on public health and climate models. As the field progresses, the development and deployment of cutting-edge optical tools will continue to play a key role in addressing the challenges posed by bioaerosols.
Fluorescence scattering technology is one of the most commonly utilized methods for bioaerosol detection. This technique capitalizes on the fluorescence emitted by specific biomolecules when exposed to light of particular wavelengths. It offers high sensitivity and rapid response, making it well-suited for real-time environmental monitoring of bioaerosols. However, the method can be prone to interference from the fluorescence of non-biological particles, leading to potential false positives. Another widely utilized method is Raman scattering, a high-precision spectroscopic technique that identifies bioaerosols by detecting molecular vibrations and rotations. These molecular “fingerprints” provide detailed information about bioaerosol components. Although Raman scattering offers high resolution and selectivity, its inherently weak signal requires the use of sophisticated, high-sensitivity detection systems, limiting its widespread application. Mass spectrometry, particularly techniques like laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry, has also gained prominence for bioaerosol analysis. This method enables rapid and precise compositional analysis of bioaerosols, offering high sensitivity and resolution. However, the high cost and operational complexity of the equipment remain major drawbacks, requiring skilled personnel for operation and maintenance. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) bioluminescence detection is another critical technology in bioaerosol research. It measures light emission from a biochemical reaction involving ATP, which serves as a universal energy carrier in biological cells, making it effective for detecting active microorganisms. The integration of ATP detection with microfluidic chips has emerged as a promising research direction, offering enhanced sensitivity and specificity for real-time monitoring of active microorganisms. Each of these optical and analytical technologies offers unique advantages and faces specific challenges in bioaerosol detection. Continued research and development will likely focus on refining these methods and integrating them with complementary technologies to further advance our understanding of bioaerosols and their impact on both the environment and human health.
Optical technologies hold immense potential for future applications in bioaerosol detection. Trends point towards the integration of artificial intelligence with optical technologies, and ongoing improvements in engineering and systematization. These advancements will drive future progress in bioaerosol research, enhancing our ability to monitor and mitigate their effects.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 04, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0600001 (2025)
Underwater imaging is significantly affected by scattering and absorption caused by suspended particles in the water, leading to a considerable decline in image quality. Existing polarization-based dehazing algorithms primarily focus on estimating backscattered light parameters during image restoration. However, underwater imaging scenarios, such as nighttime or deep-sea environments, often require active light sources for illumination. The non-uniform distribution of these active light sources results in uneven image brightness, complicating the estimation of backscattered light. This challenge makes it difficult to fully suppress backscattered light, which adversely affects the restoration process. In addition, non-uniform illumination can cause overexposure or underexposure in captured images, leading to the loss of critical object information. This hampers subsequent tasks such as underwater detection, object recognition, and object tracking. To address these challenges, we propose a novel image restoration method that leverages polarimetric imaging to handle non-uniform illumination. The method employs low-rank sparse matrix decomposition to separate backscattered light from object information light. Subsequently, backscattered light is corrected and combined with an underwater imaging model to achieve clarity and uniformity in the restored images. The proposed approach holds significant potential for applications in underwater polarization imaging, object recognition, and tracking.
The proposed method focuses on the difference in matrix dimensions between object information light and backscattered light during underwater imaging. Initially, four images with varying polarization angles, captured using a split-focus plane camera, are preprocessed. Polarized images at any given angle are represented using Stokes vectors. Based on the regional detail richness of the images, two polarization sub-images are selected for processing. Since backscattered light exhibits low-rank characteristics while object information light is sparse, the method uses low-rank sparse matrix decomposition to achieve preliminary separation. The backscattered light is then corrected for uniformity through adaptive brightness adjustment, Gamma correction, and local brightness equalization. Using an underwater scattering model, the intensity of backscattered light at infinity and the transmittance map are estimated to restore the two polarized sub-images. Finally, these restored images are fused to produce a clear underwater image.
Polarization imaging experiments are conducted in turbid water at various concentrations under non-uniform illumination conditions (Fig. 3). The results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively corrects non-uniform illumination and significantly enhances the clarity and contrast of underwater images. Using light emitting diode (LED) lighting as an active illumination source, experiments are performed in water bodies with low, medium, and high turbidity levels. Comparisons with other descattering methods reveal superior results, with uniformly distributed brightness and no overexposure. The method also significantly enhances contrast and clarity (Fig. 6). Partial zoomed-in views reveal richer image details, particularly as water turbidity increases, highlighting the method’s advantages (Fig. 7). In addition, three-dimensional grayscale analyses before and after restoration further verify the method’s effectiveness in correcting non-uniform illumination. Compared with the original image, pixel grayscale values in the restored images exhibit a more even distribution (Fig. 8). A quantitative analysis using five image quality metrics, eight-neighbor contrast, enhancement measure evaluation (EME), average gradient (AG), edge intensity (EI), and underwater image quality measures (UIQM), further confirms the proposed method’s effectiveness and superiority (Table 1).
To address the degradation of underwater image quality caused by non-uniform illumination and scattering effects, we propose a restoration method based on low-rank sparse matrix decomposition and illumination correction. Two polarized sub-images are selected based on image contrast, and low-rank sparse matrix decomposition is applied to separate backscattered light from object information light. After homogenizing the backscattered light, parameters such as the transmittance map and backscattered light at infinity are estimated. These are combined with an underwater scattering model to restore the two polarized sub-images. The restored images are fused to produce a clear and enhanced underwater image. Multiple experiments are conducted in turbid water with different concentrations under non-uniform illumination methods. The proposed method’s results are qualitatively and quantitatively compared with other descattering techniques. The findings demonstrate that the method effectively corrects non-uniform illumination and significantly improves image contrast and detail richness, resulting in enhanced image quality.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 25, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0629001 (2025)
Chemical enterprises generate significant amounts of organic pollutants during production, often due to inadequate or aging pollution treatment facilities. These shortcomings pose a risk of organic contamination to nearby groundwater. Among these pollutants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are persistent organic compounds known to be carcinogenic, teratogenic, and mutagenic, causing significant harm to ecosystems and human health. Groundwater contamination with PAHs is often difficult to detect due to complex sample characteristics and the limitations of traditional detection methods, such as cumbersome operational procedures and secondary pollution caused by chemical reagents. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a rapid, reliable method for detecting PAHs in groundwater. Three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy offers a rapid and sensitive approach to water analysis. However, the overlapping fluorescence characteristics of PAHs make it challenging for conventional linear models to achieve accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis of multi-component samples. In addition, real-world groundwater conditions often introduce fluorescence interferences, further complicating the analysis. In this context, an effective solution for detecting multi-component PAHs based on three-dimensional fluorescence spectra is essential.
In this paper, we utilize the fluorescence characteristics of organic pollutants to measure the three-dimensional excitation?emission matrix (3DEEM) of PAH solutions using a fluorescence spectrophotometer. A convolutional neural network (CNN)-based approach is proposed to enable rapid qualitative and quantitative analysis of PAHs in groundwater. Two distinct CNN models are developed for the qualitative identification and quantitative measurement of PAHs. The fluorescence characteristics of eight representative PAHs are analyzed using correlation statistical methods applied to deionized water. To enhance the spectral dataset, two 3DEEM data augmentation techniques, superposition and interpolation, are applied. The expanded dataset is then used to train the CNN models. The method is validated in laboratory conditions with PAH solutions and further tested on groundwater samples collected from areas surrounding chemical enterprises.
For the PAH solutions prepared with deionized water under laboratory conditions, the fluorescence characteristics of eight PAHs are preliminarily analyzed. Two CNN models are then trained using the proposed method. The model achieves a qualitative analysis accuracy of 99.8% and an average relative error of 10.71% for quantitative analysis. The models are further retrained to account for the fluorescence background of actual groundwater samples, and the method is applied to detect PAH mass contamination in real-world groundwater samples. In cases where the fluorescence background of the groundwater is unknown, the method still provides reliable qualitative analysis results. The relative error in quantitative analysis, despite interference from water background disturbance and varying levels of pollution, is maintained within an acceptable range. For instance, in groundwater sample 1, which has a low fluorescence background, the model achieves 100% qualitative accuracy, and the quantitative analysis errors range from 0 and 40 μg/L. In groundwater sample 2, which has a higher fluorescence with a broader range of overlapping PAH characteristics, the model achieves 95.83% accuracy for qualitative analysis. After removing PAHs that are significantly affected by the groundwater background spectrum, the average relative error in quantitative analysis drops to 27.53%, demonstrating the model’s effective prediction capabilities and high analysis efficiency.
In this paper, we propose a novel method for the detection of PAHs in groundwater using fluorescence spectroscopy and CNN models. By leveraging an extensive spectral dataset for training, the proposed method achieves effective qualitative and quantitative analysis of PAHs in both deionized water and real-world groundwater samples. Detailed results from different groundwater locations demonstrate the method’s practical applicability. The experimental results show that this method offers a viable and efficient solution for the rapid on-site analysis of groundwater contamination by multi-component organic pollutants. Improvement measures based on model performance in real-world scenarios are also discussed.
.- Publication Date: Mar. 26, 2025
- Vol. 45, Issue 6, 0630001 (2025)