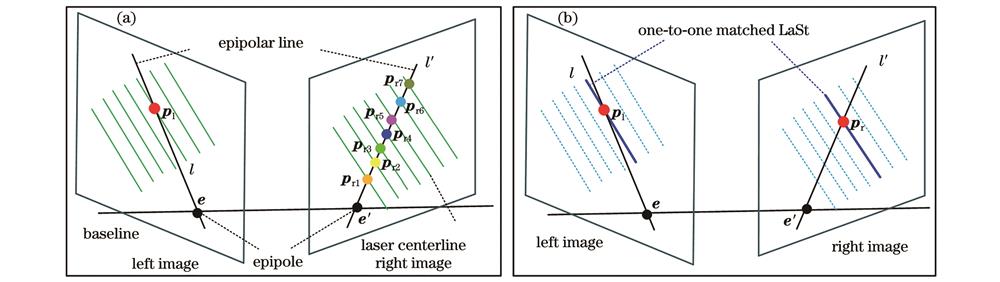
Known for its high efficiency, accuracy, and robustness, the binocular multi-line laser (BMLL) three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction system has significant applications in fields such as industrial inspection, reverse engineering, and cultural heritage preservation. However, when multiple laser planes are projected onto the surface of 3D objects with substantial geometric variations, the modulations caused by the object often result in irregular discontinuities, overlaps, distortions, and deformations of laser stripes (LaSt) in the two-dimensional (2D) images. Additionally, due to the disparity in viewpoints between the left and right cameras, the same LaSt may exhibit different discontinuity patterns in the left and right images, thereby making it difficult to realize stereo matching of laser points across the two views. Existing LaSt matching methods struggle to yield accurate matching of LaSt between the left and right views, particularly for complex object surfaces or in dynamic scenarios. We aim to tackle the challenge of LaSt matching in a handheld BMLL 3D reconstruction system, and thus improve the accuracy and robustness of the matching process, thereby enhancing the overall reconstruction performance of the handheld BMLL 3D reconstruction system.
A novel LaSt matching method for the handheld BMLL 3D reconstruction system is proposed. Firstly, sensor parameters are obtained via system calibration, including the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the cameras, 2D line equations, and 3D laser plane equations. Next, regional consistency (RC) is utilized for coarse matching, which enables the rough localization of the corresponding points of laser centroids from the left image to the right image, thus narrowing down the search range for potential matches. Subsequently, precise LaSt matching is achieved by a combination of reprojection and voting scoring mechanism. The reprojection step calculates the matching point for a single laser point from the left image to the right image, while the voting scoring mechanism enhances matching reliability by maximizing the number of matching points, reducing the influence of a single-point error. Finally, a reverse matching strategy is employed to ensure accurate matching of previously unmatched LaSt in the right image, further improving the completeness of the matching process.
Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed LaSt matching method exhibits superior matching performance across various scenarios involving different test objects and LaSt with varying breakage forms. Comparative experiments reveal that the proposed method outperforms existing techniques in matching continuous, monotonically changing, and non-monotonically changing LaSt, with significant improvements in matching accuracy and reconstruction rates, particularly in non-monotonic scenarios (Figs. 12 and 13). The method achieves an average matching accuracy of 98.746% and an average reconstruction rate of 81.599% across multiple test objects (Table 1). For the reconstruction of a standard 3D sphere, the diameter error is less than 0.107 mm, and the error in sphere center distance is less than 0.143 mm, which further validates the effectiveness of the proposed method (Fig. 15). Additionally, the method demonstrates excellent adaptability across different experimental objects and hardware platforms, confirming its stability and robustness in complex scenarios and diverse hardware conditions (Figs. 16?18). Additionally, the entire system utilizes CUDA acceleration, yielding a processing speed of 17 frame/s.
A novel LaSt stereo matching method based on RC and a voting scoring mechanism is introduced. This method employs system calibration, coarse matching, fine matching, and a reverse matching strategy to tackle the challenges of irregular discontinuities and deformations of LaSt caused by surface modulation and occlusion of the test objects. It significantly improves the LaSt stereo matching performance in the BMLL 3D reconstruction system. 1) Matching accuracy increase. The proposed algorithm mitigates the mismatches in traditional methods, particularly in scenarios with significant deformations. 2) Robustness improvement. By incorporating RC constraints and a voting scoring mechanism, the method suppresses mismatches and enhances the stability and reliability of the algorithm. 3) By leveraging CUDA-based parallel computing, the proposed method achieves a processing speed of 17 frame/s in experiments, while maintaining high matching accuracy and robustness, thereby providing support for real-time 3D reconstruction. The proposed LaSt matching method enhances the overall performance of the BMLL 3D reconstruction system, with significant potential for applications in highly accurate 3D measurements. The method provides technological support for practical applications such as intelligent manufacturing, navigation, localization, and automated repair. Future work will focus on both optimizing the algorithm for wider application scenarios and further improving the extraction of laser center lines.


 AI Video Guide
AI Video Guide  AI Picture Guide
AI Picture Guide AI One Sentence
AI One Sentence